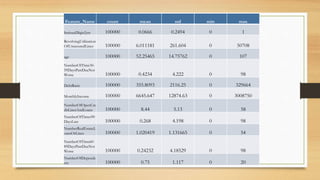
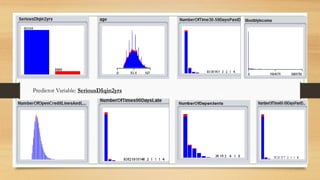
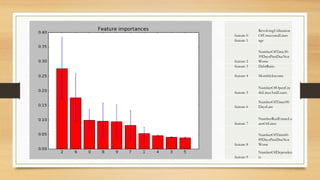
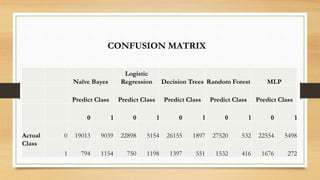
The document discusses the development of a credit default prediction model called Def_Catch using machine learning algorithms. Def_Catch was trained on a dataset of 100,000 examples with 11 attributes related to borrowers' credit histories and demographics. Random forest achieved the highest accuracy of 93.14% at predicting which borrowers would default in the next 2 years, outperforming logistic regression, naive bayes, decision trees, and multi-layer perceptron models. The top predictors of default included credit utilization, age, number of late payments, debt ratio, and income. Def_Catch provides insights into borrower risk that are difficult to discern from raw data alone.