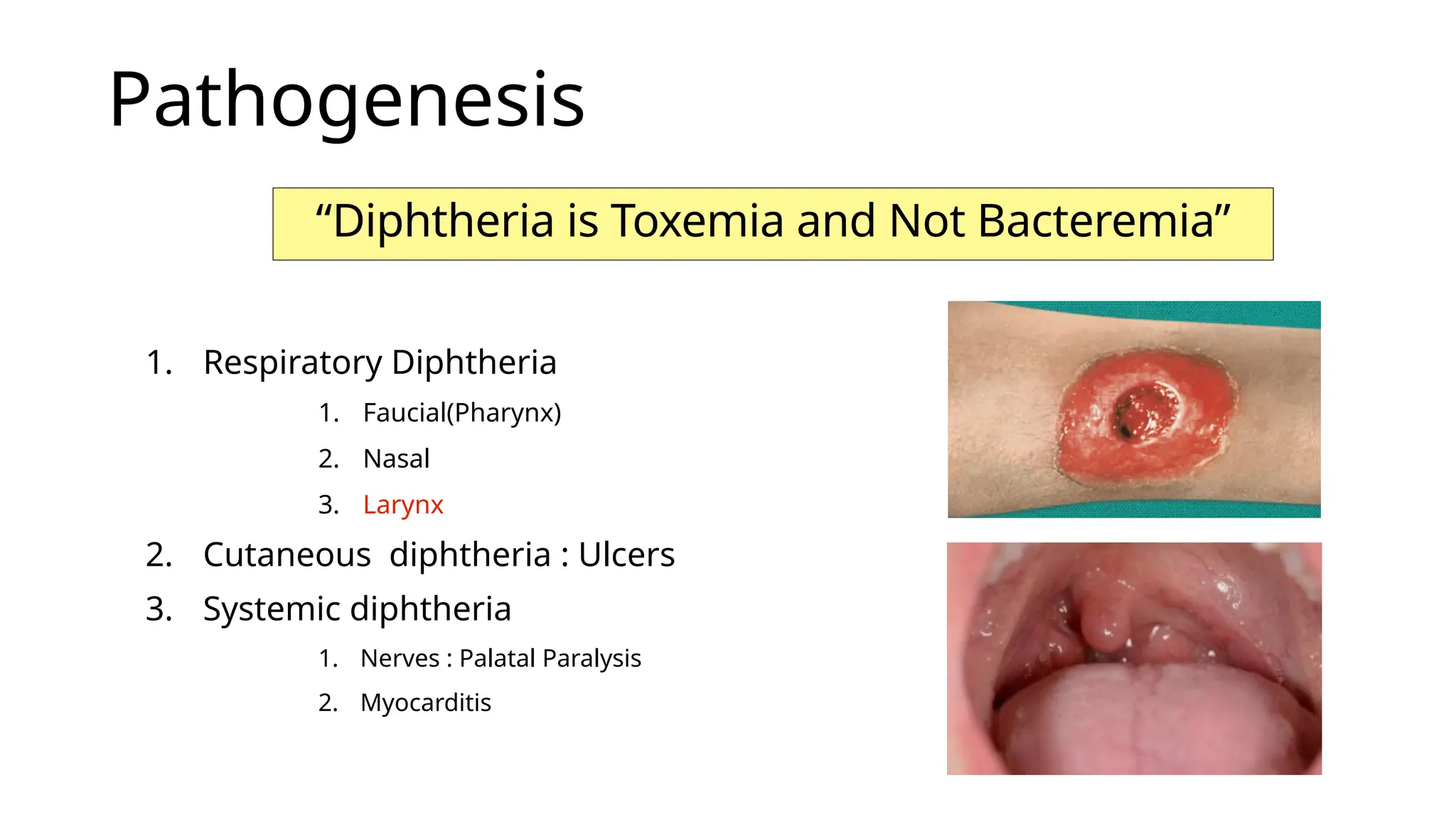
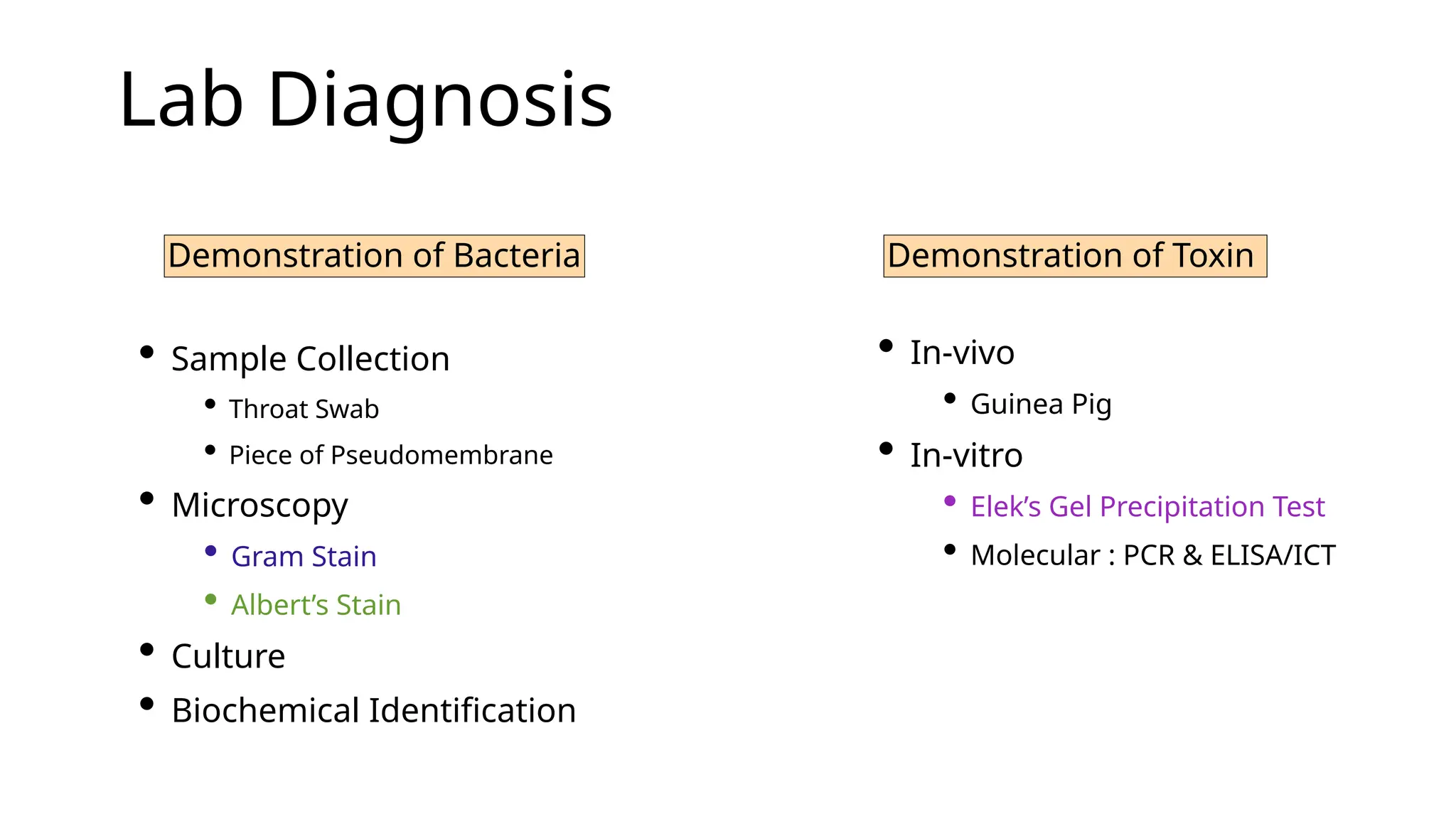
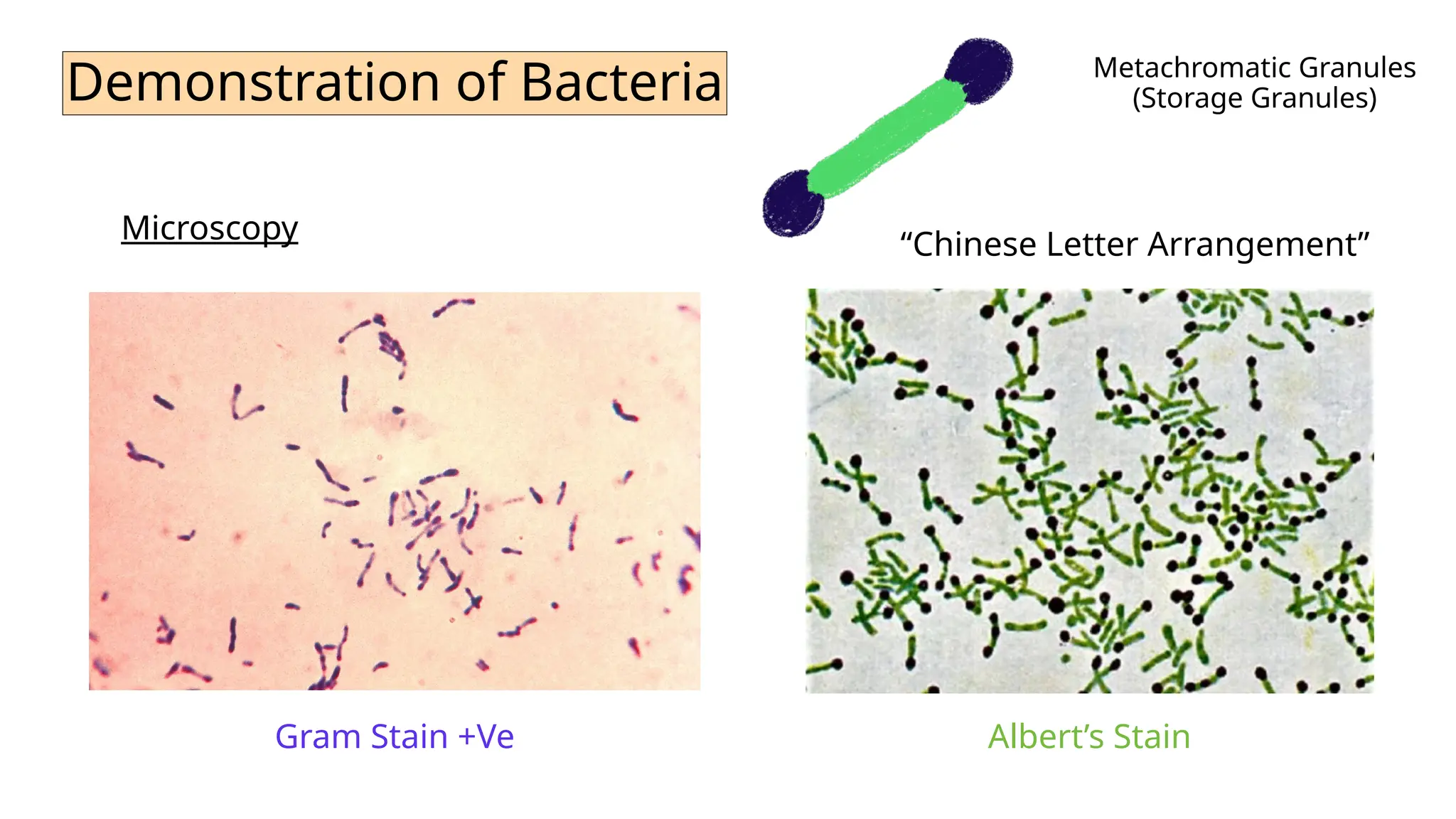
Corynebacterium diphtheriae, known as the 'Klebs-Loeffler bacillus,' causes diphtheria, characterized by a toxic and antigenic diphtheria toxin that primarily affects the heart and nerves. The disease is identified by the formation of a pseudomembrane in the throat, which can lead to asphyxiation. Diagnosis involves culturing the bacterium and demonstrating the toxin through various tests, with immediate antitoxin treatment required if diphtheria is suspected.