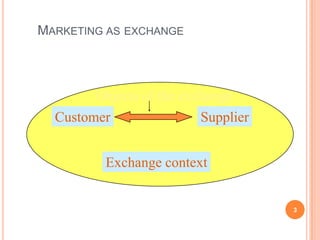
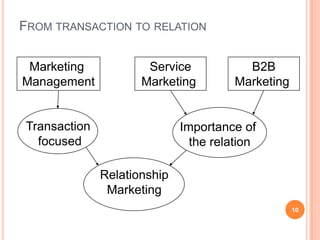
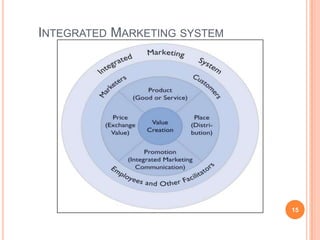
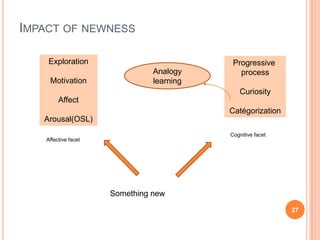
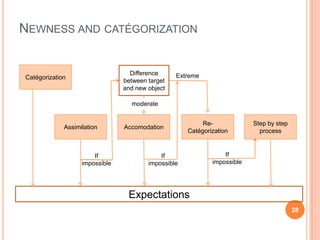
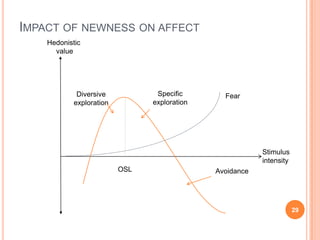
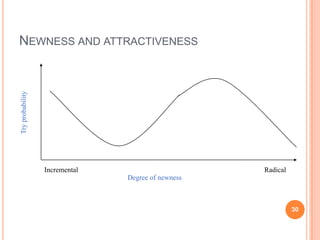
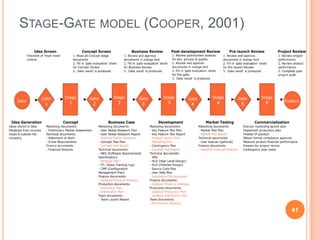
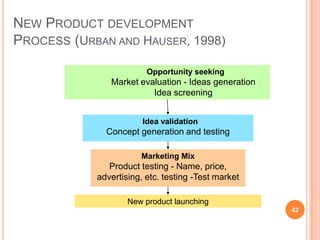
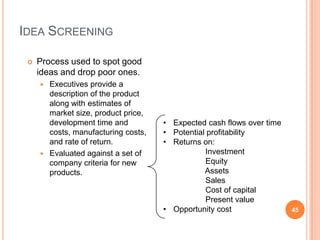
The document discusses marketing and innovation from a classical perspective. It describes the marketing concept, exchange processes, and marketing management paradigm of segmentation, targeting, and positioning using the marketing mix. It also discusses limits of this approach for business-to-business marketing, services, and relationships. The new product development process involves opportunity identification, concept development and testing, marketing strategy development, product development, and test marketing before commercialization.