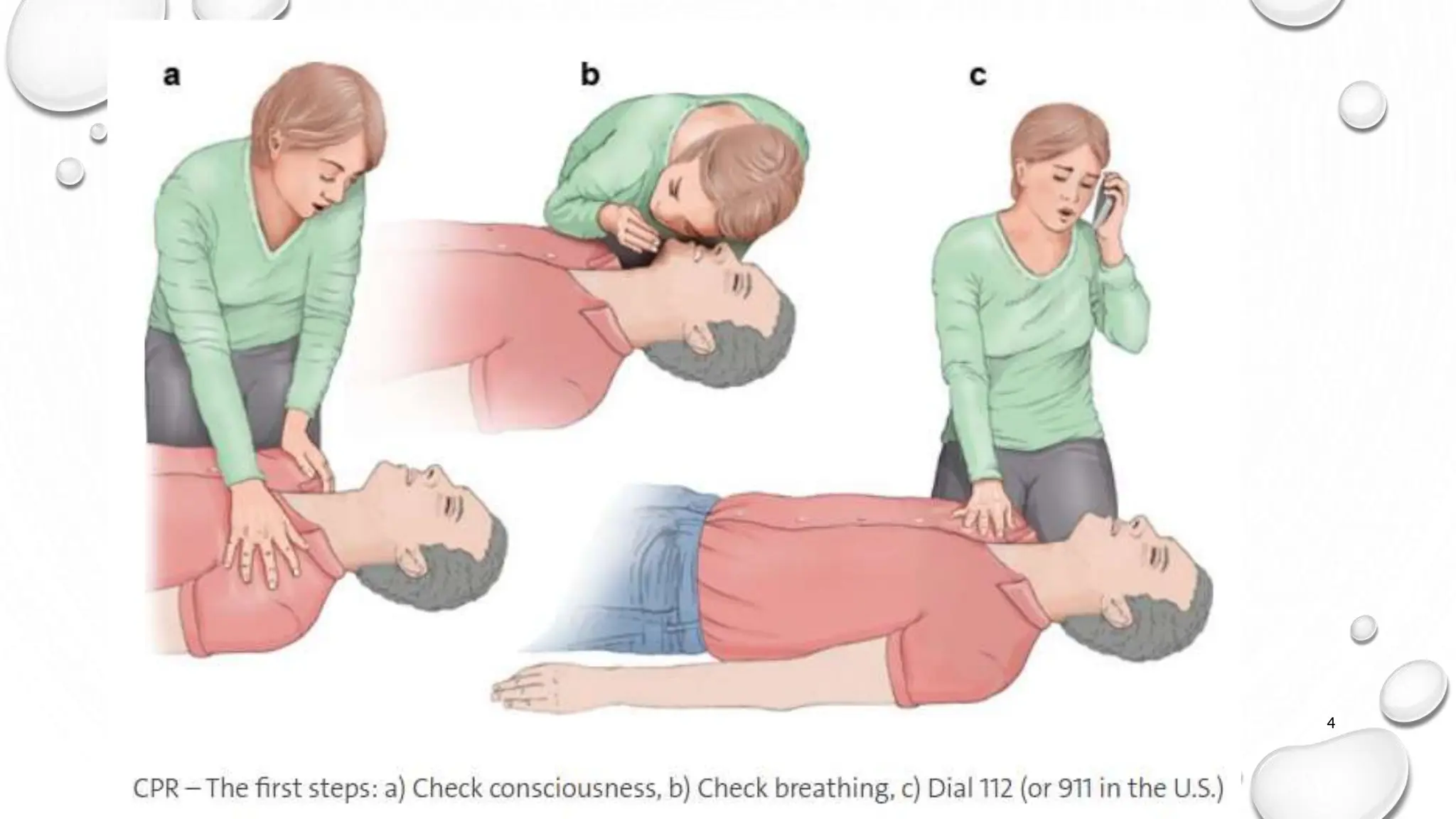
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure performed when a person's heart stops beating or they stop breathing. The goal of CPR is to maintain blood flow and oxygen to vital organs like the heart and brain until emergency medical personnel arrive. There are two main types of CPR - hands-only CPR which involves chest compressions only, and CPR with breaths which combines chest compressions with rescue breathing. CPR should be administered if a person collapses, is unresponsive, and not breathing or does not have a pulse. The steps of CPR are easily remembered with the acronym C-A-B which stands for compressions, airway, and breathing.