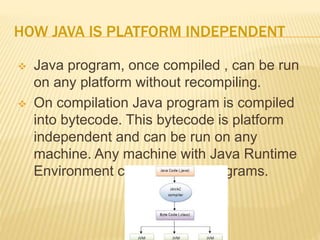
The document provides an overview of core Java concepts including classes, objects, primitive data types, arrays, object-oriented programming principles like inheritance, abstraction, encapsulation and polymorphism. It also discusses packages and libraries in Java. Key topics covered are the difference between classes and objects, how classes are used to define objects, and the standard Java packages that are included in the Java Runtime Environment.








![OBJECT:
object or instance is basic runtime entity. E.g. Maruti Alto, WaganR, Maruti
Swift etc.
Example :
public class Puppy{
Public puppy(string name){
Sop(passed name is:”+name);
}
Public static void main(string[]args){
//this object
Puppy mypuppy =new puppy(“tommy”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-190415121330/85/Core-java-9-320.jpg)

![ARRAY INDEX
int[] age = new int[5];
The first element of array is age[], second is age[1] and so on.
If the length of an array is n, the last element will be arrayName[n-1]. Since the
length of arr array is 5, the last element of the array is age[4]
The default initial value of elements of an array is 0 for numeric types
and false for boolean.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-190415121330/85/Core-java-11-320.jpg)




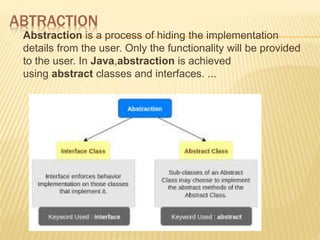





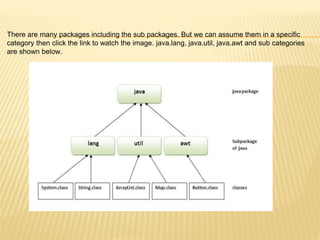
![WHAT IS PACKAGE IN JAVA?
A Package is a collection of related classes. It helps organize your classes into a folder
structure and make it easy to locate and use them,
Although interfaces and classes with the same name cannot appear in the same package,
they can appear in different packages. This is possible by assigning a separate namespace
to each package.
example
Package c1;
Class c1(){
Pulblic void m1(){
System.out.println(“m1 of c1”);
}
Public static void main (String args[]);
C1 obj = new c1();
Obj.m1();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-190415121330/85/Core-java-24-320.jpg)