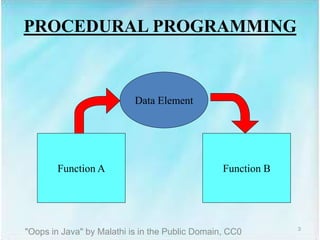
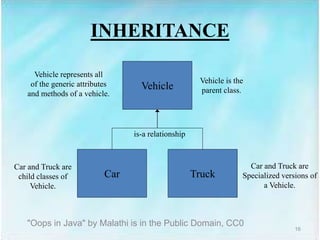
The document introduces object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts, contrasting them with procedural programming. Key aspects include encapsulation, data hiding, inheritance, and polymorphism, emphasizing how these principles enhance code reusability and reduce debugging time. OOP is exemplified in Java, highlighting classes as blueprints for creating objects that interact to achieve specific goals.