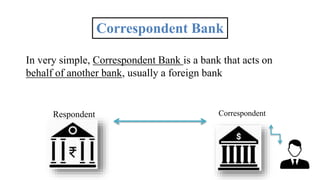
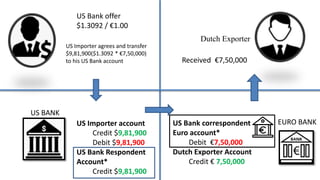
Correspondent banking allows banks to conduct business and provide services in foreign countries where they do not have a physical presence. A correspondent bank acts on behalf of another bank, usually handling transactions internationally. This network facilitates international trade and finance. For example, a US importer can purchase goods from a Dutch exporter by transferring funds from their US bank account, through the US bank's correspondent account at a Dutch bank, to pay the Dutch exporter directly in euros. The correspondent banking relationship and networks allow for efficient currency exchange and money transfers globally.