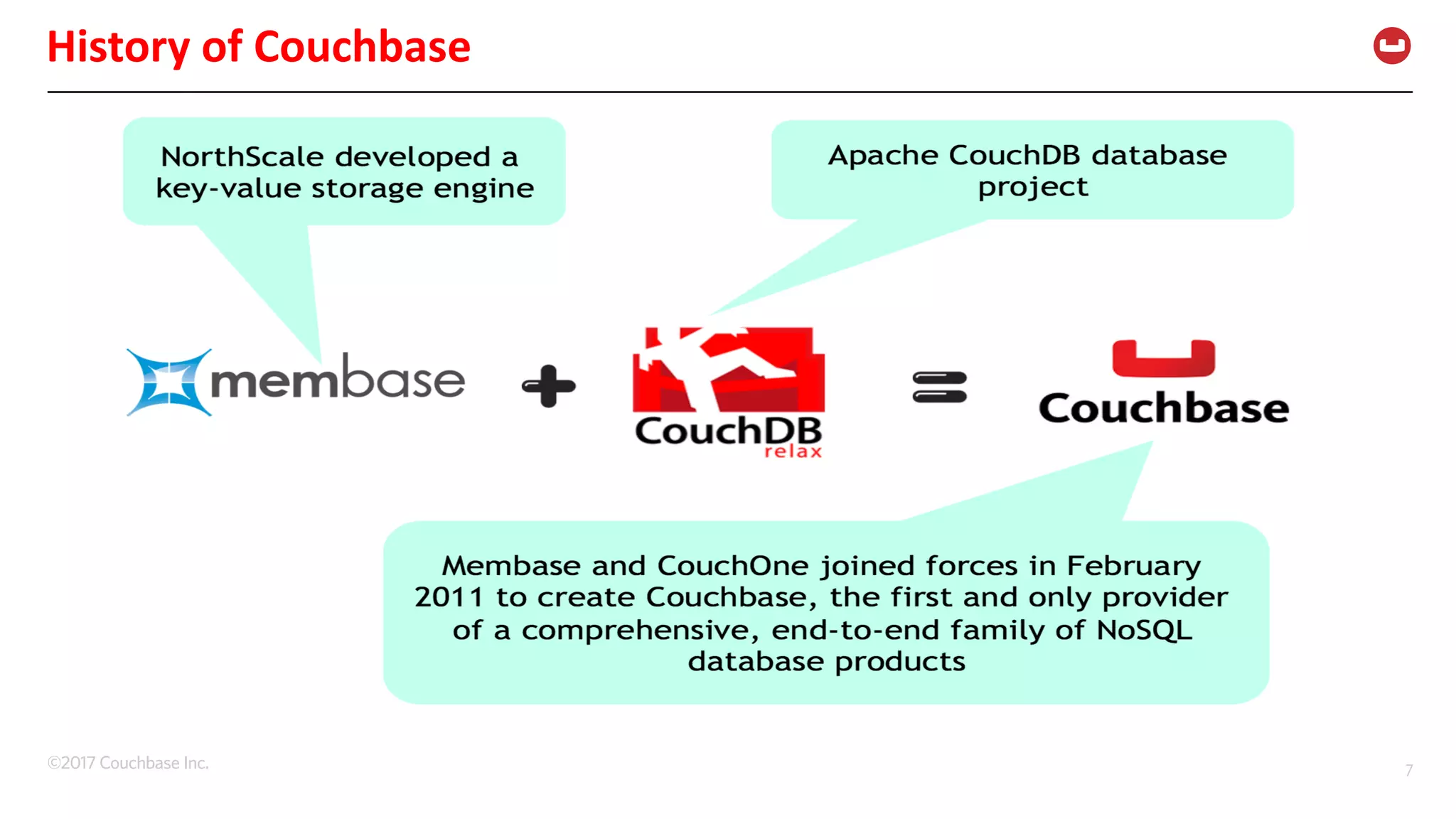
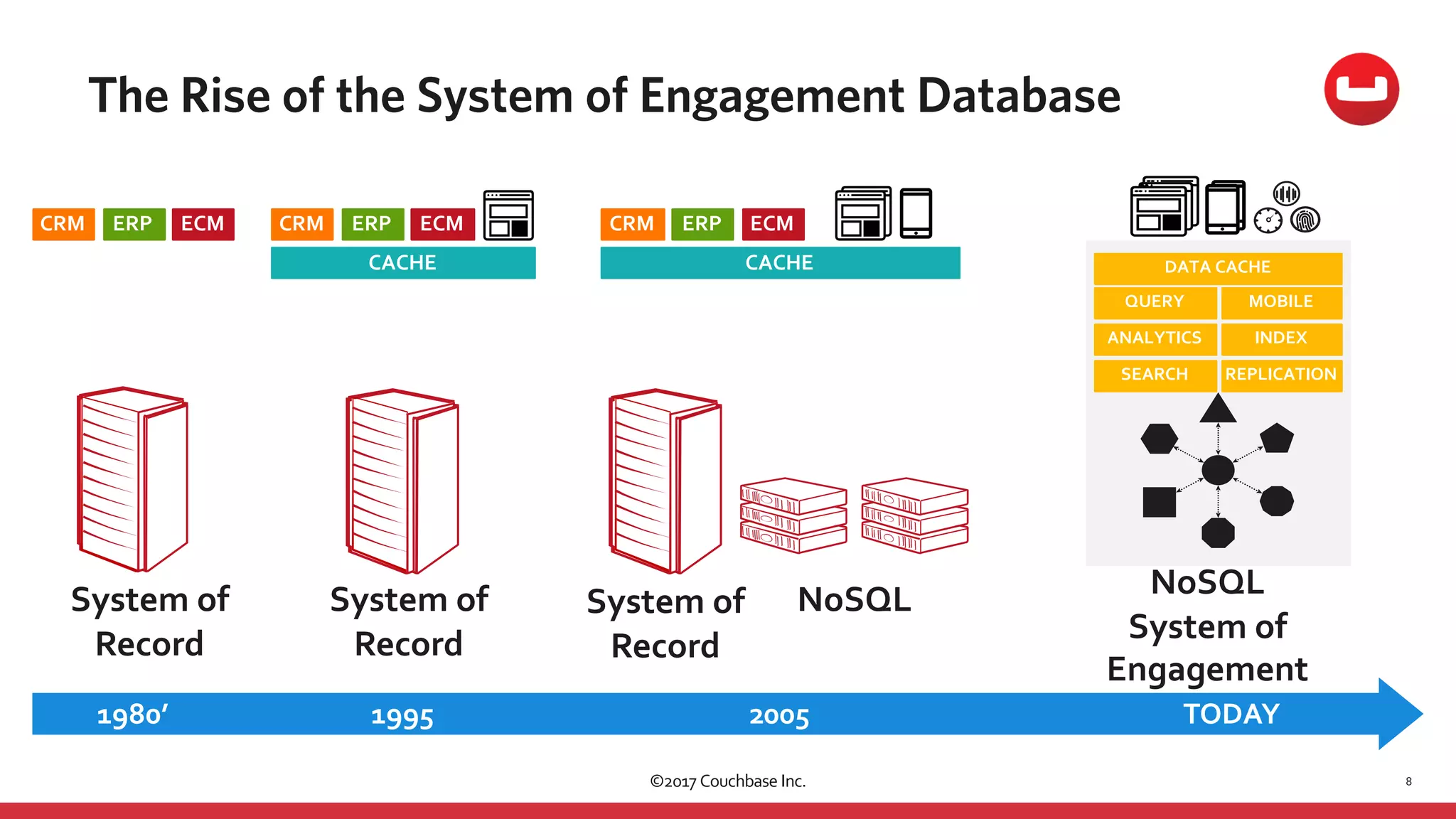
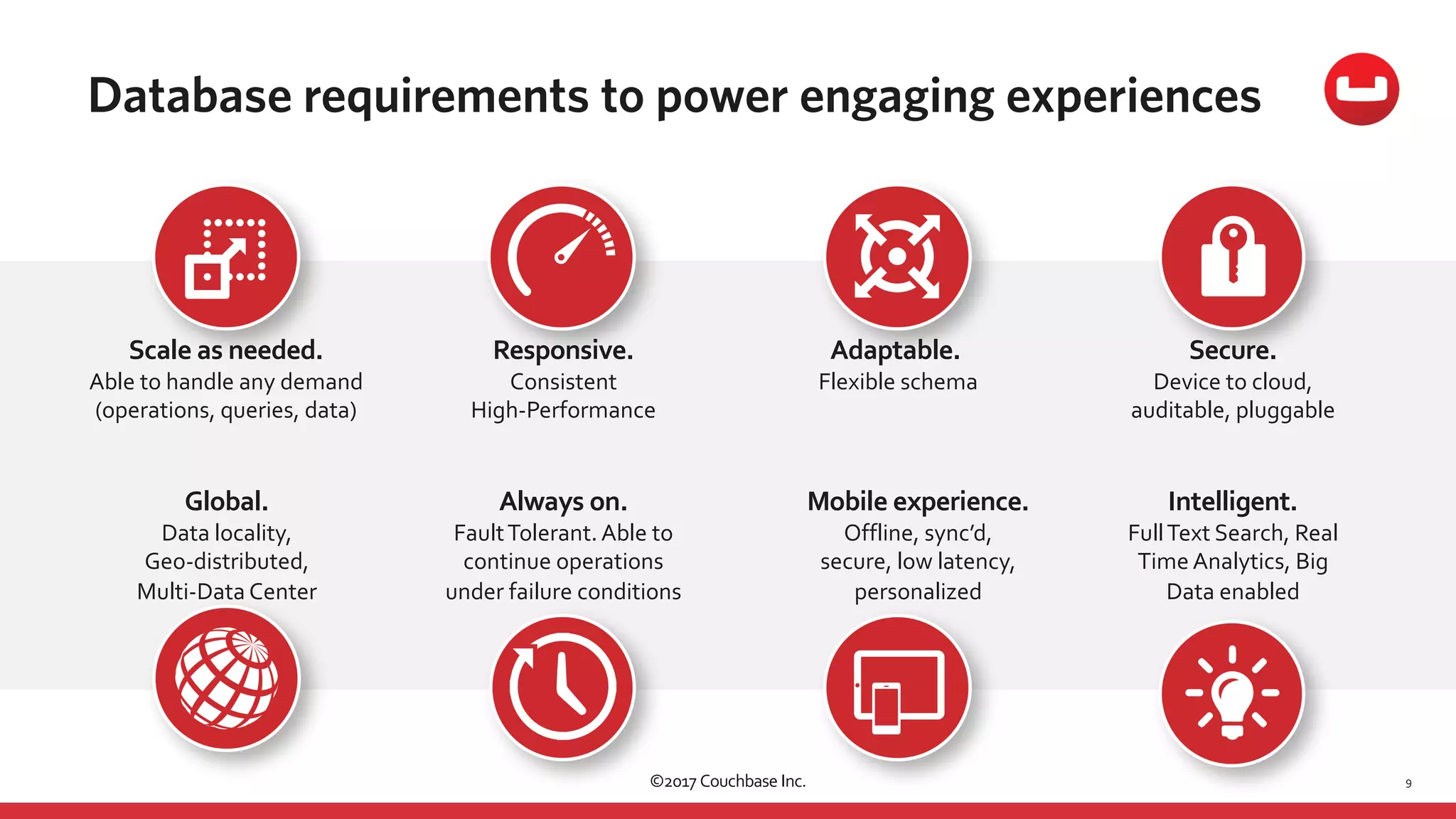
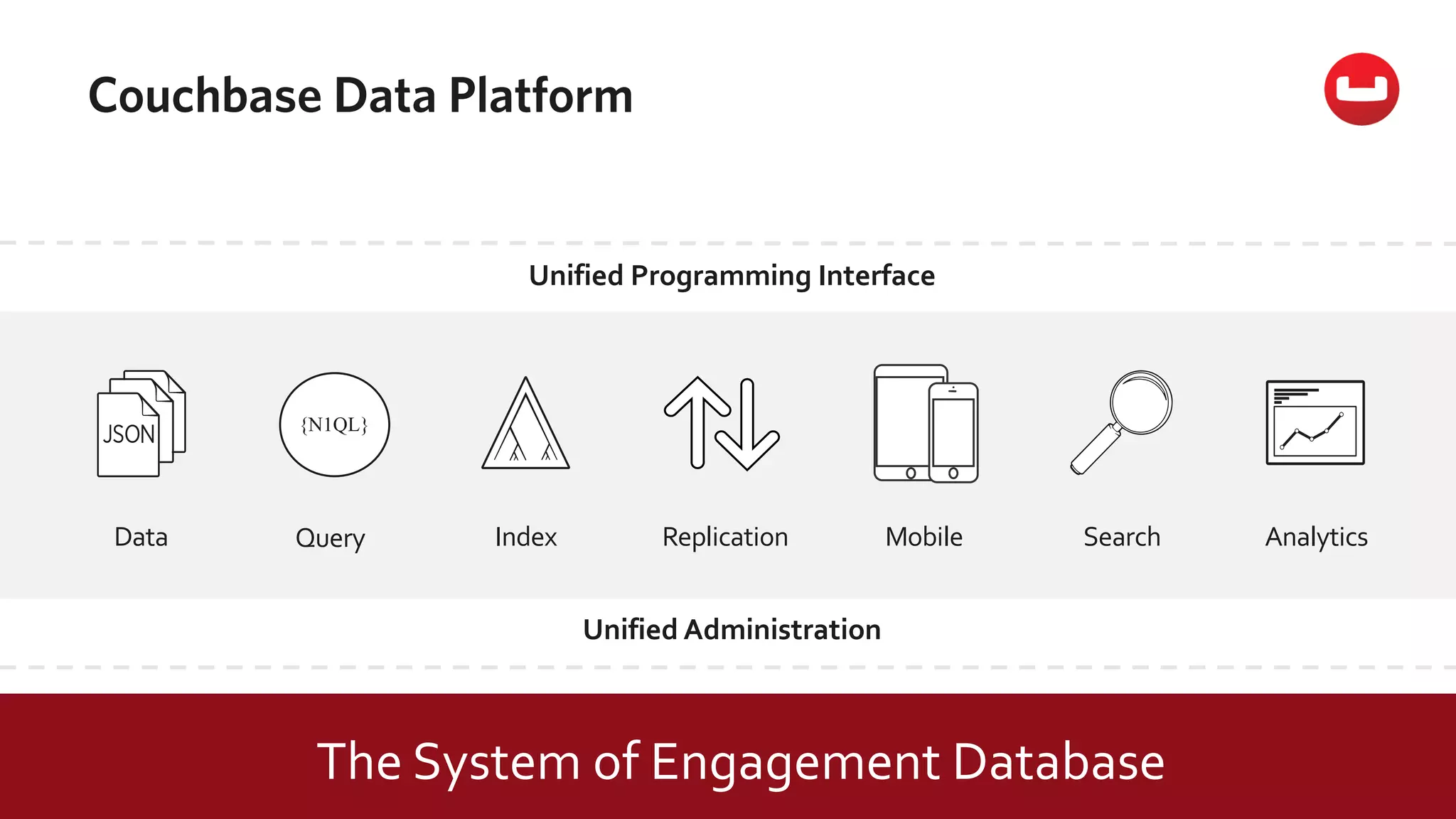
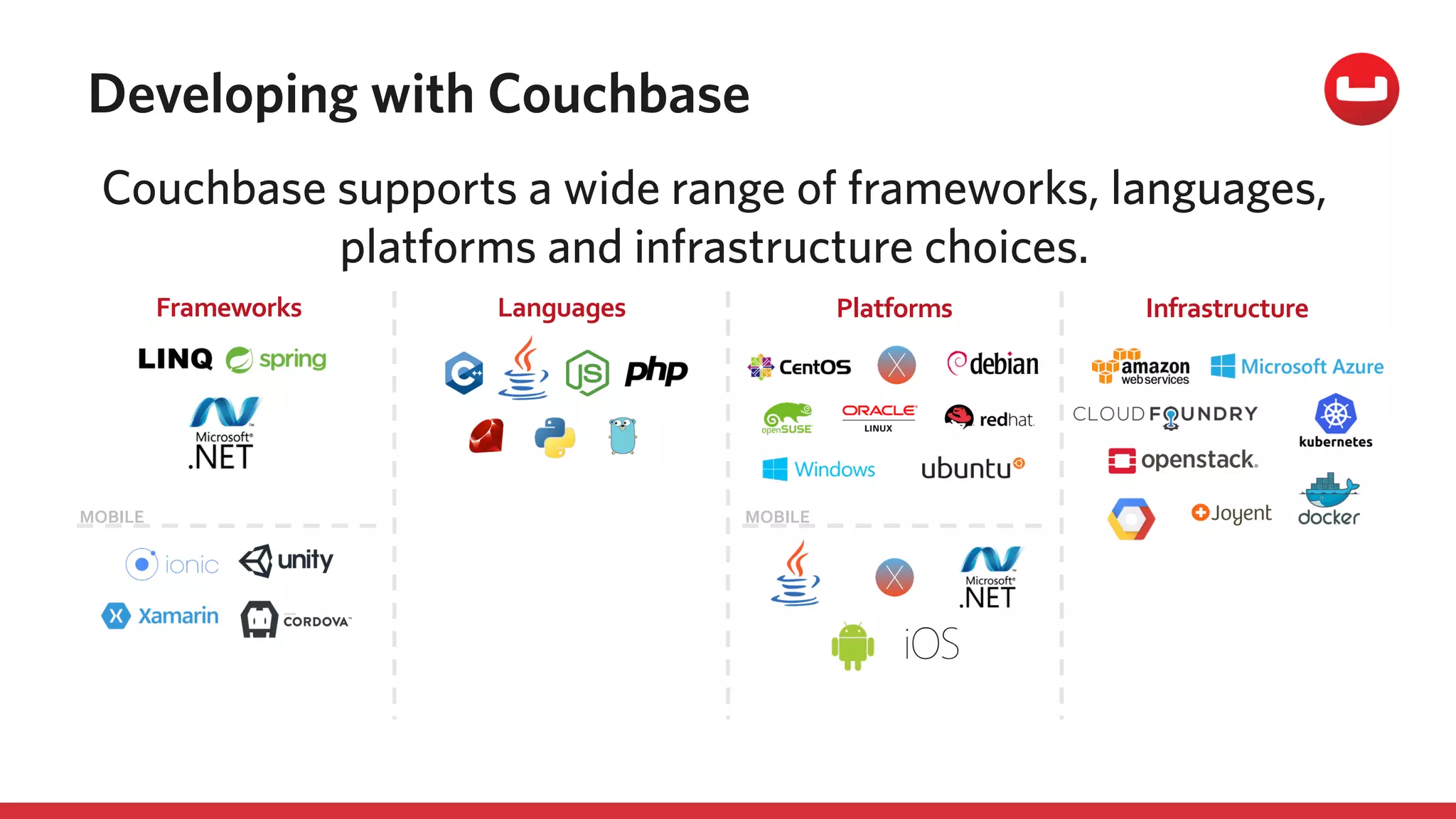
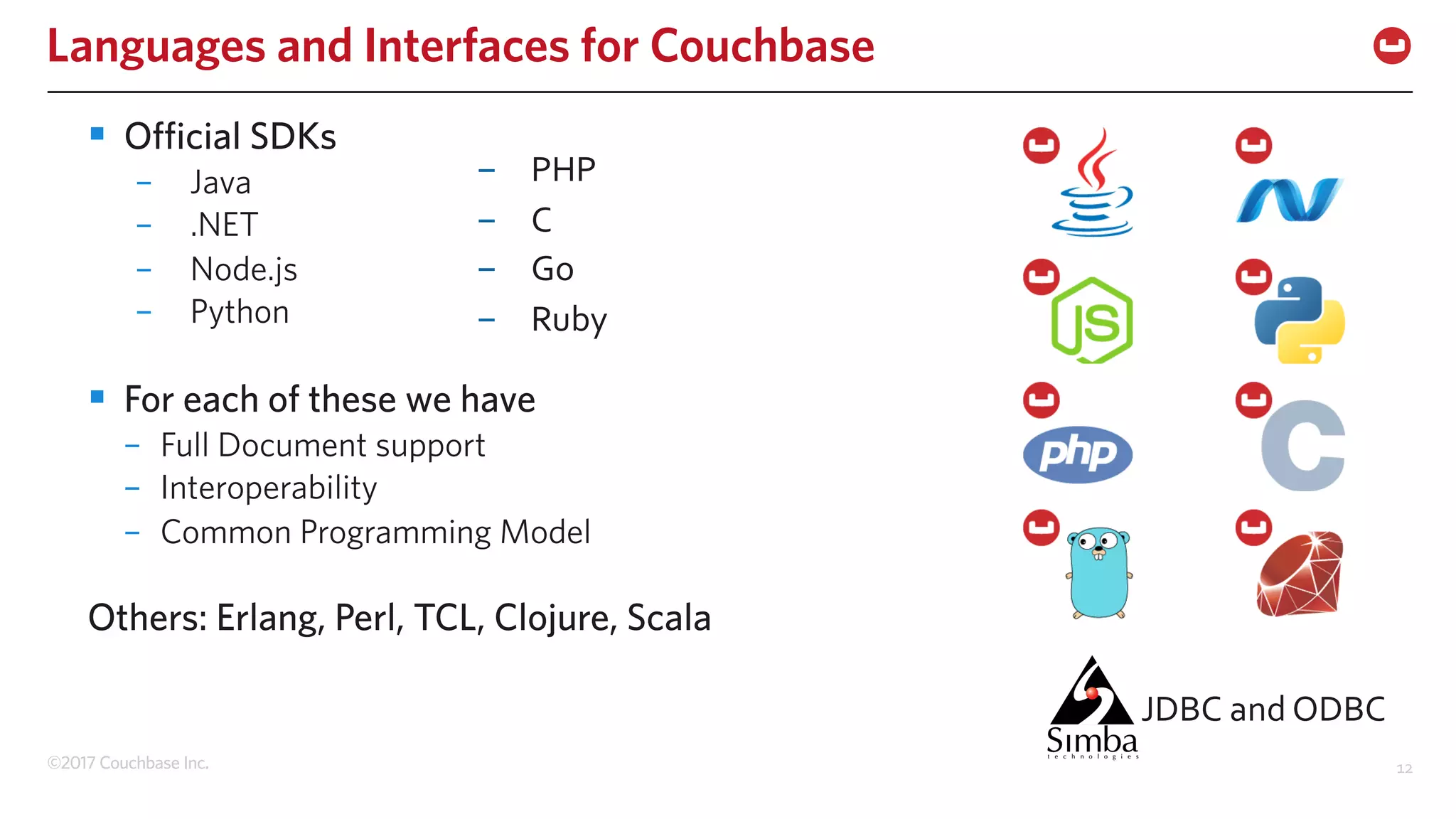
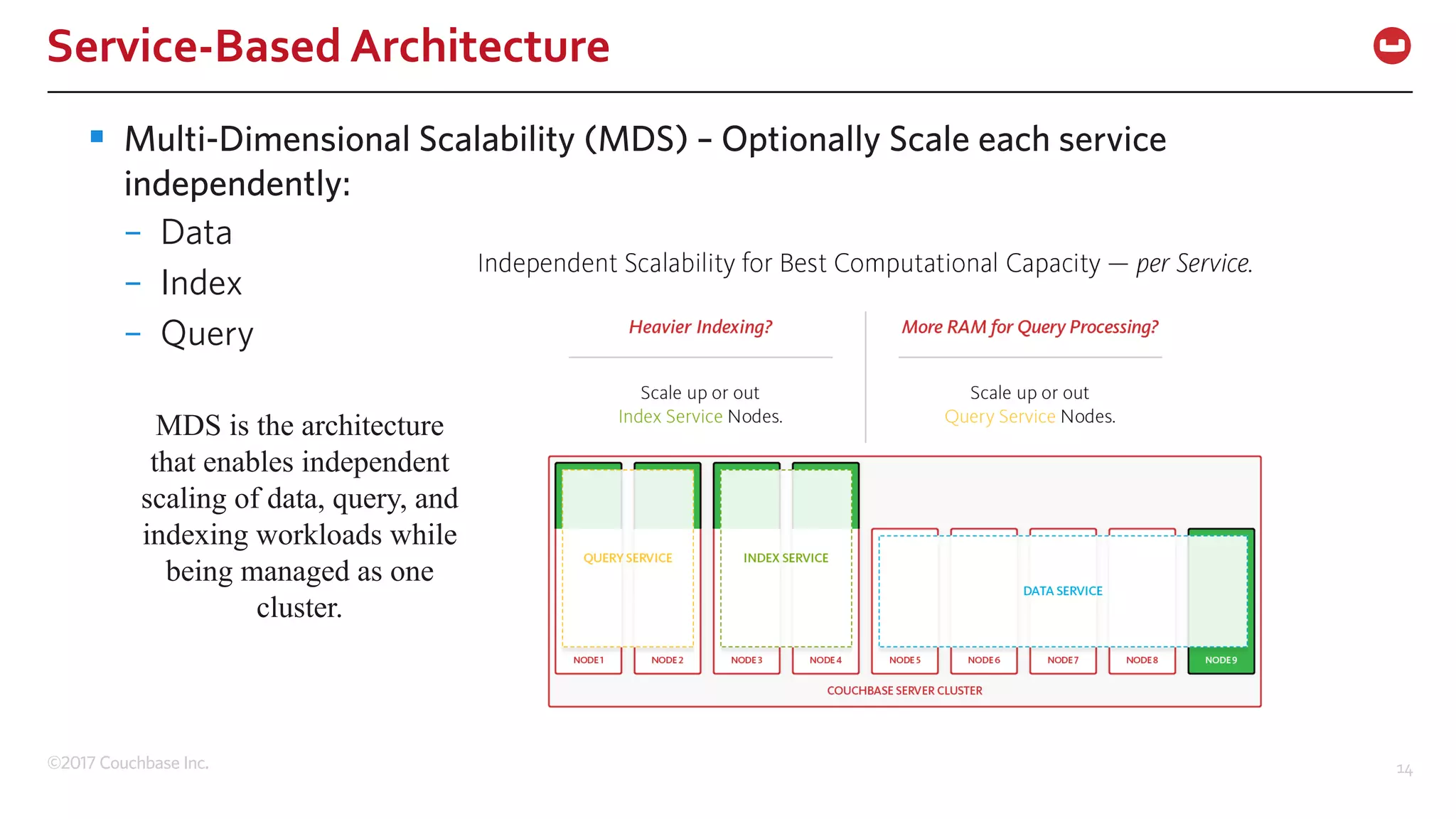
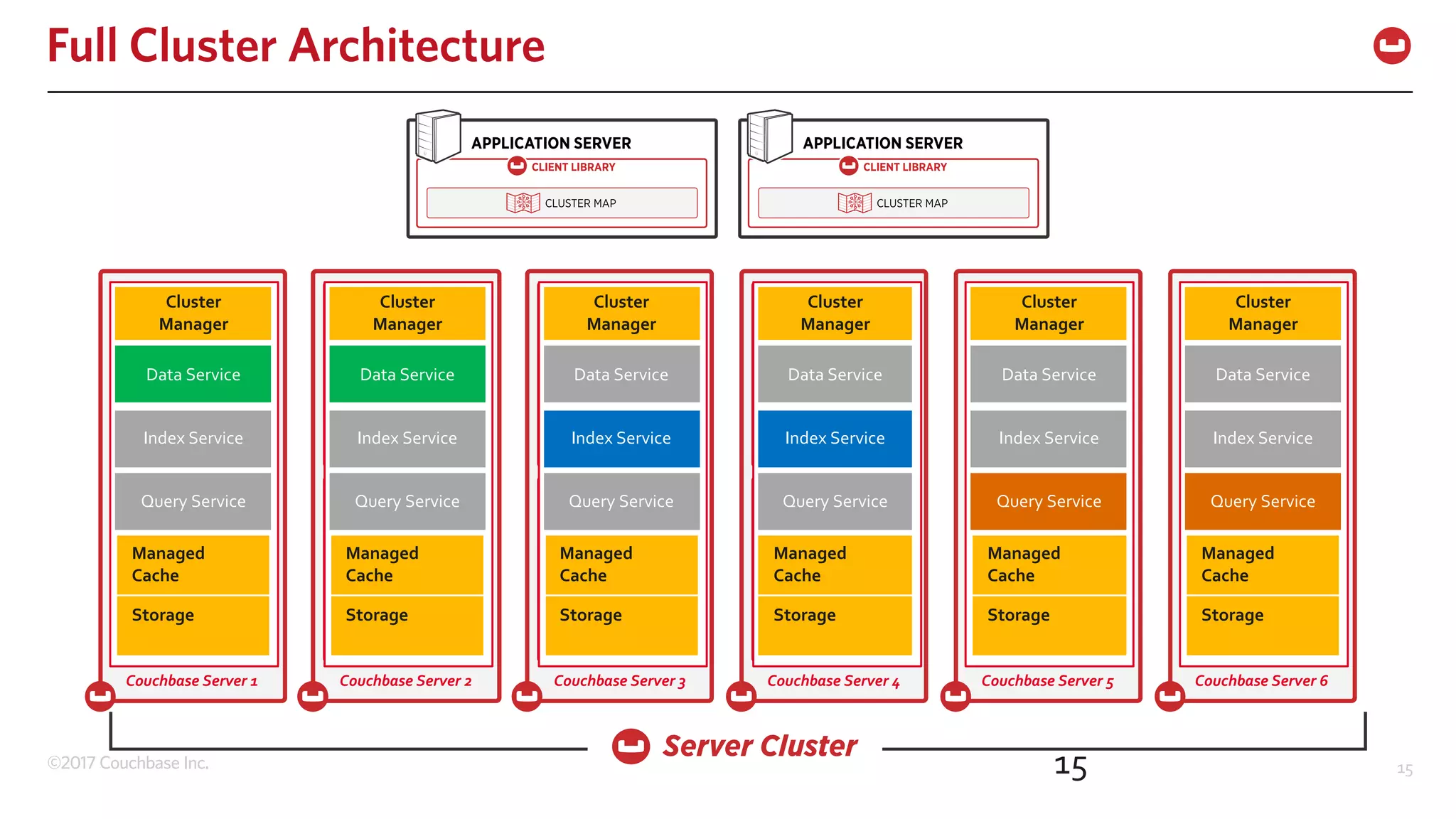
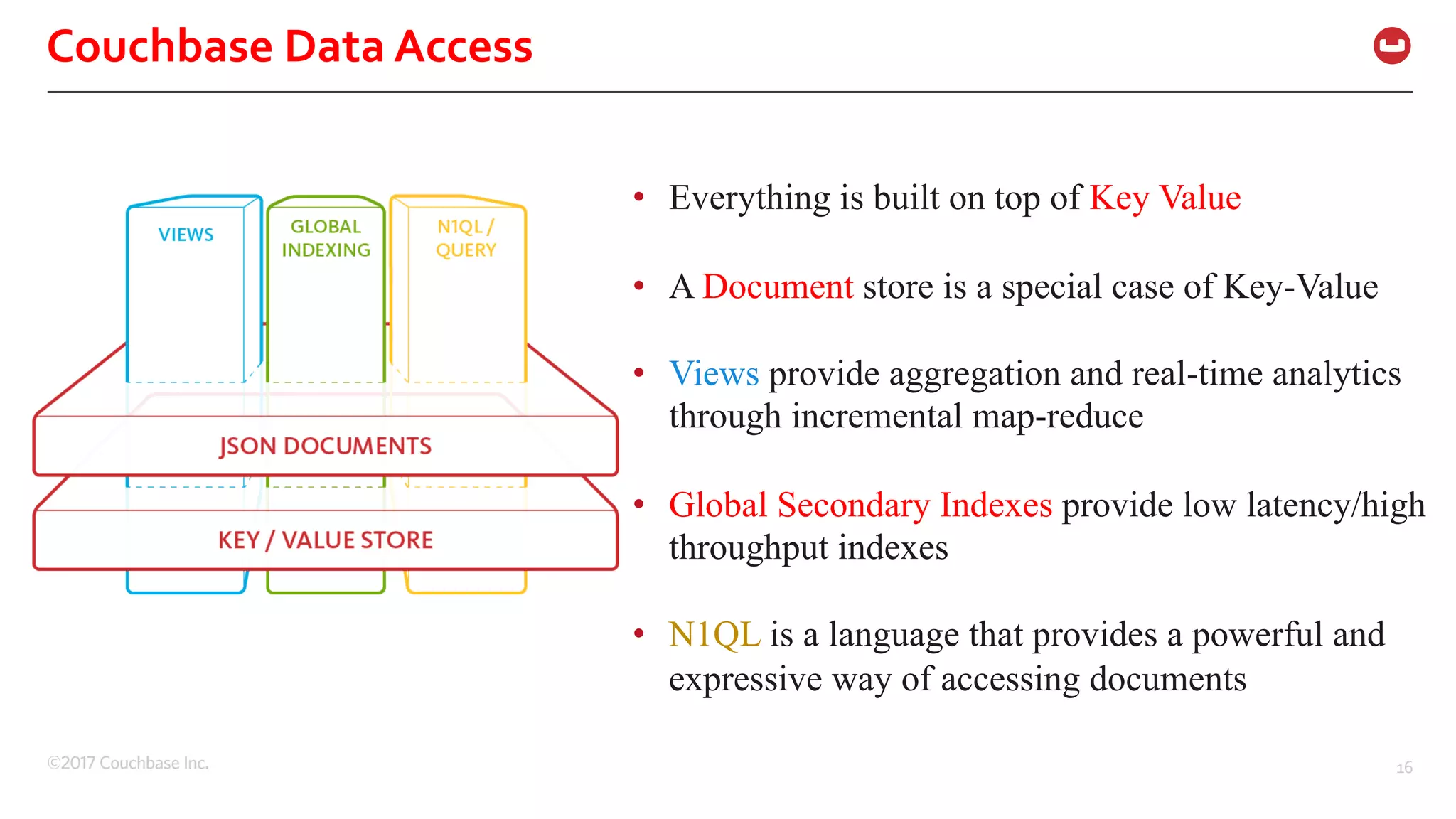
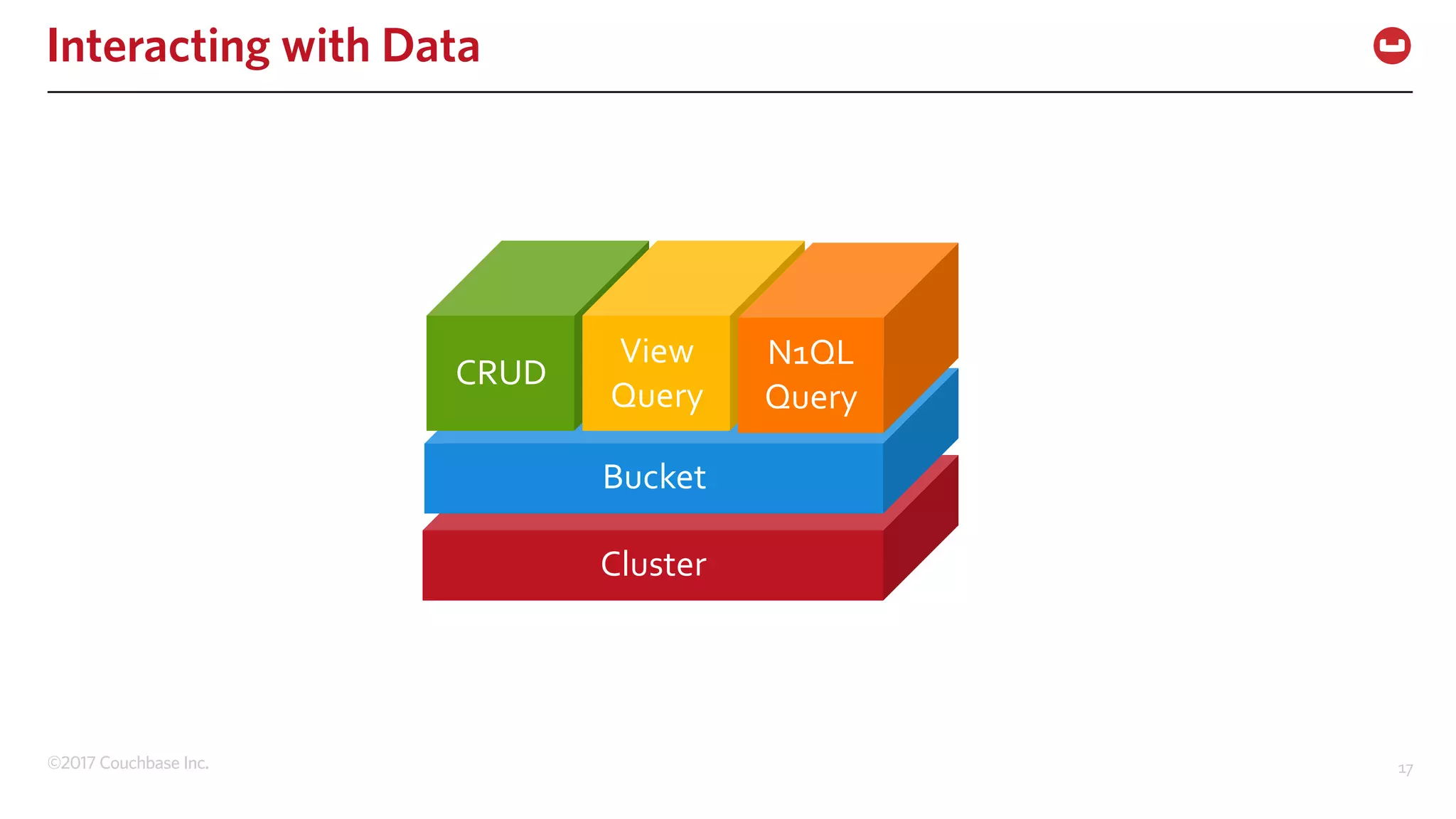
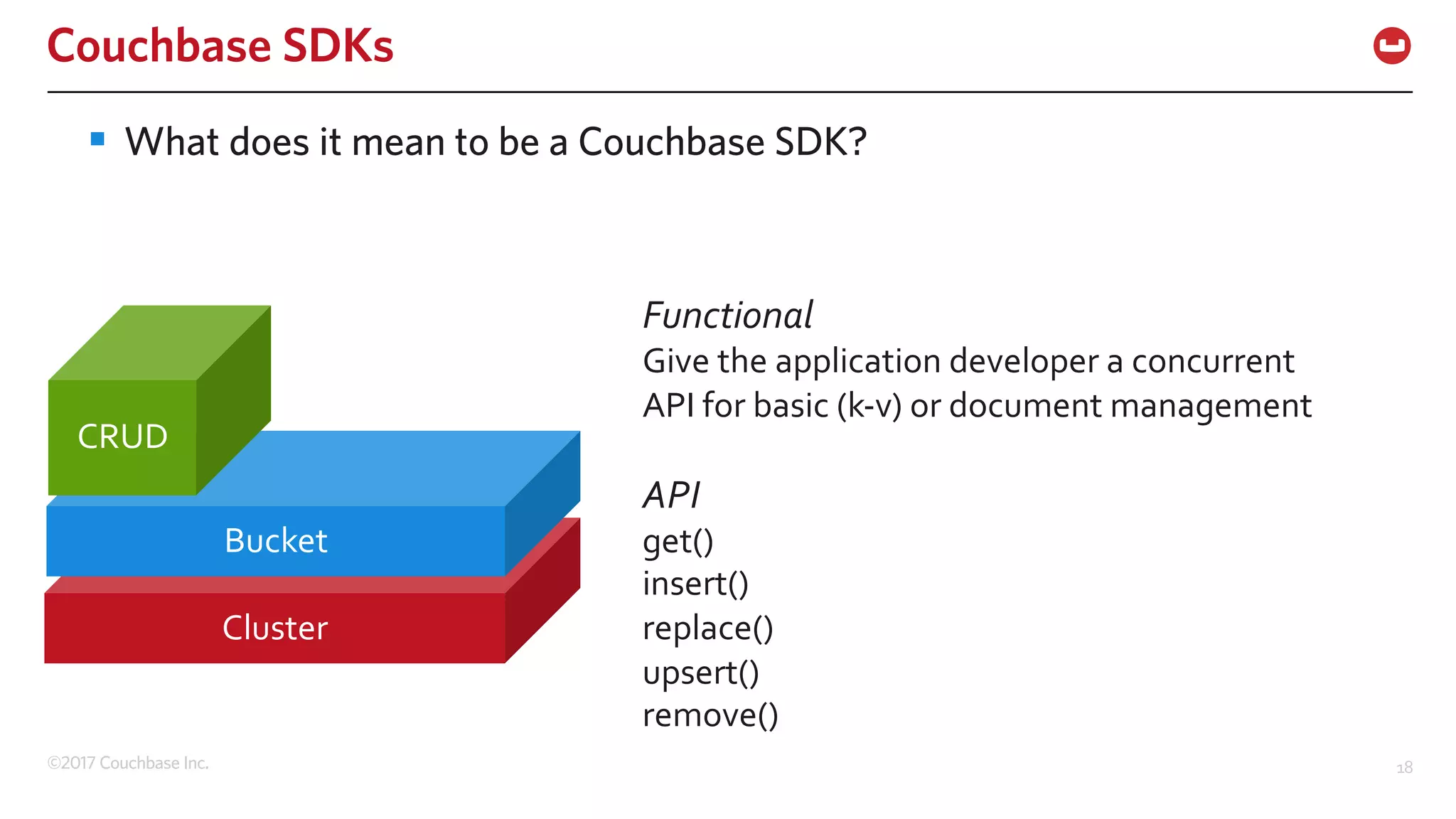
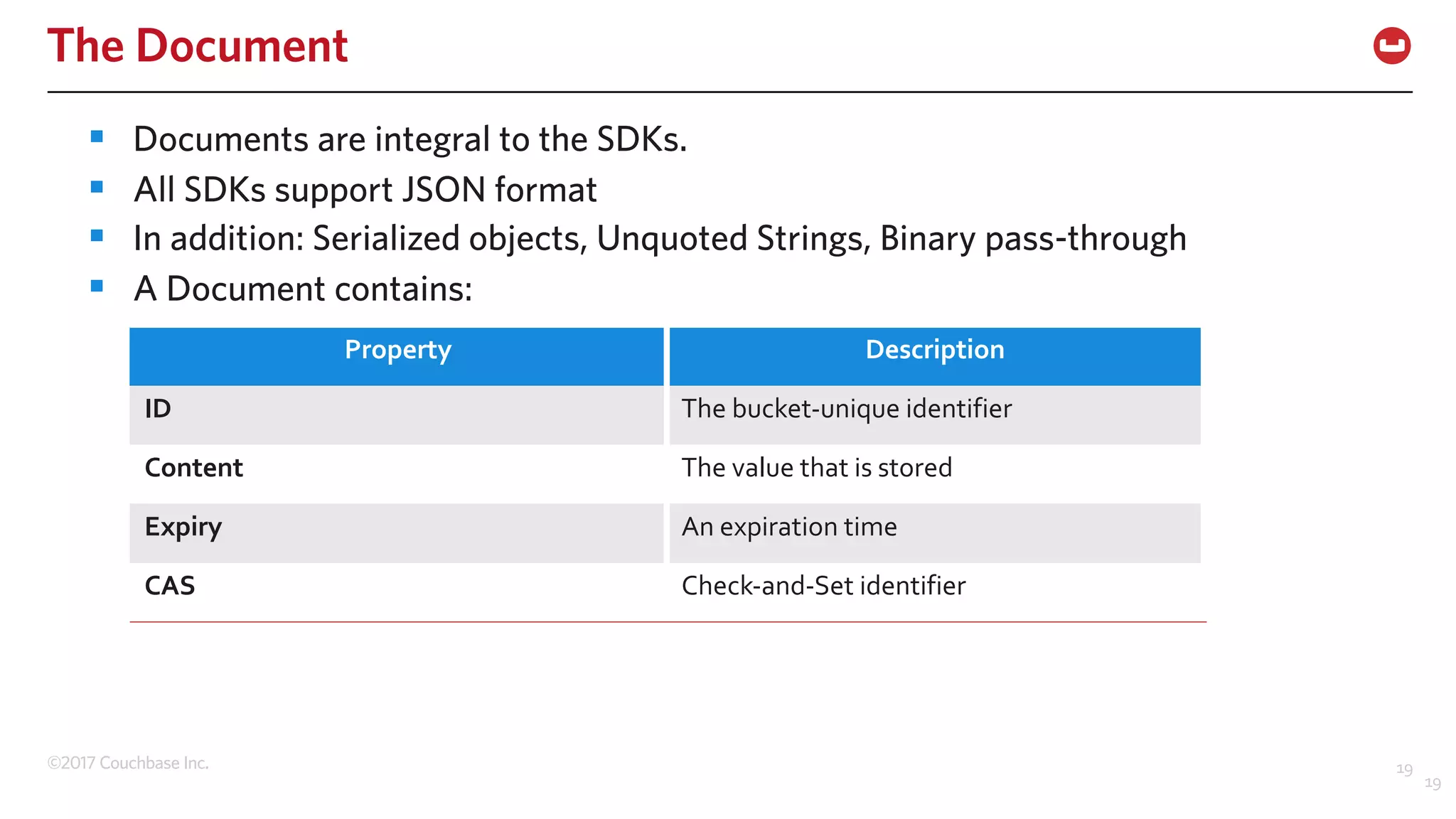
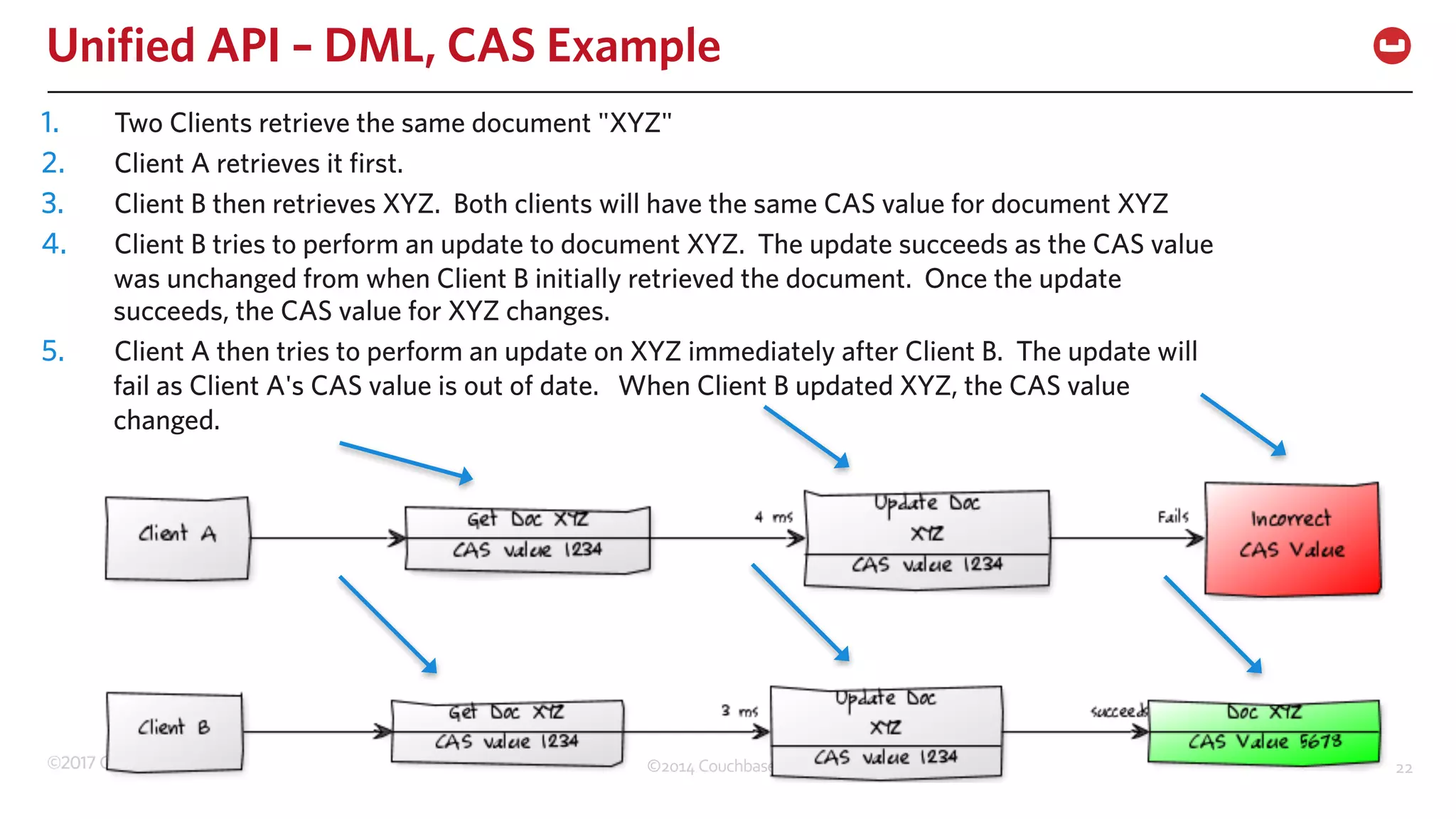
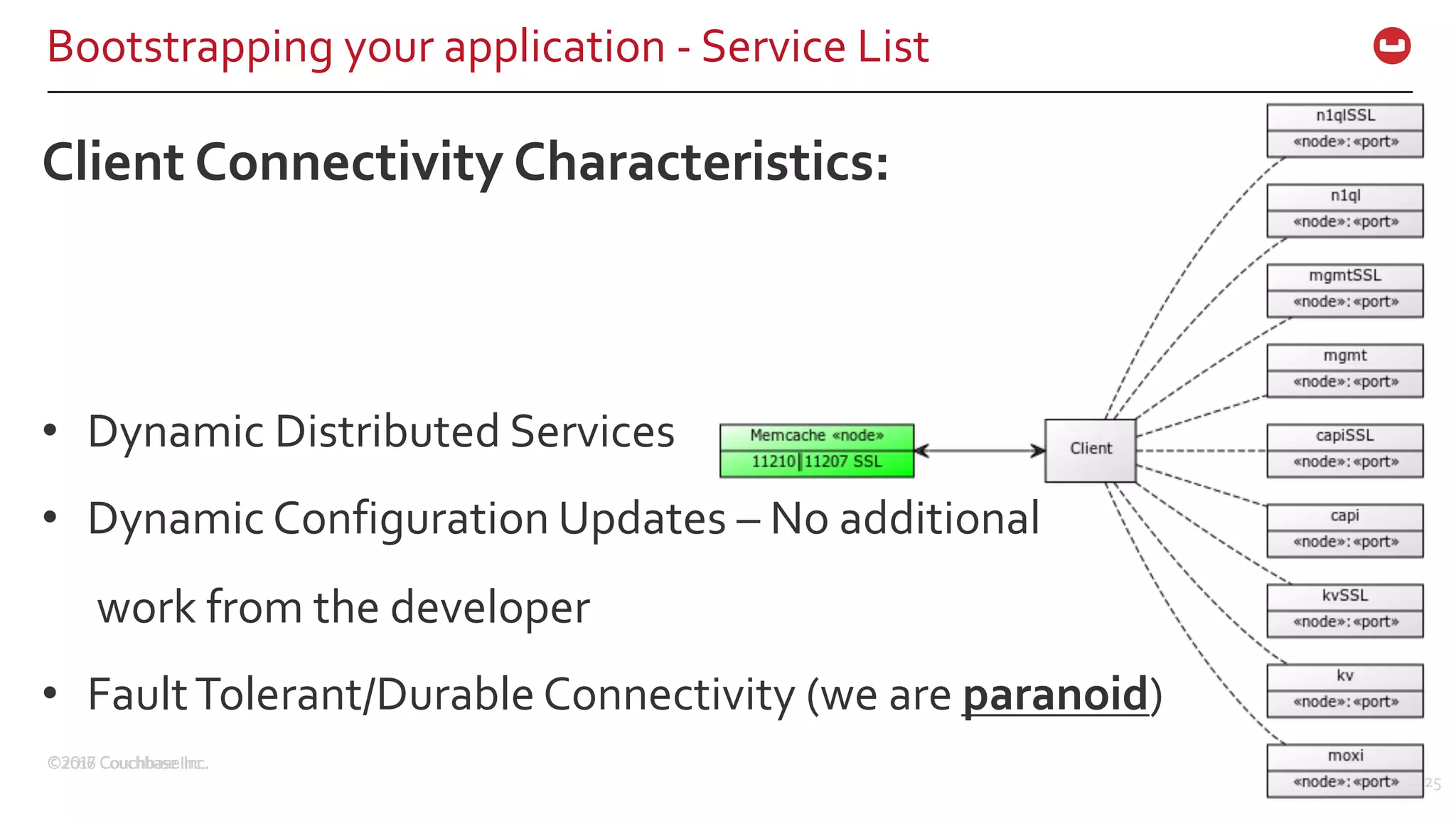
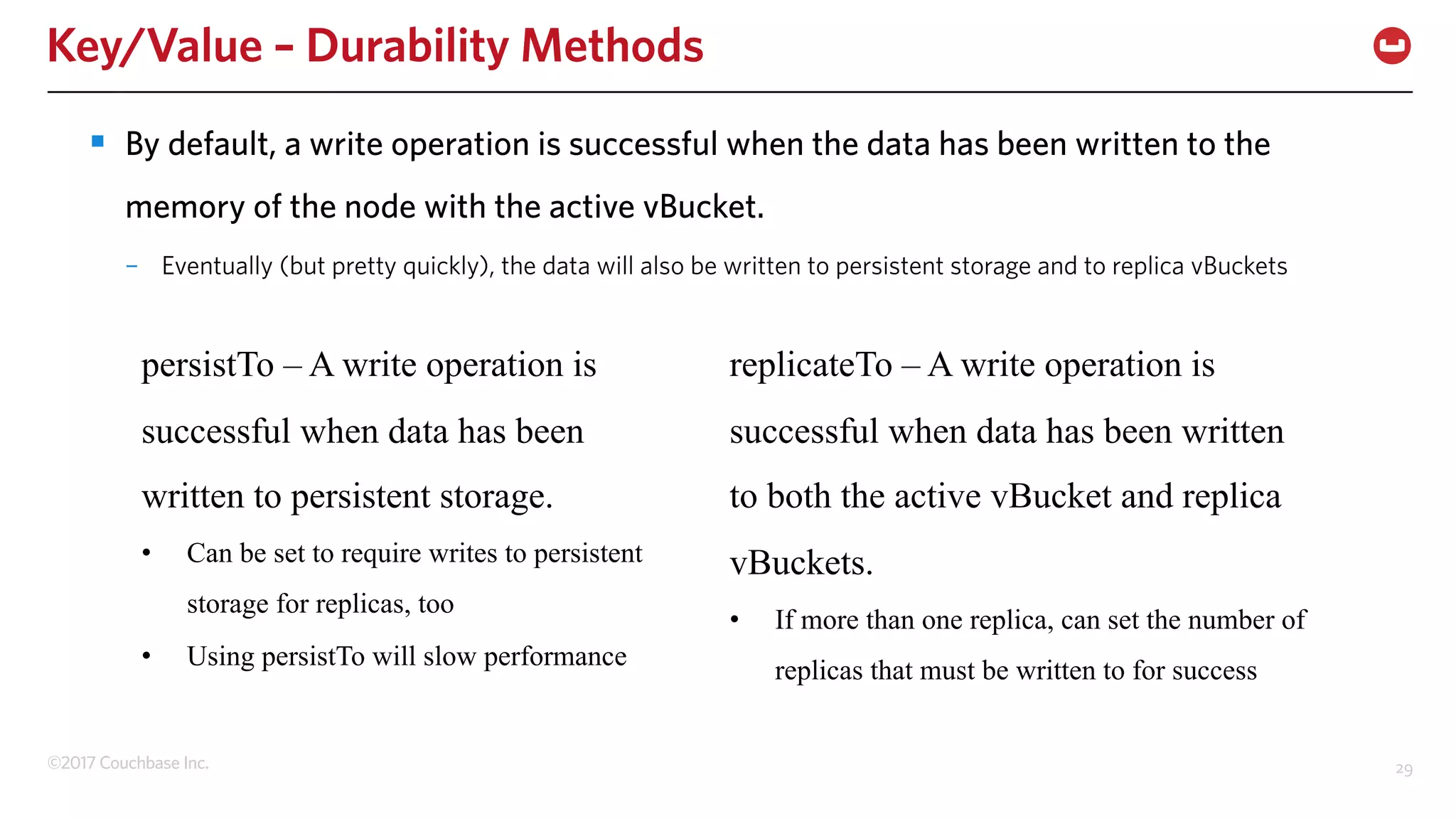
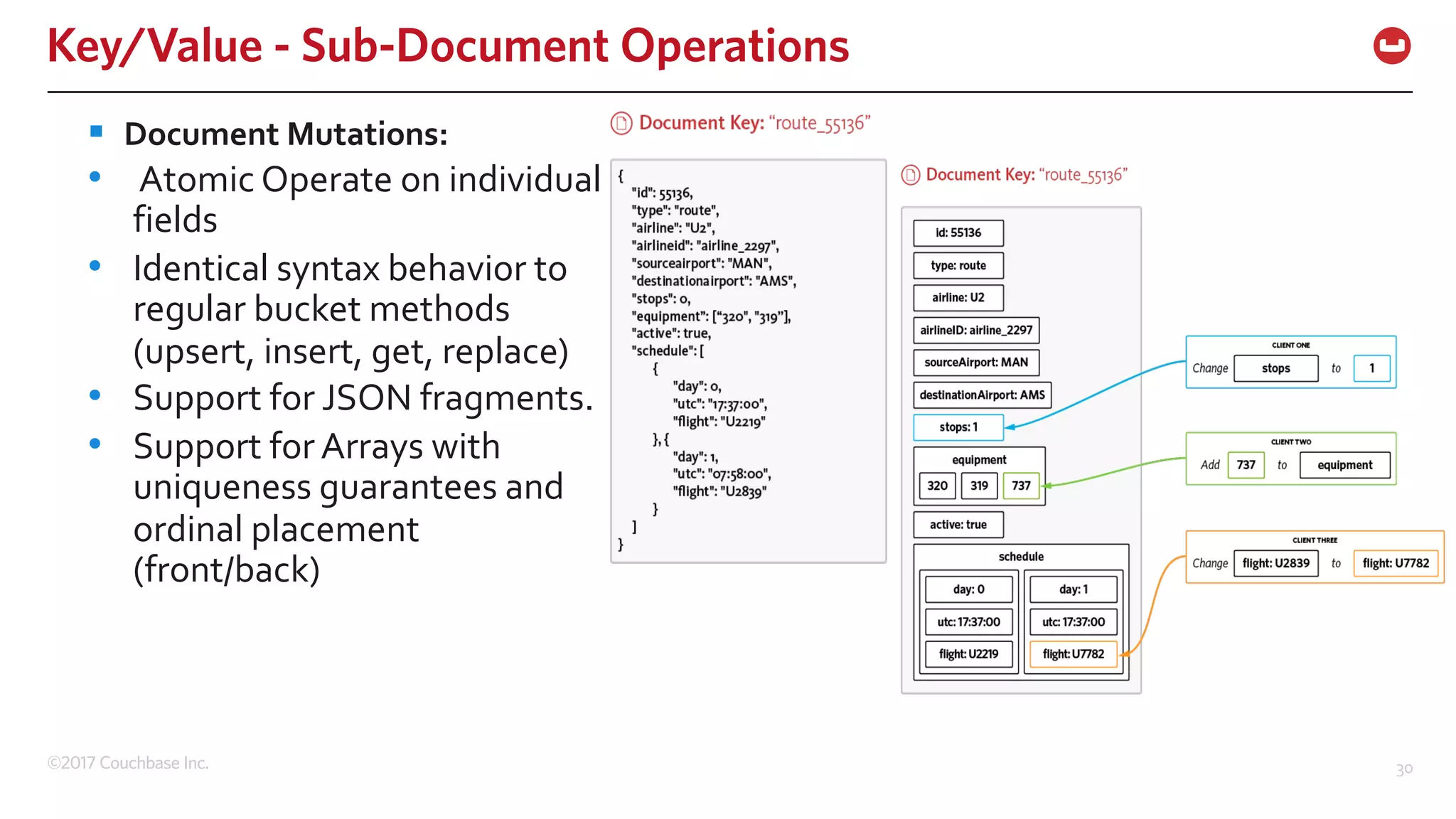
The document discusses the changing landscape of digital engagement, emphasizing the need for adaptable database solutions to support responsive customer experiences across multiple channels and devices. It presents Couchbase as a powerful NoSQL database with features like a flexible schema, mobile access, and data locality, highlighting its service-based architecture and versatile SDK support for various programming languages. Additionally, it outlines key operations related to document management and querying, demonstrating how developers can effectively utilize Couchbase for modern application development.