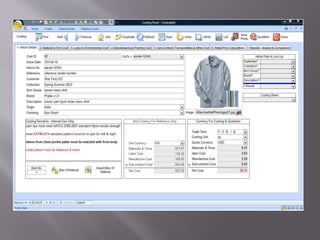
The document discusses various factors to consider when estimating costs for garment production. It notes that total cost allocation has become more complex as indirect costs now make up a significant percentage. It also highlights that accepting or rejecting sales prices is key to profitability and challenges include knowing variable costs and margins before approving orders. Costing is a complex process that involves all activities from raw material purchasing to shipping and overheads. Proper costing requires thorough knowledge of costs, procedures, advantages and risks for all activities.