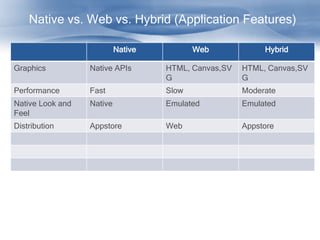
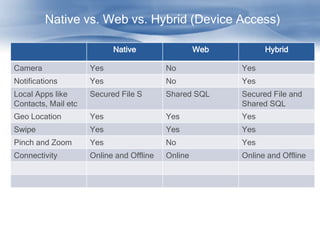
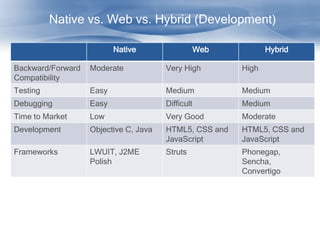
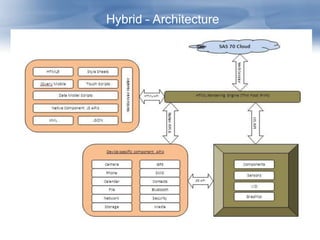
The document discusses cross-platform mobile application architecture for enterprises. It covers the need for enterprise mobile apps due to workforce mobility trends. It compares native, web, and hybrid approaches and recommends hybrid for supporting multiple platforms. Key elements of hybrid apps include device and screen agnosticism, offline storage, security, and access to device capabilities. Frameworks like Phonegap and technologies like HTML5, CSS, and JavaScript enable hybrid development.