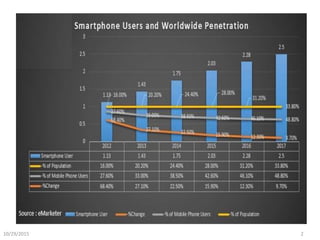
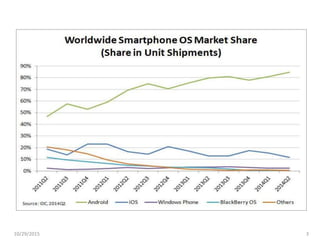
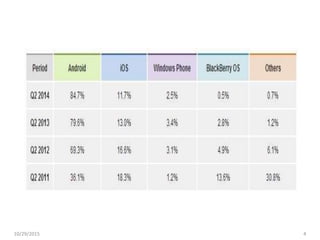
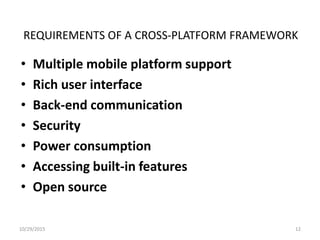
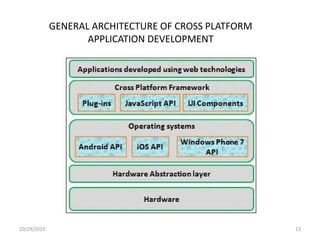
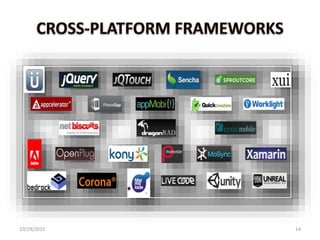
The document discusses cross-platform mobile application development. It describes native apps, web apps, and hybrid apps. Native apps are developed for a specific platform but have full access to device features. Web apps use web technologies but have limited access to device APIs. Hybrid apps combine web technologies with native wrappers to bridge web apps and device features. The document then examines various cross-platform frameworks like PhoneGap, Titanium, Sencha Touch, and jQuery Mobile, outlining their advantages and disadvantages. It concludes by noting areas where cross-platform development may be restrictive compared to native development.