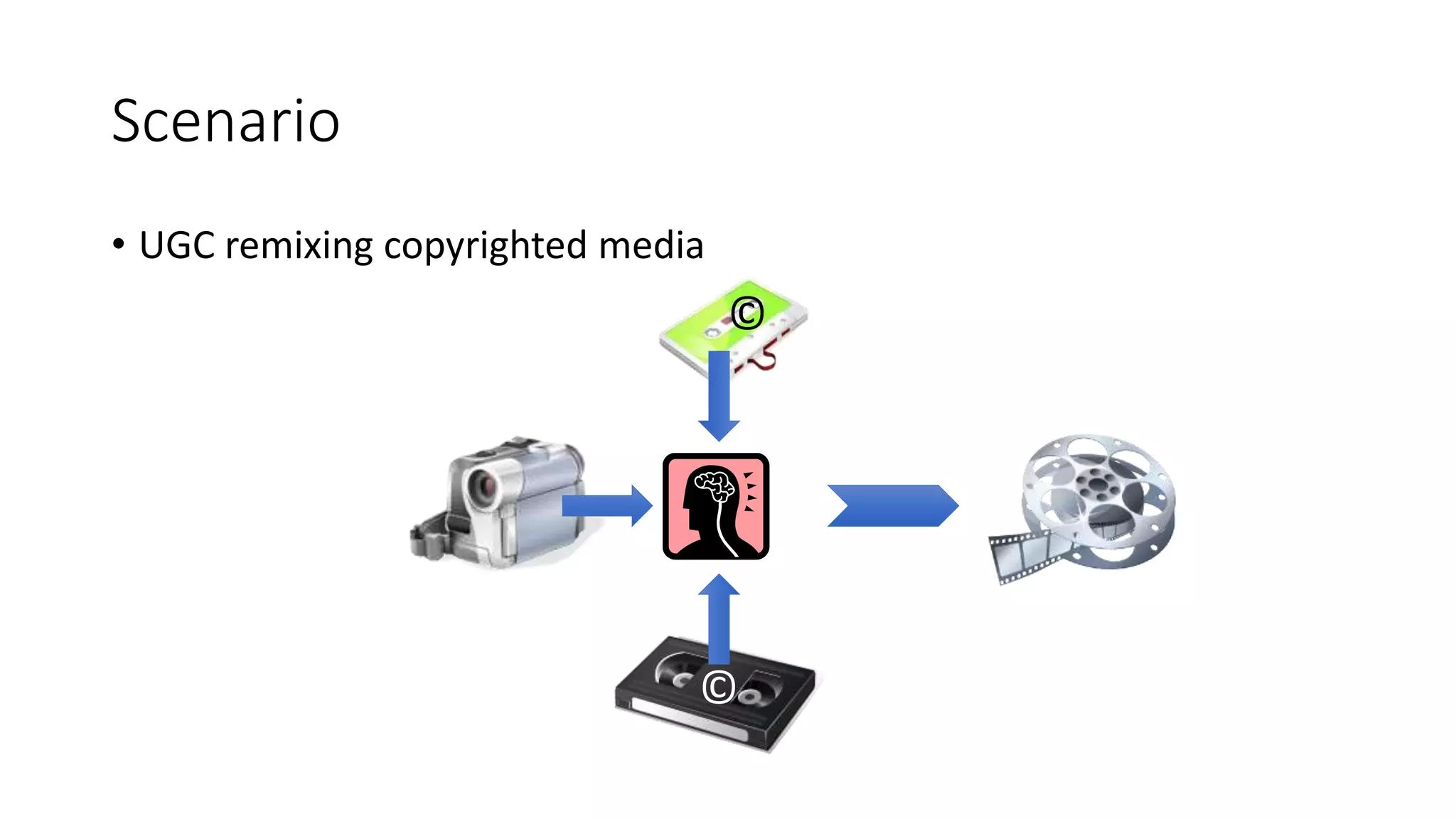
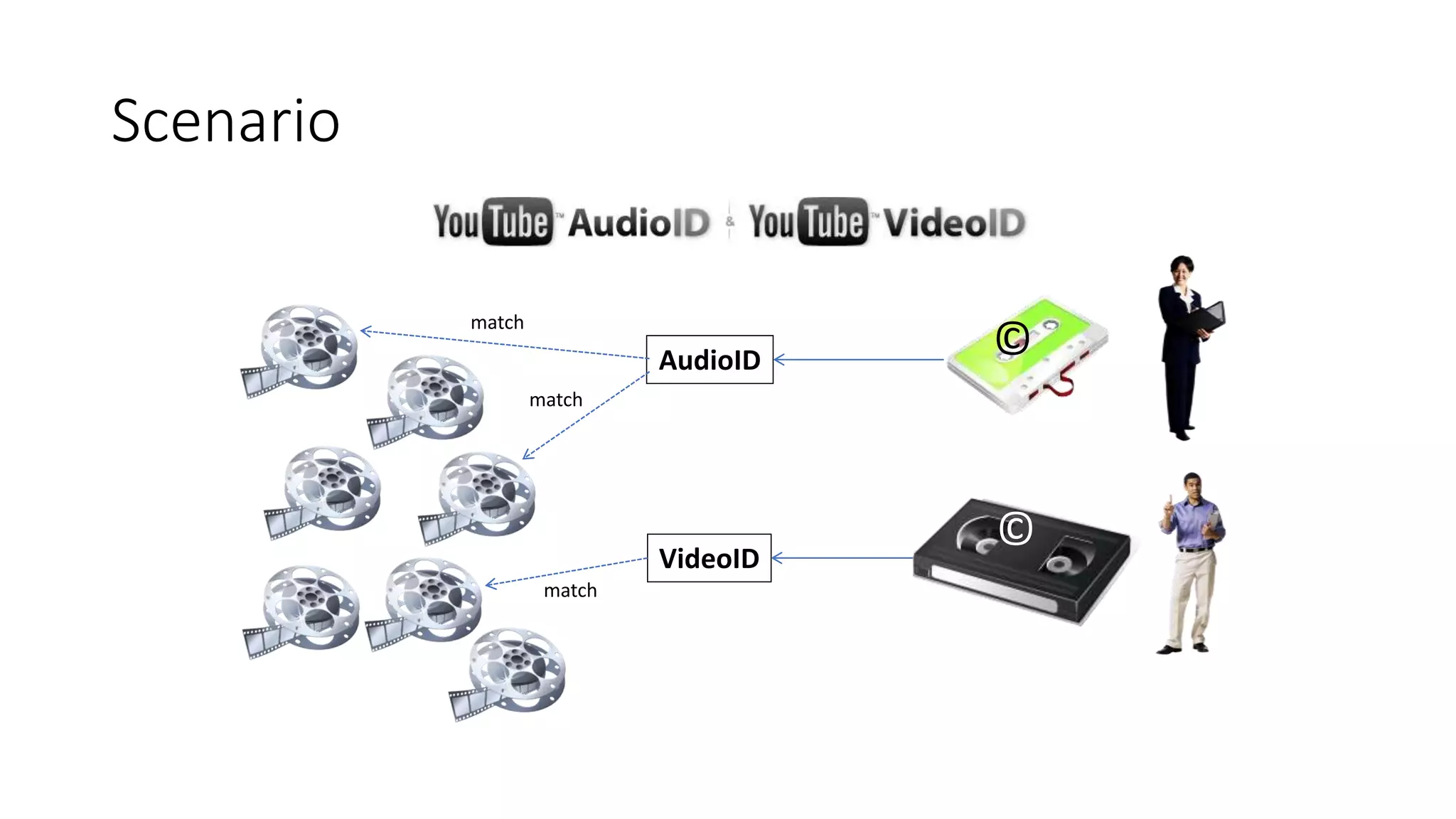
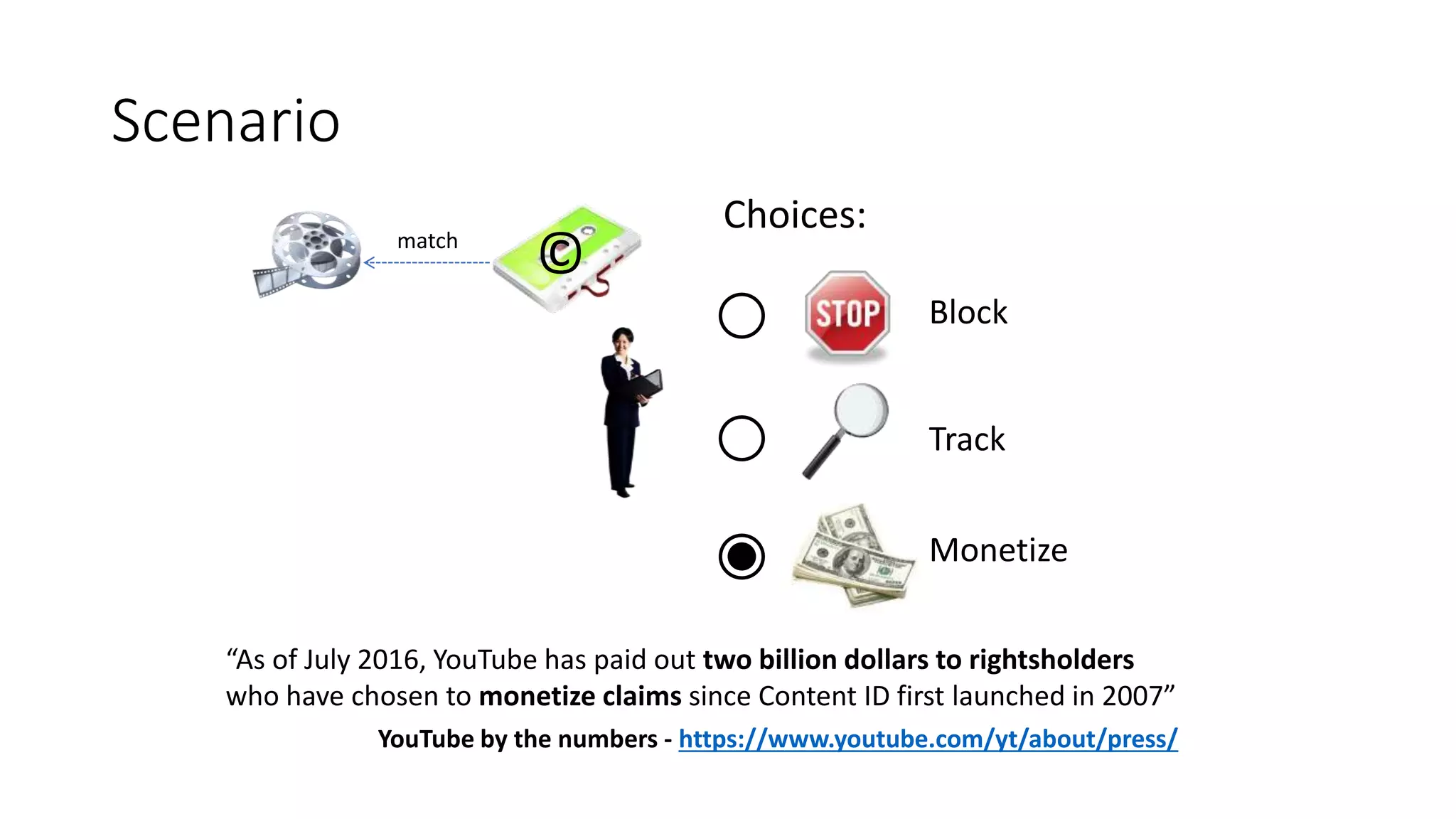
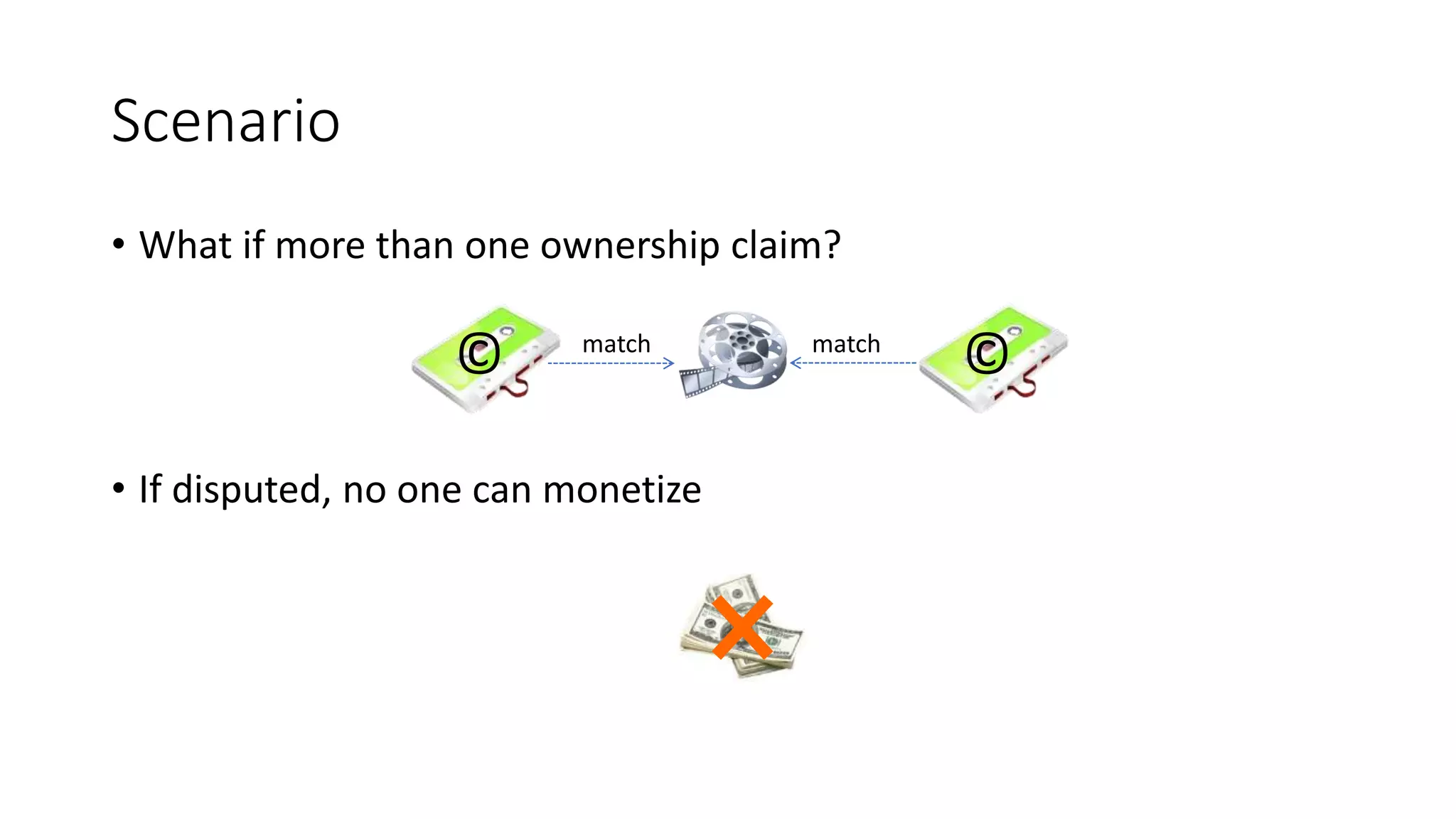
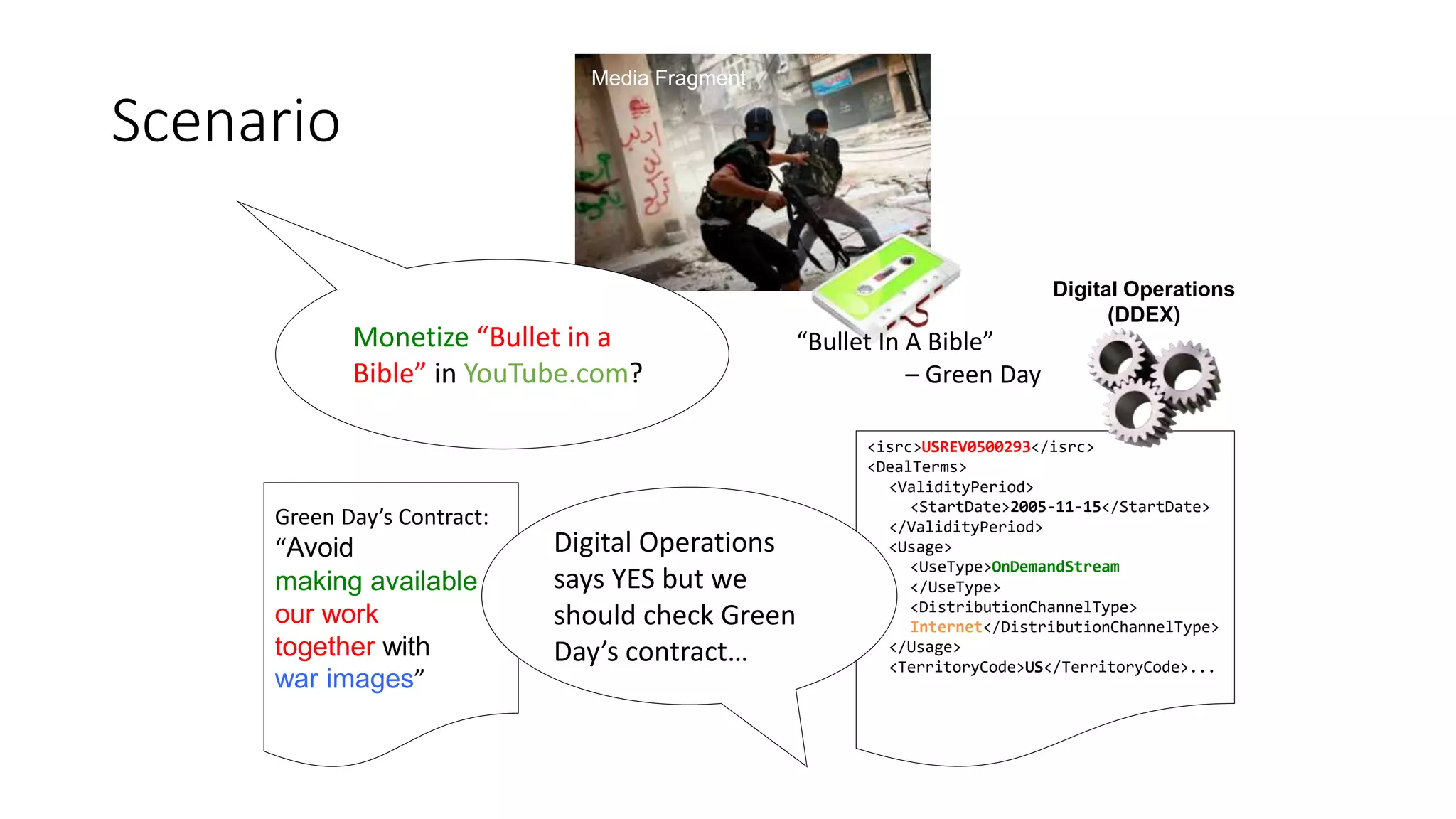
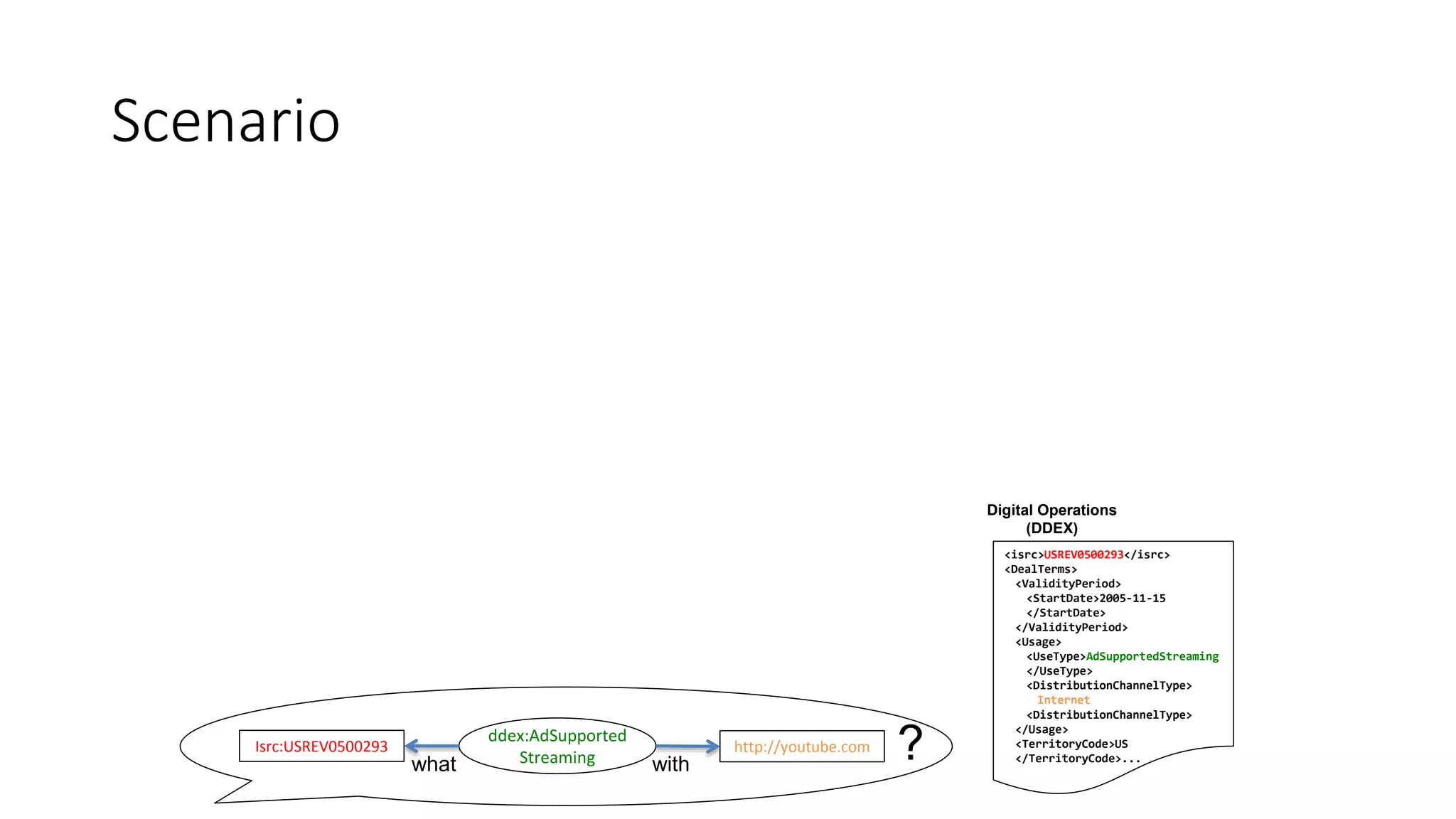
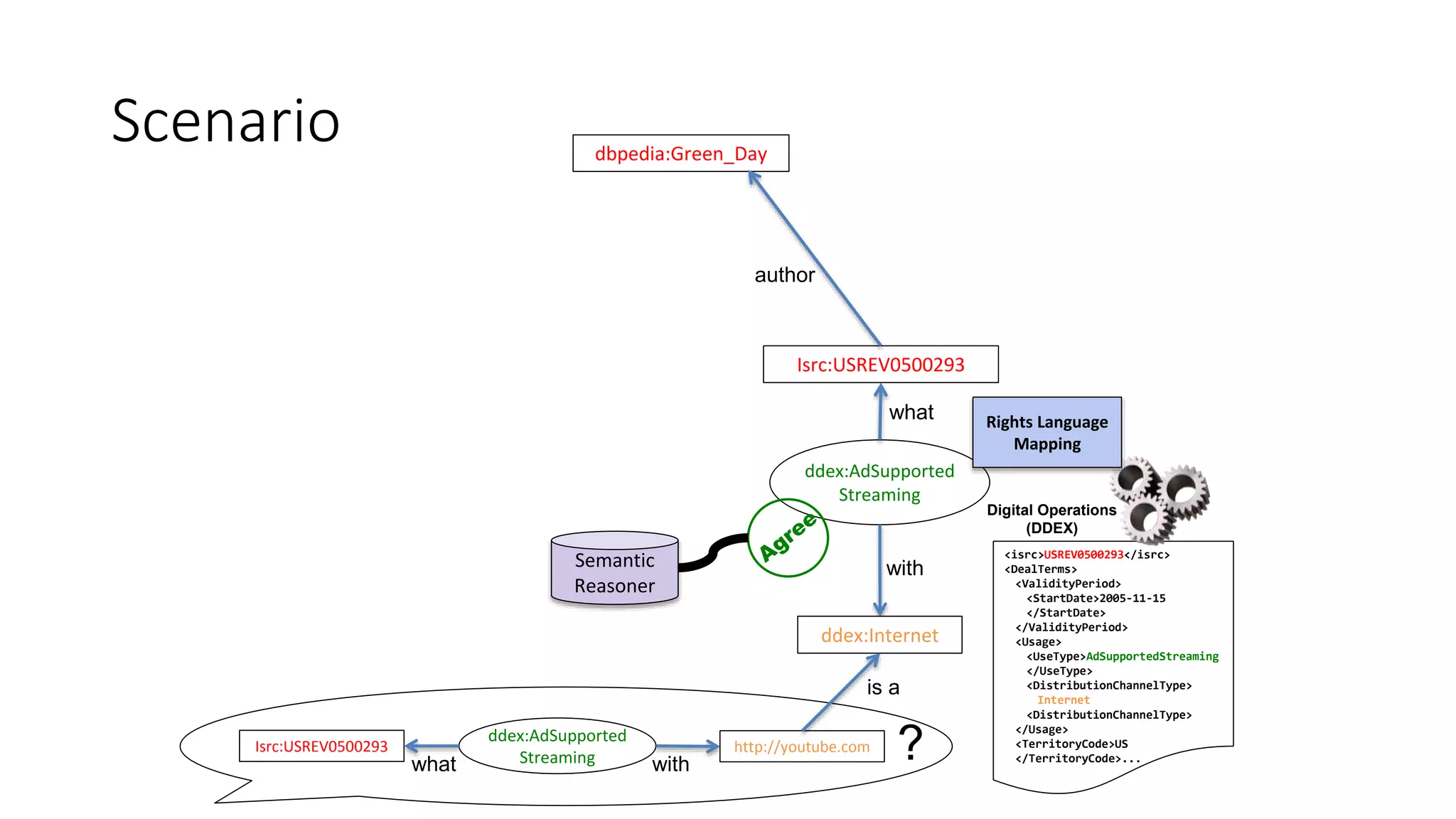
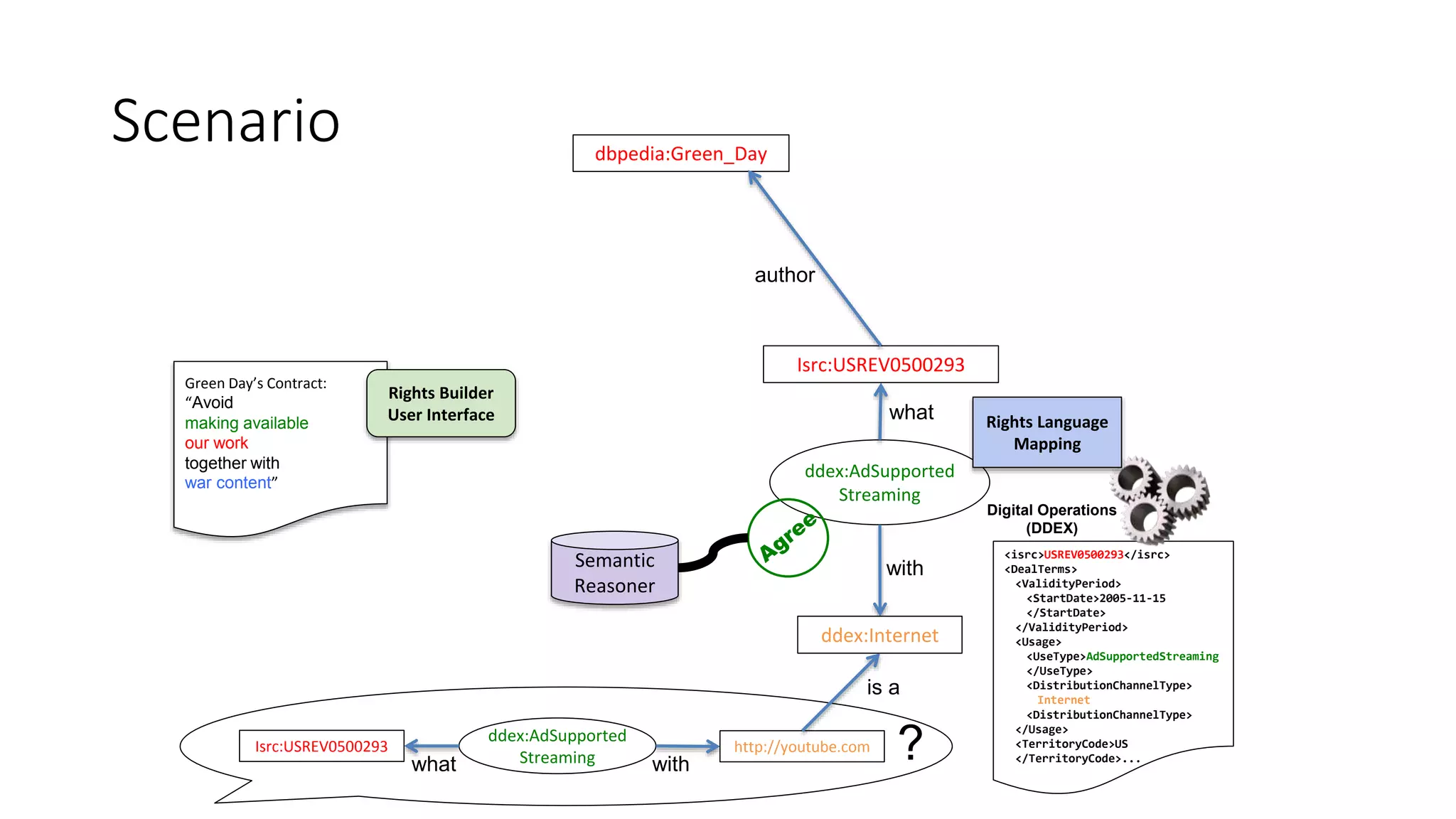
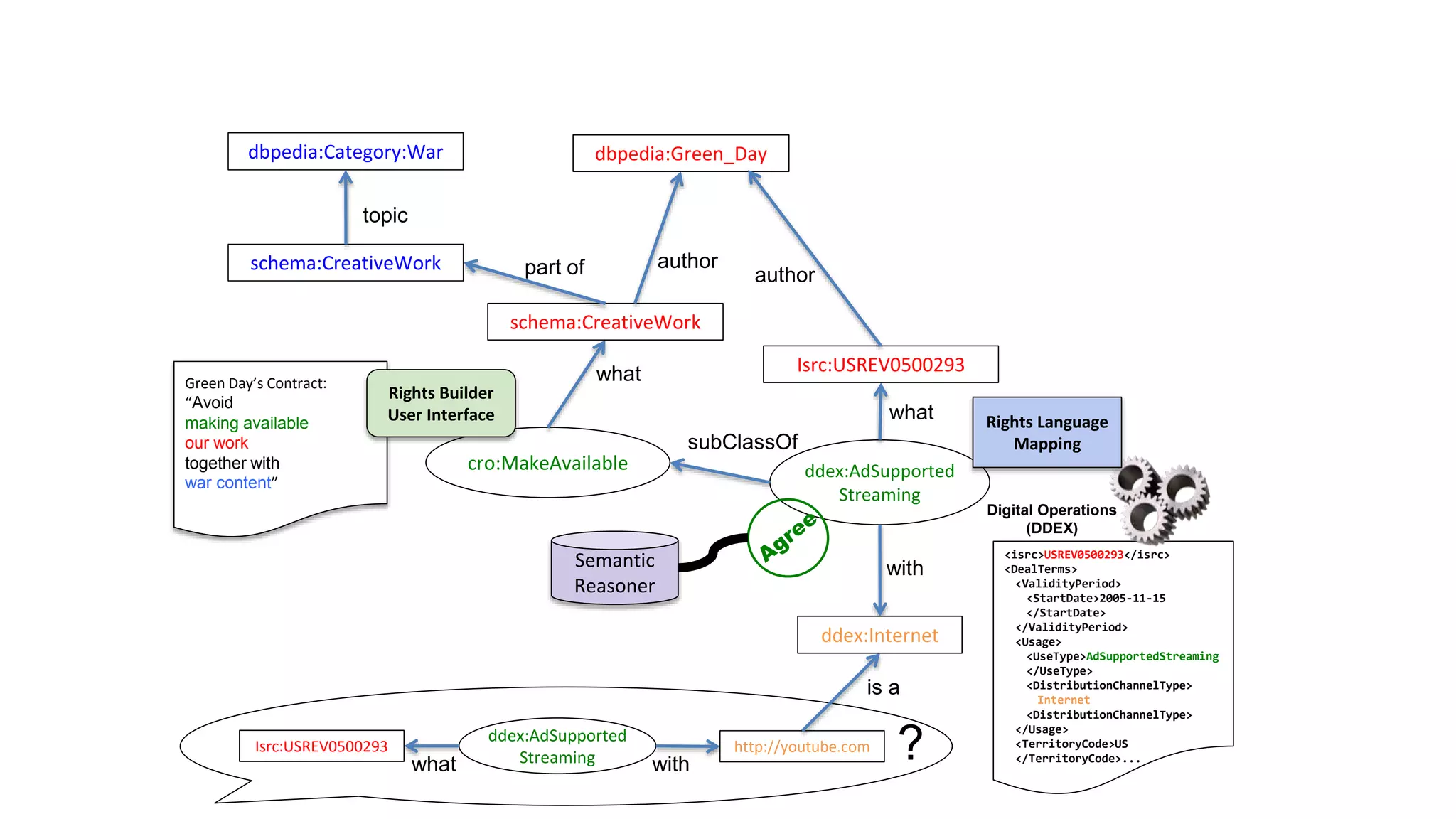
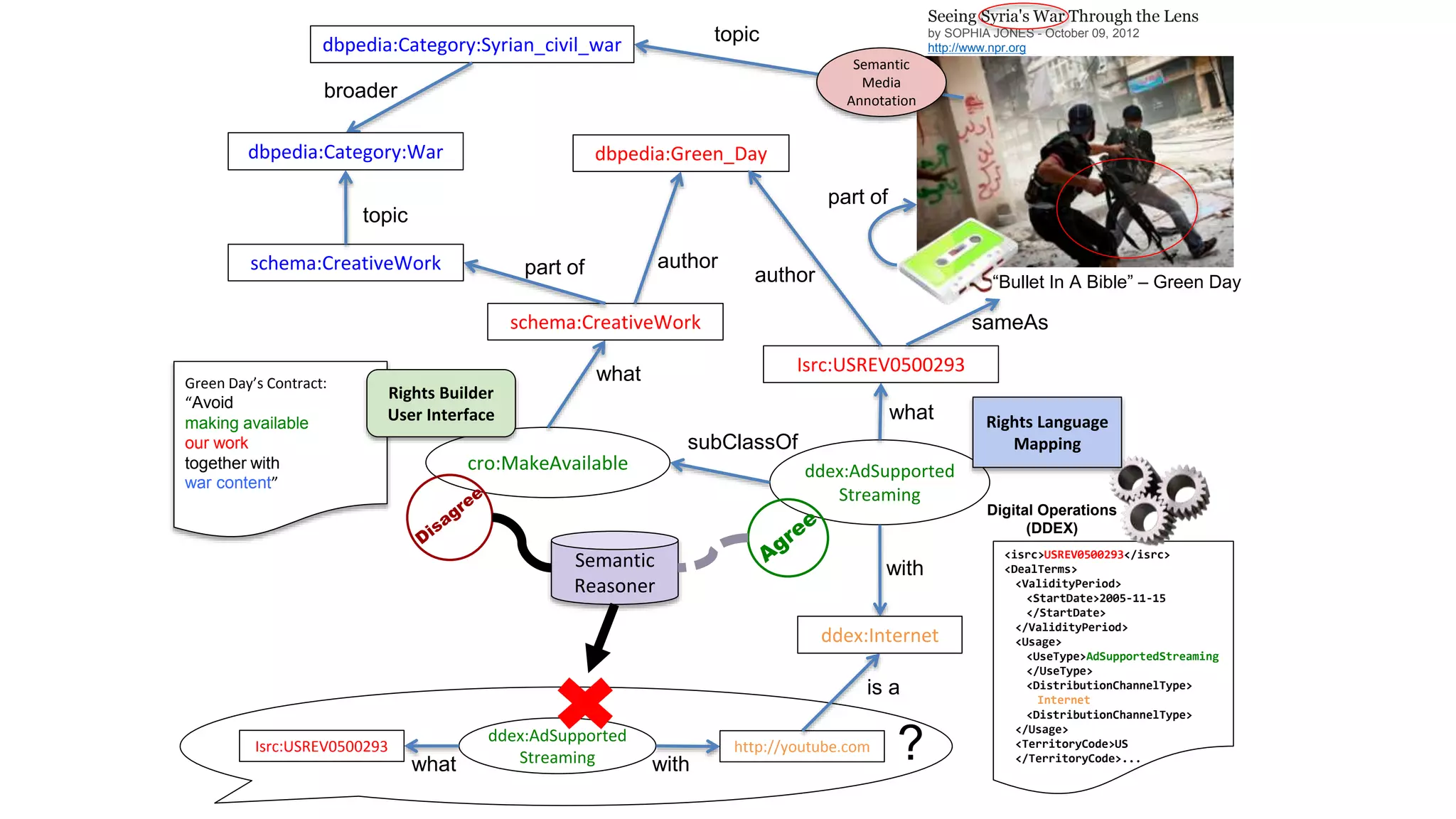
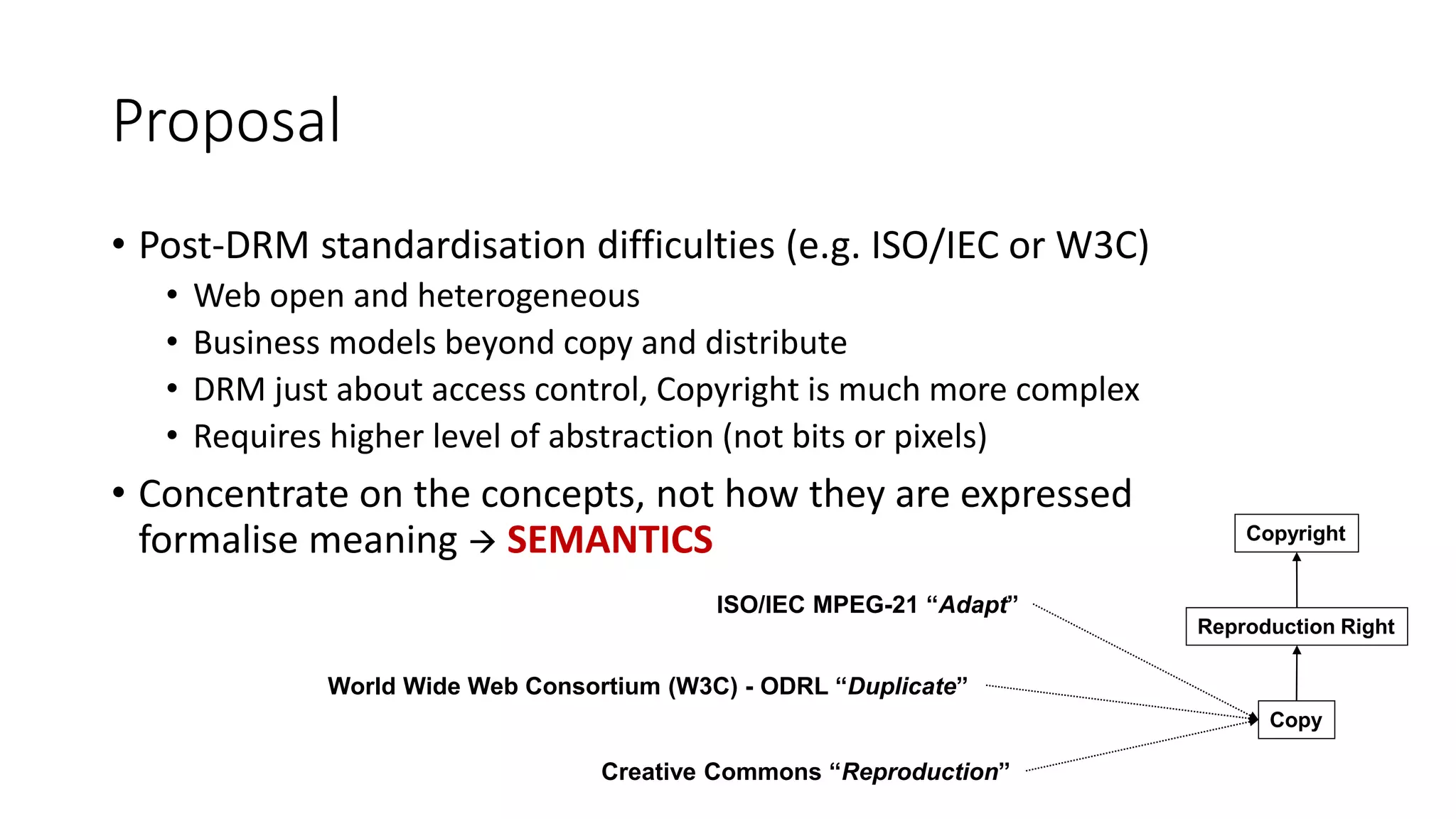
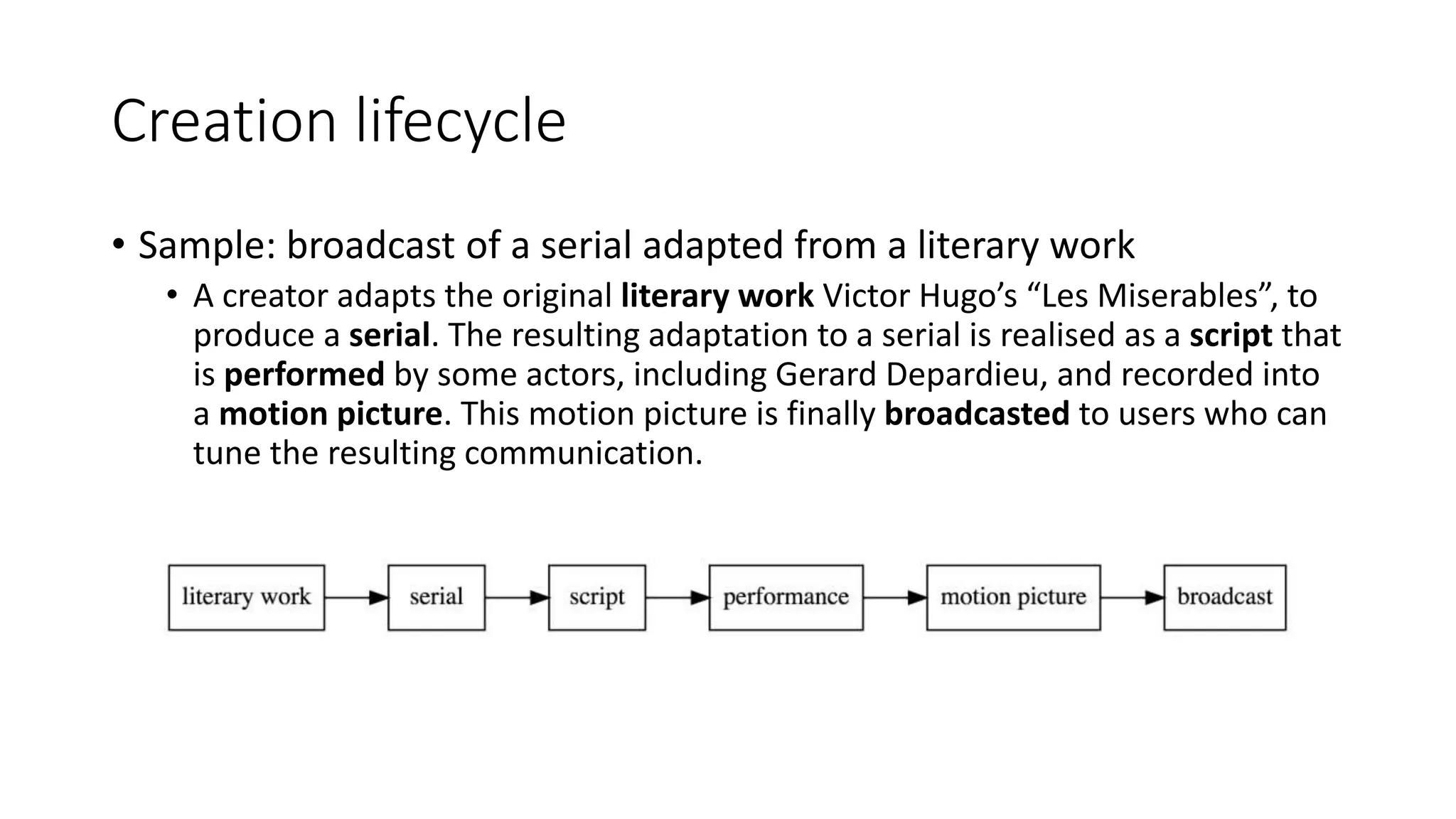
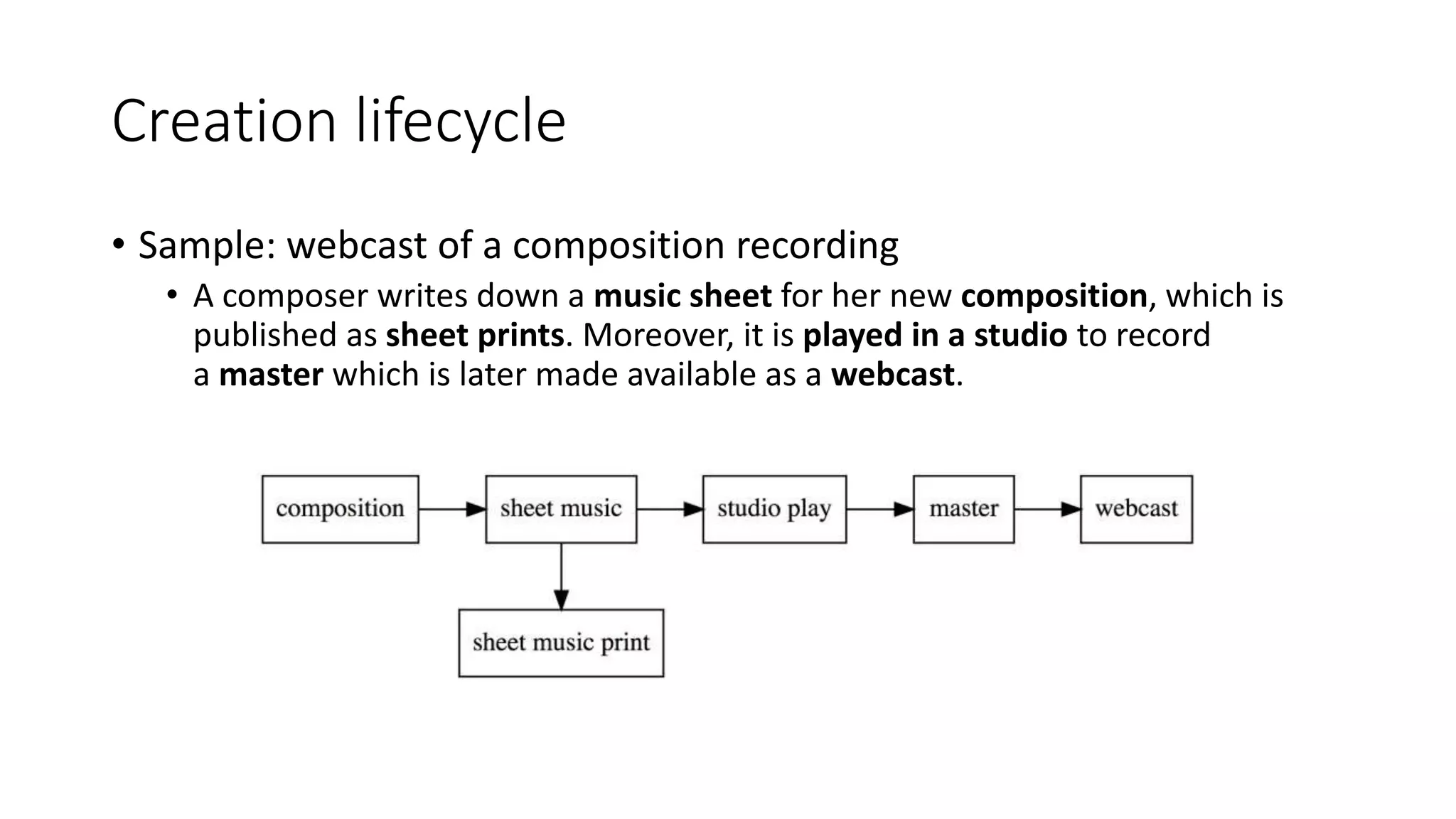
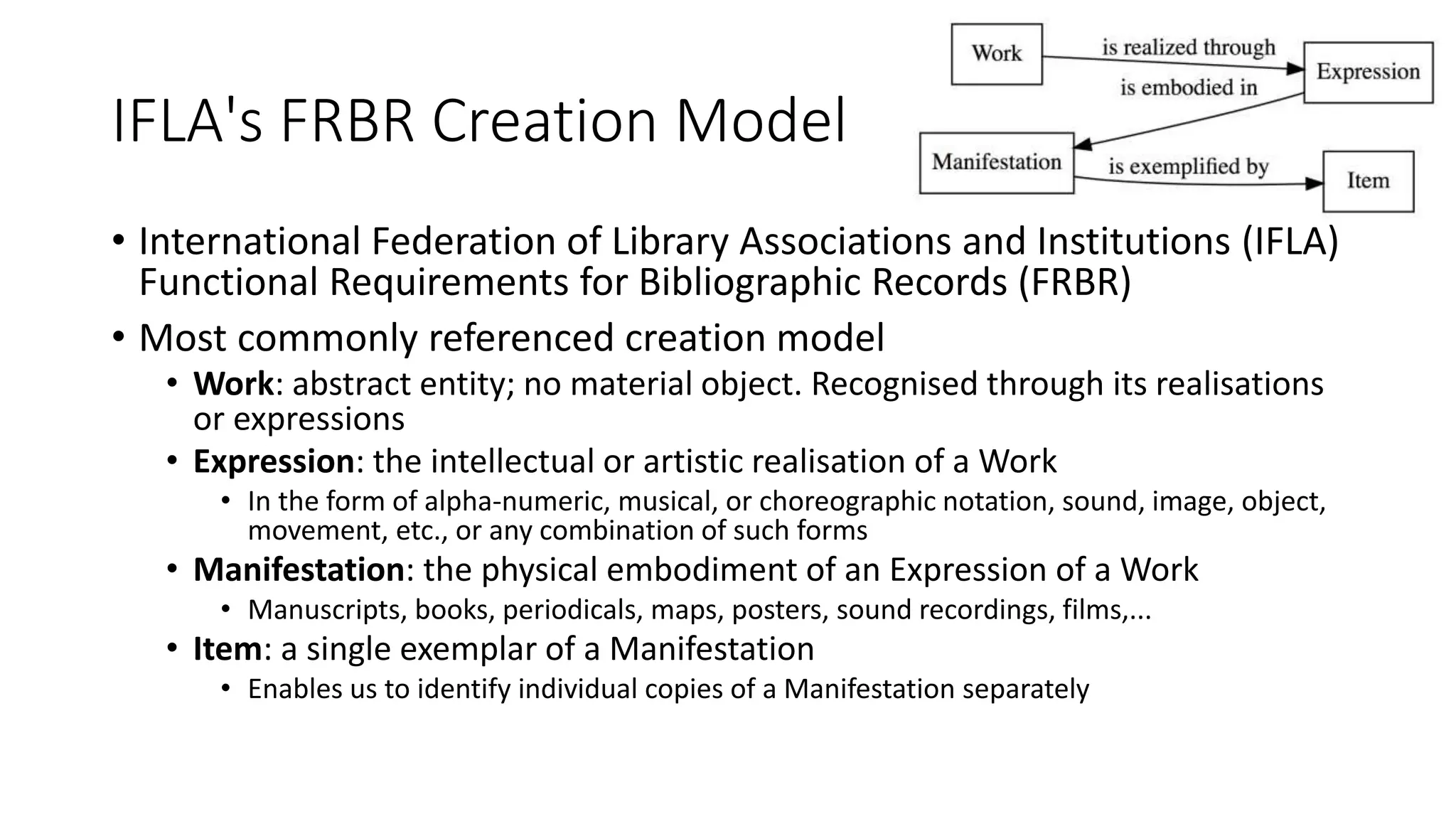
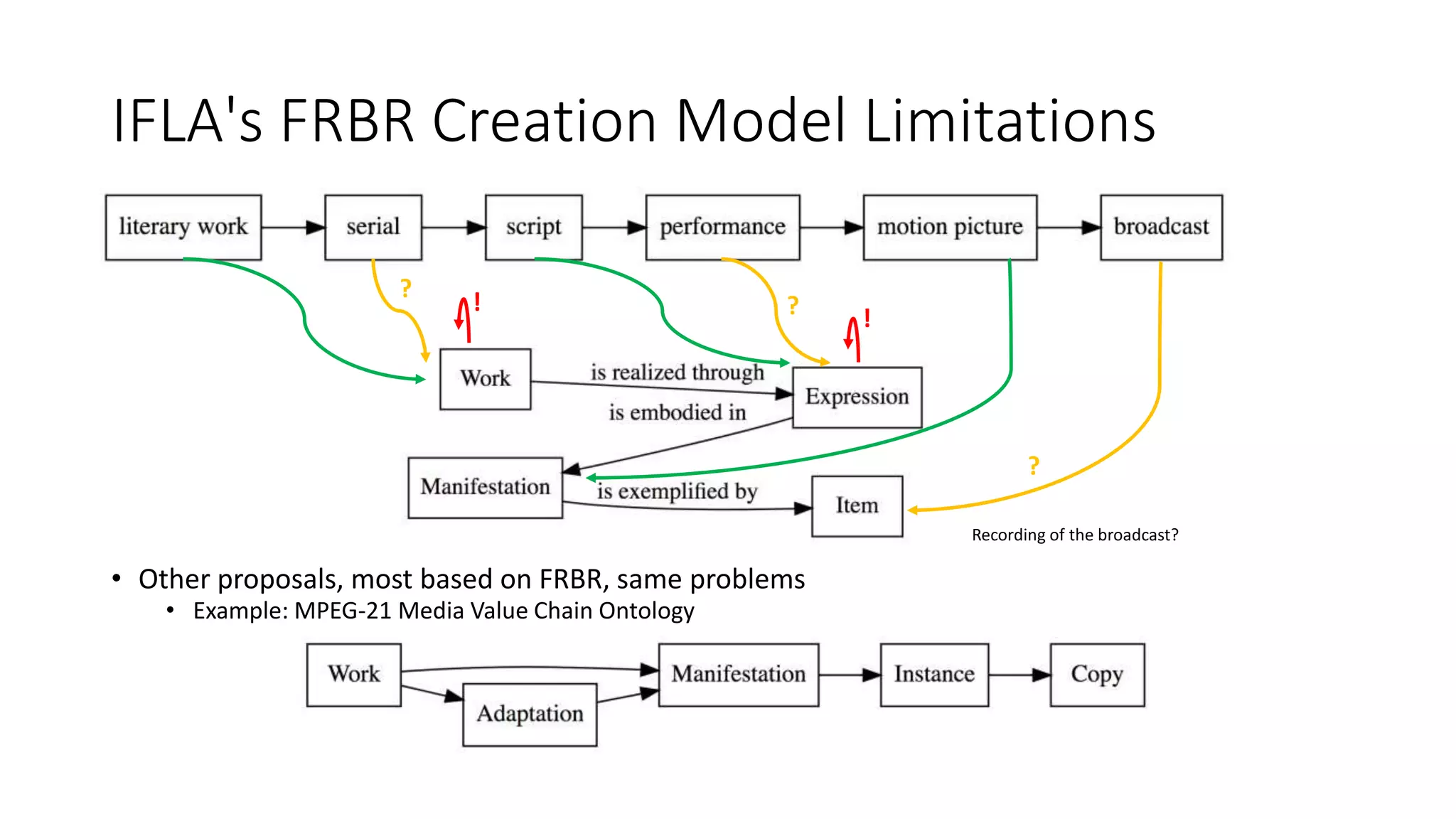
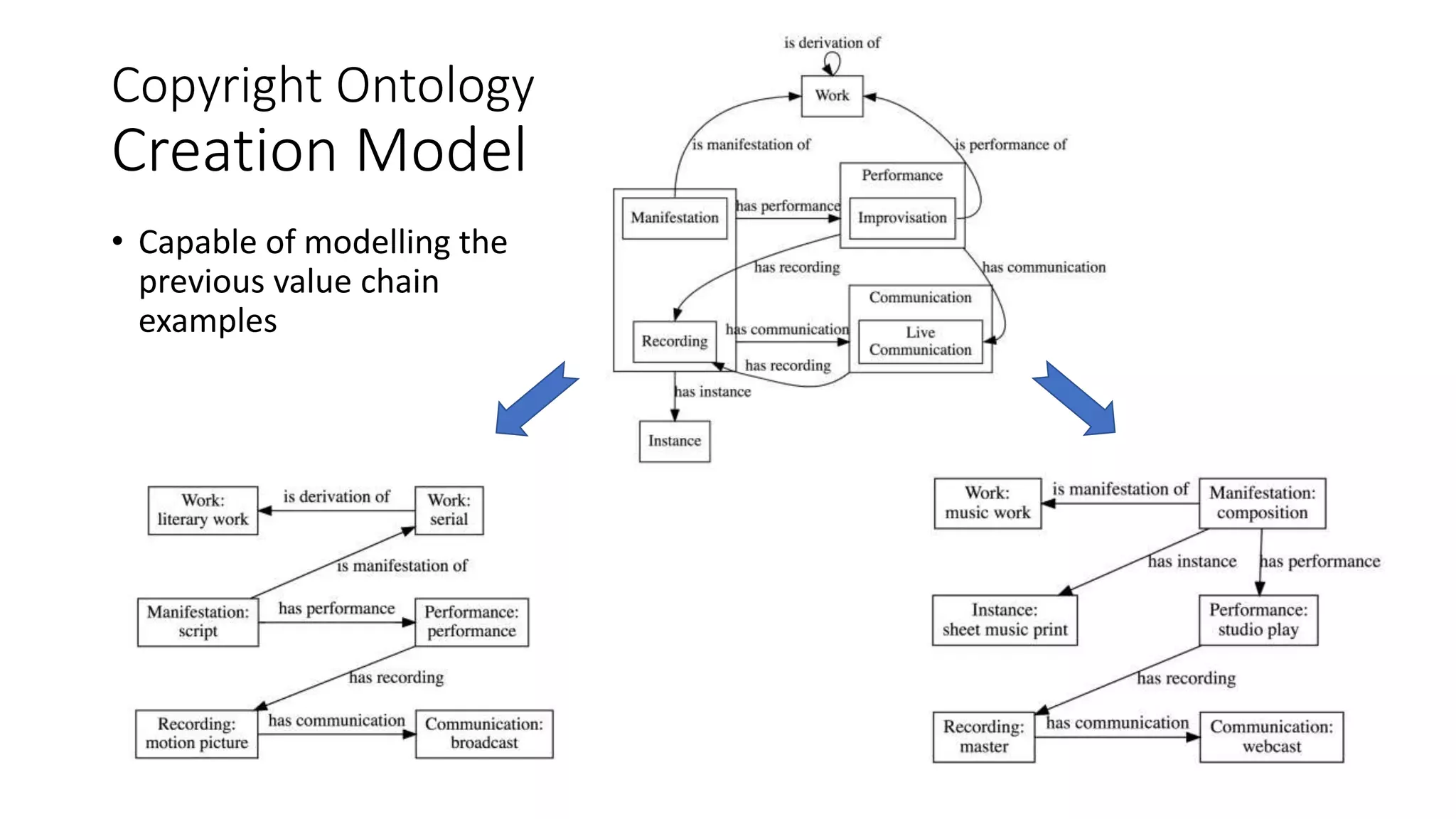
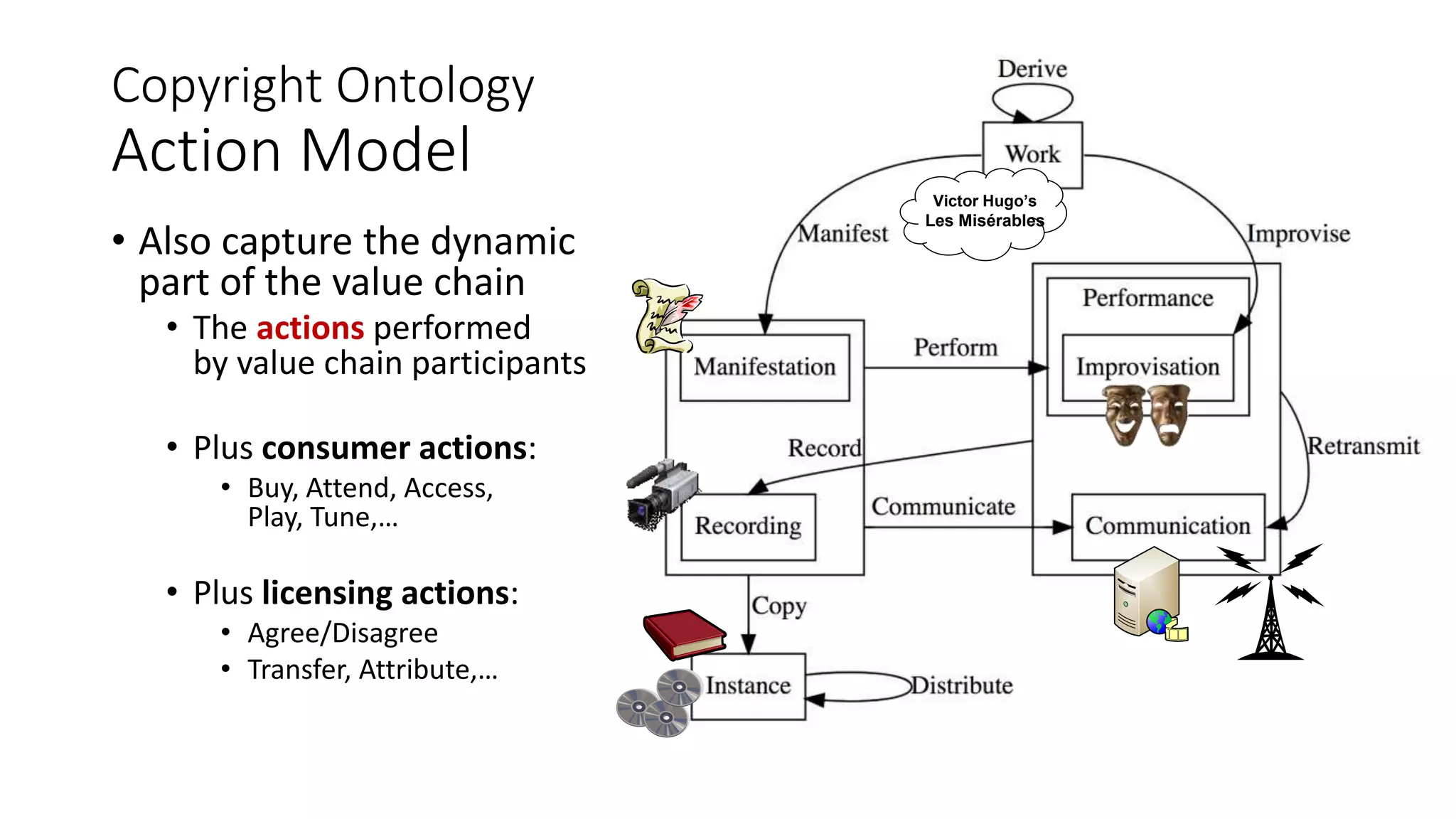
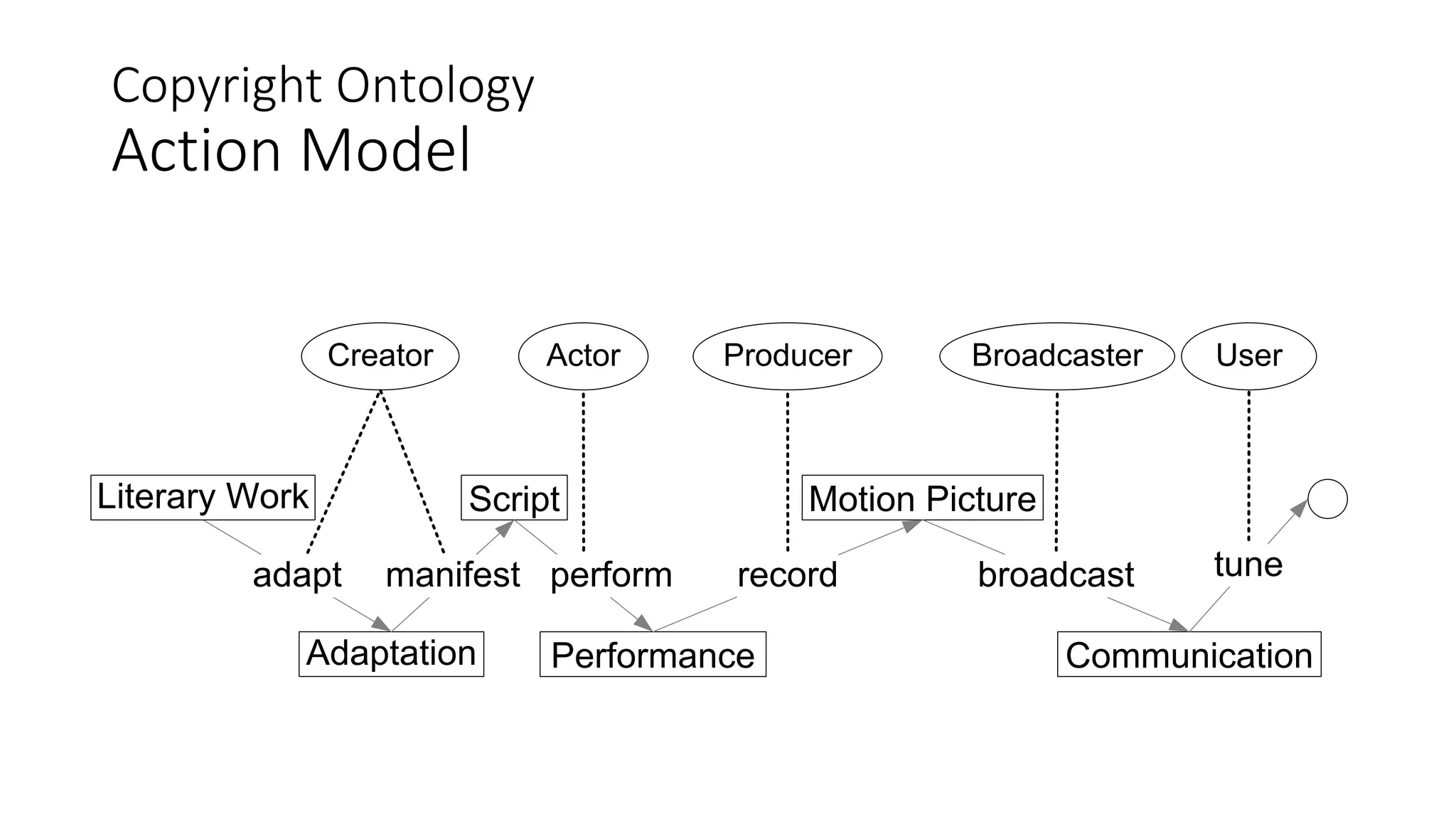
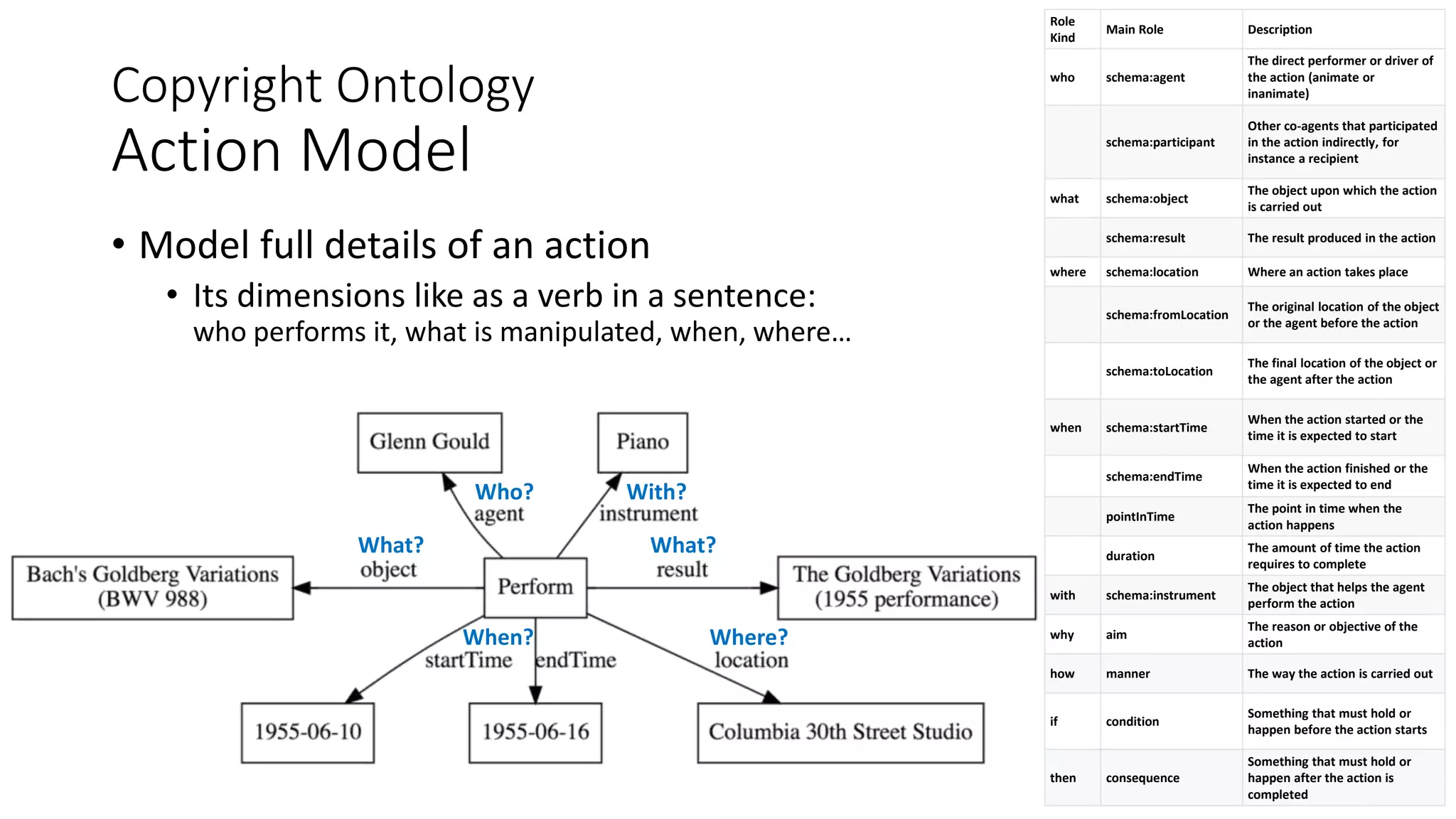
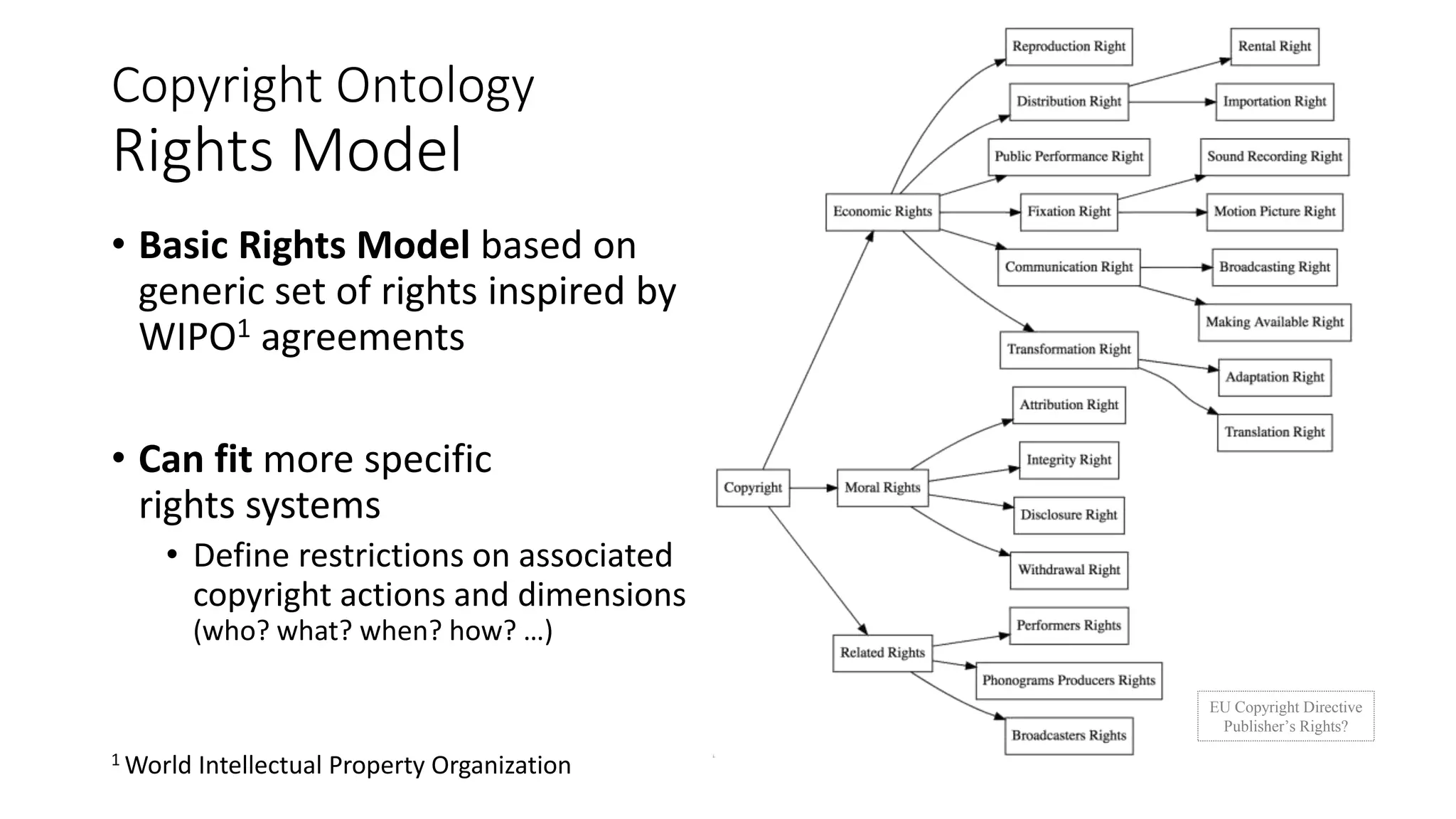
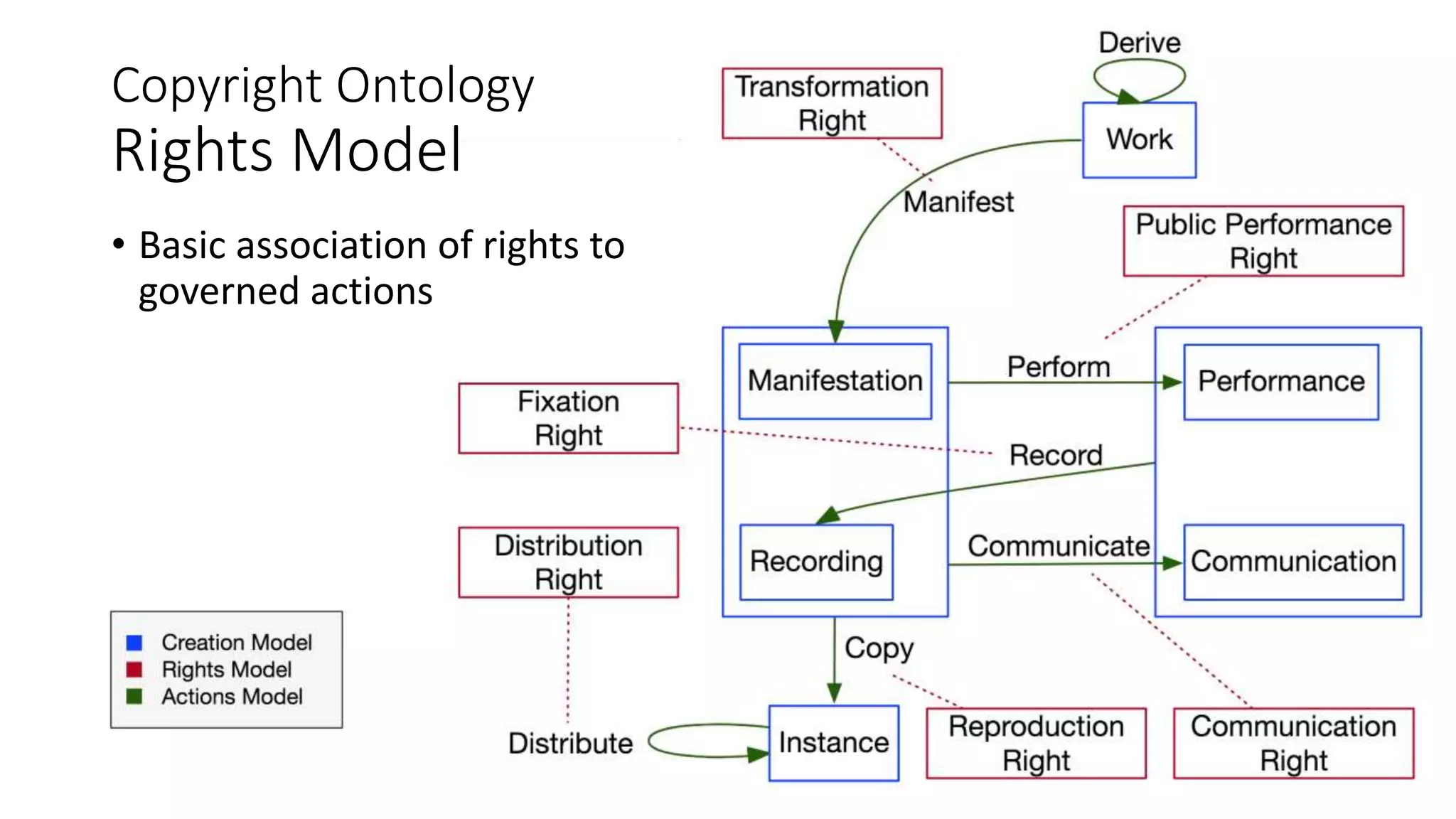
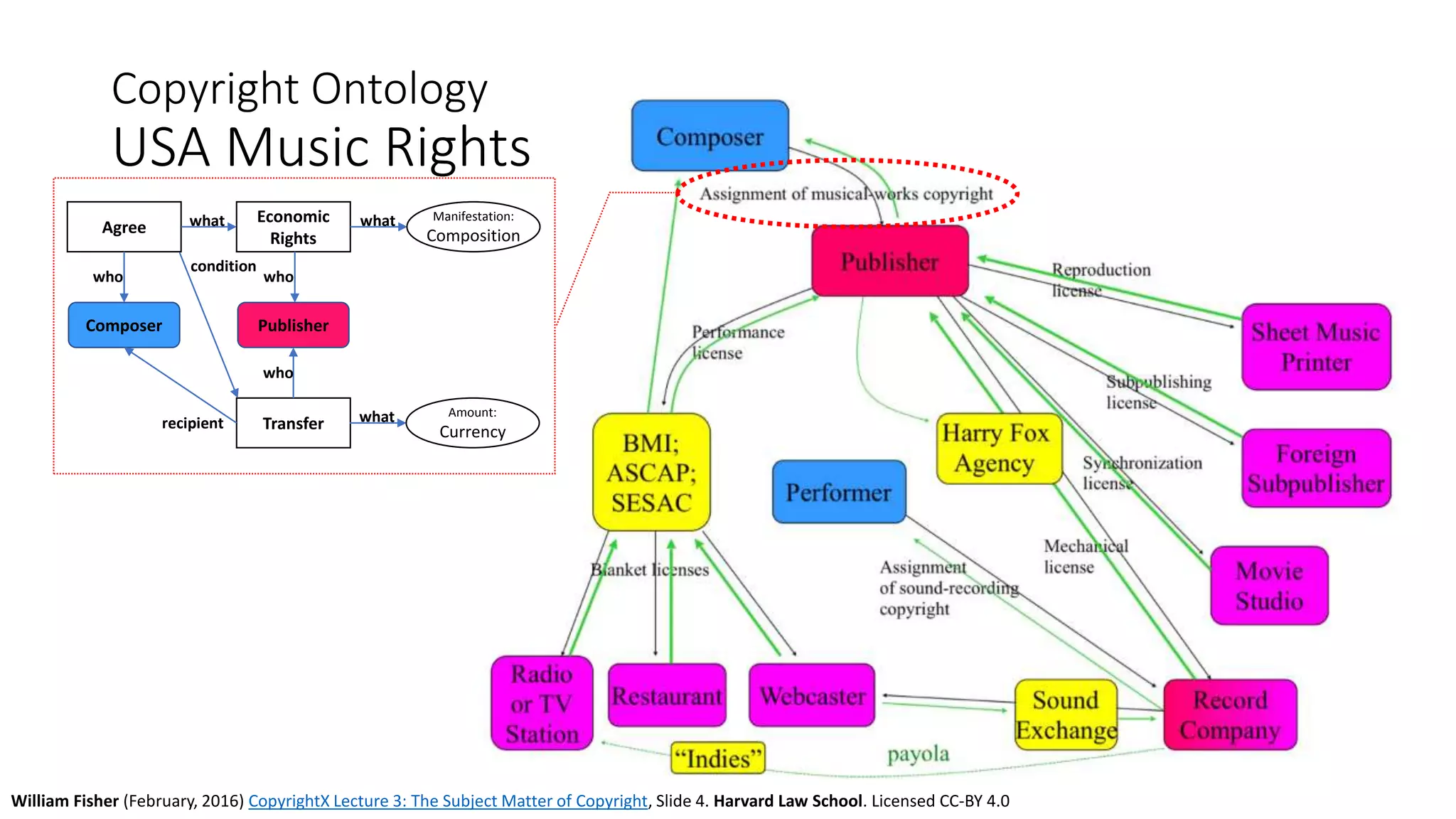
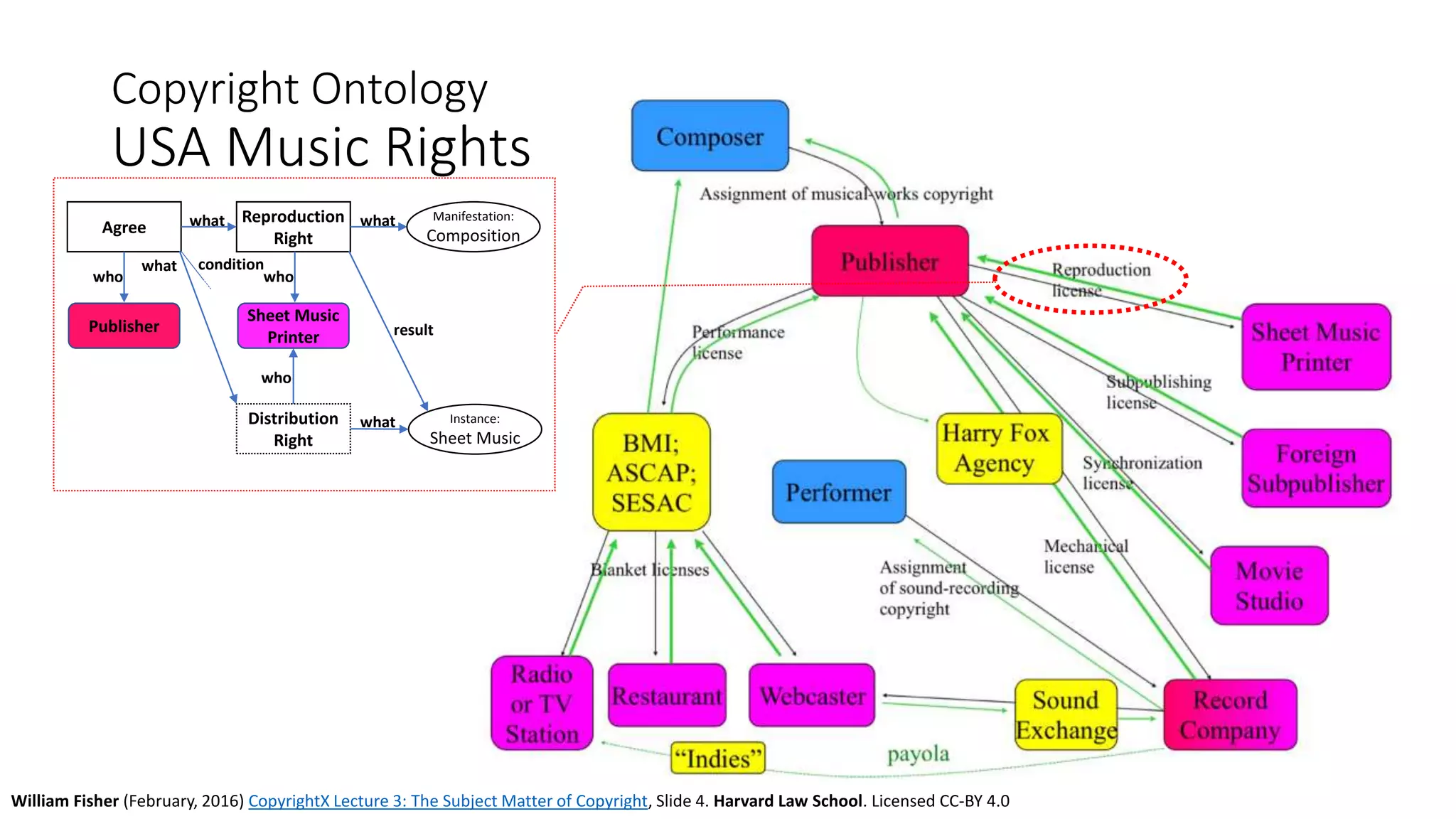
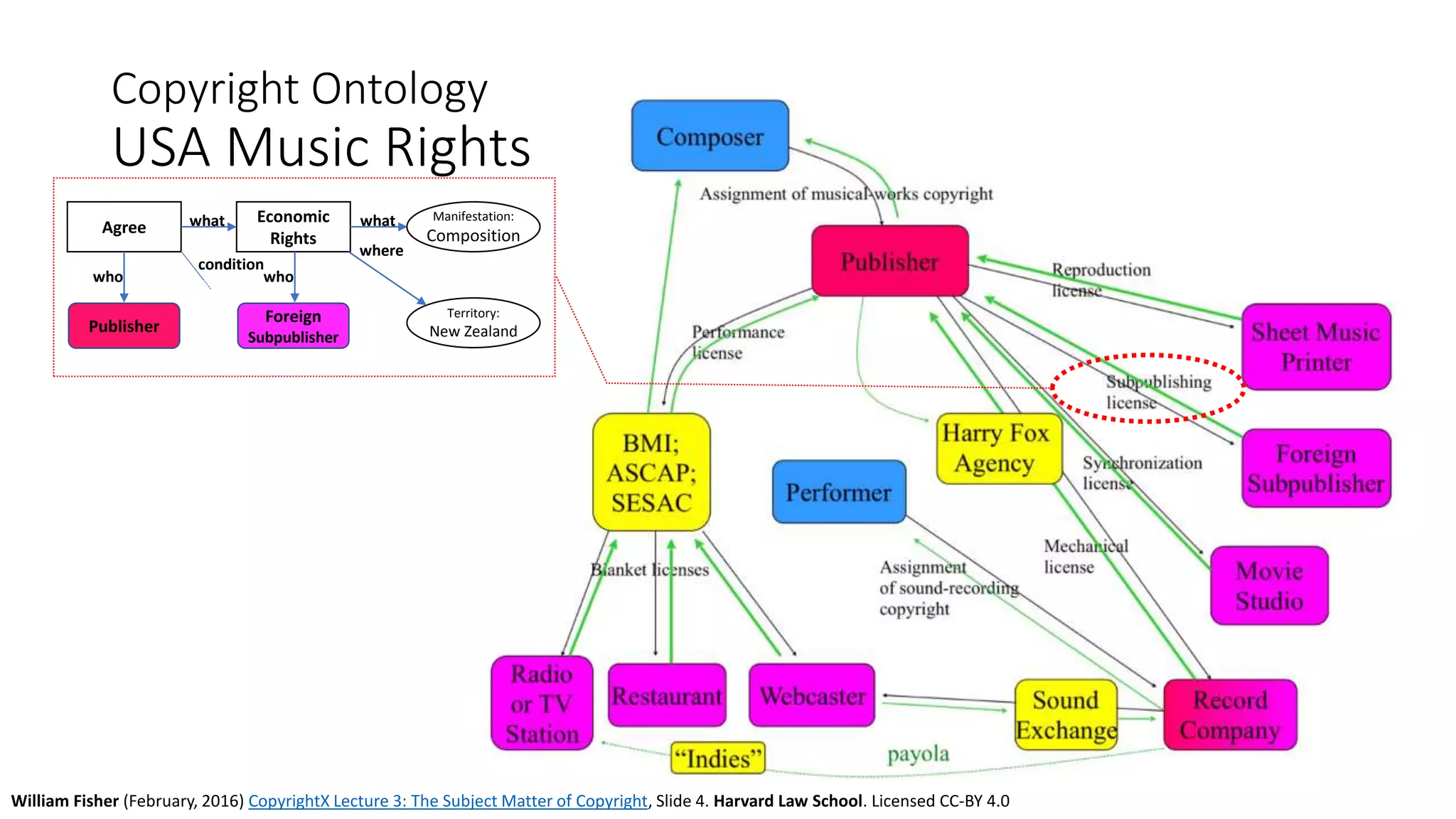
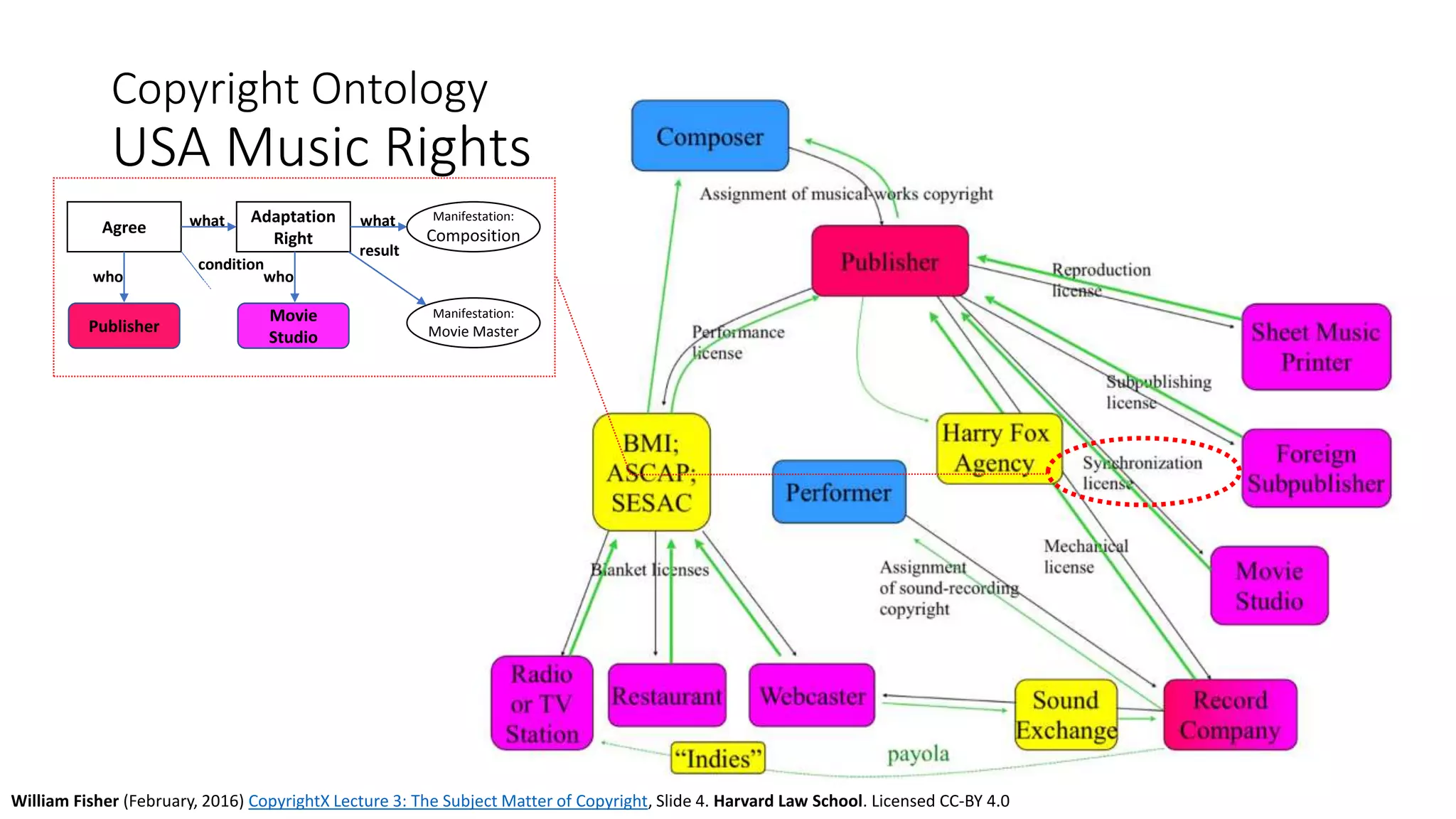
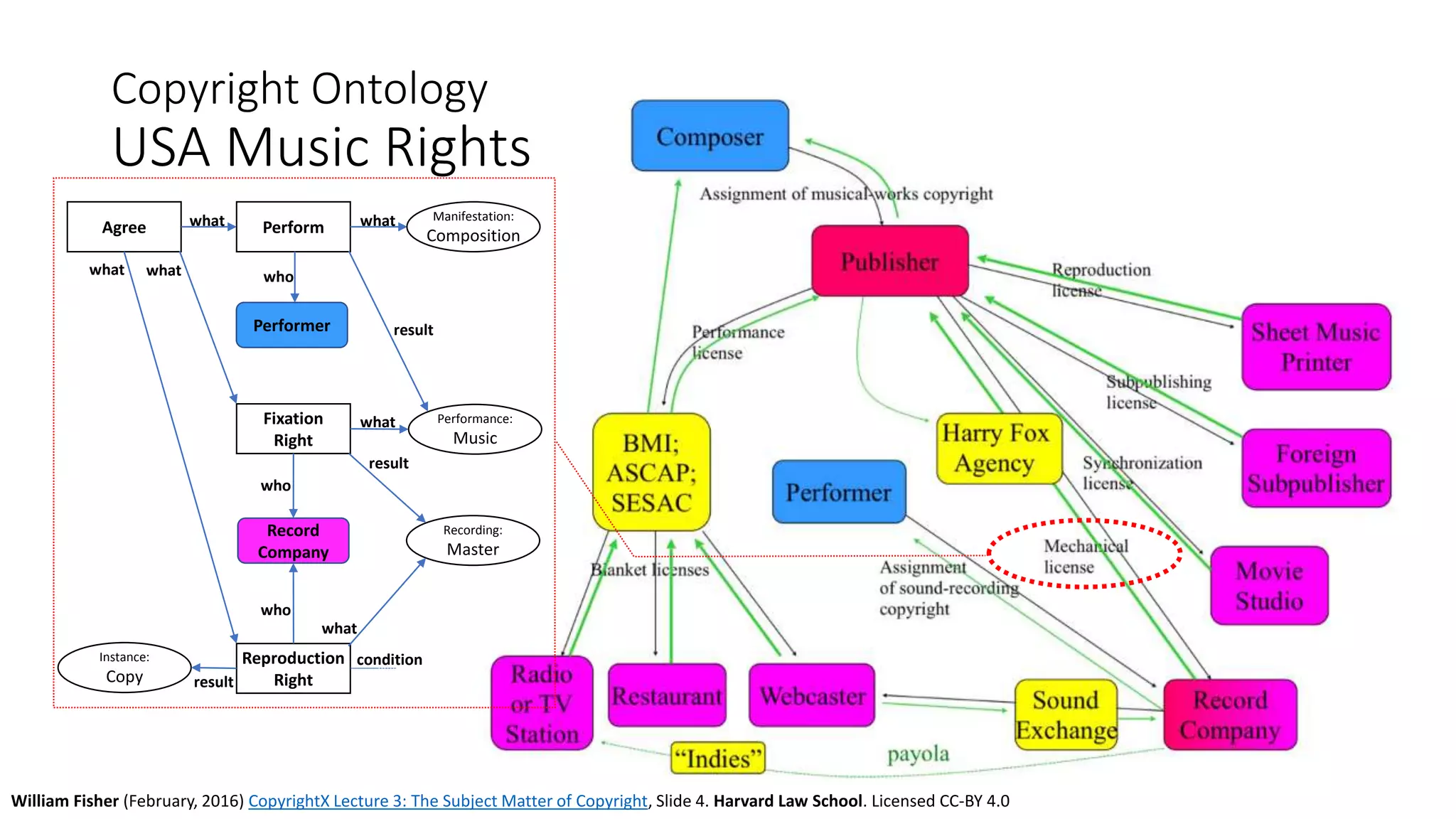
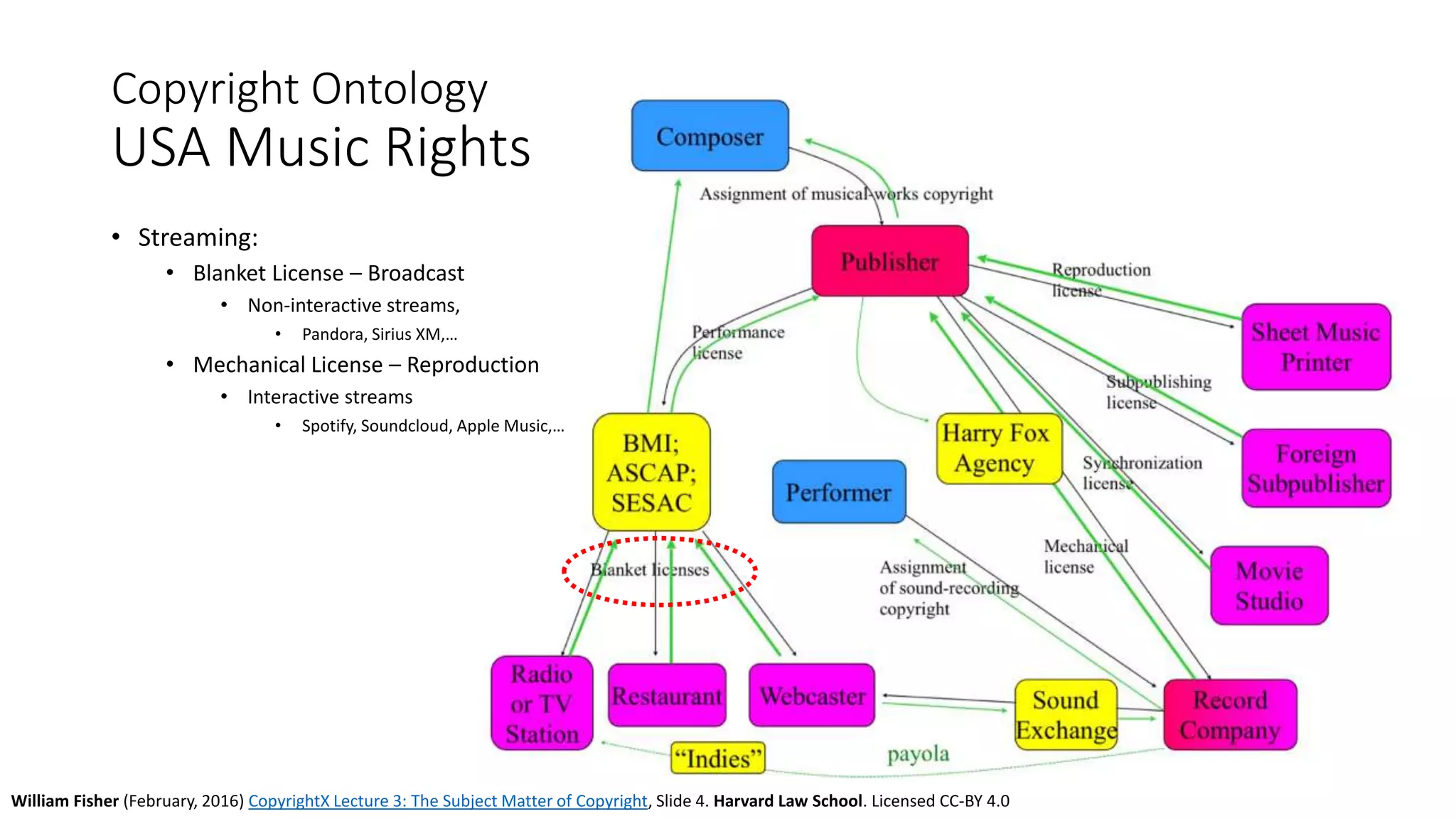
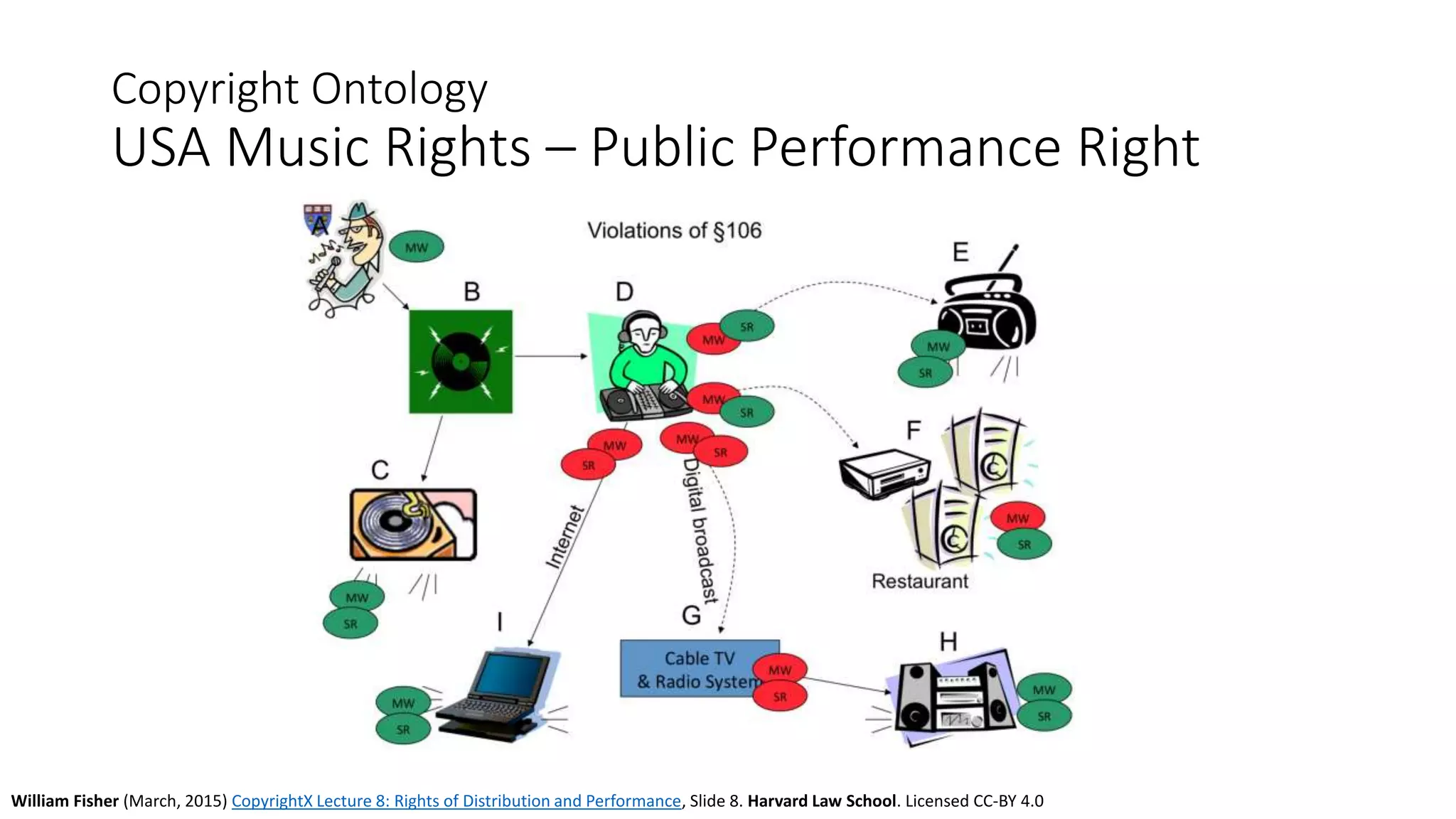
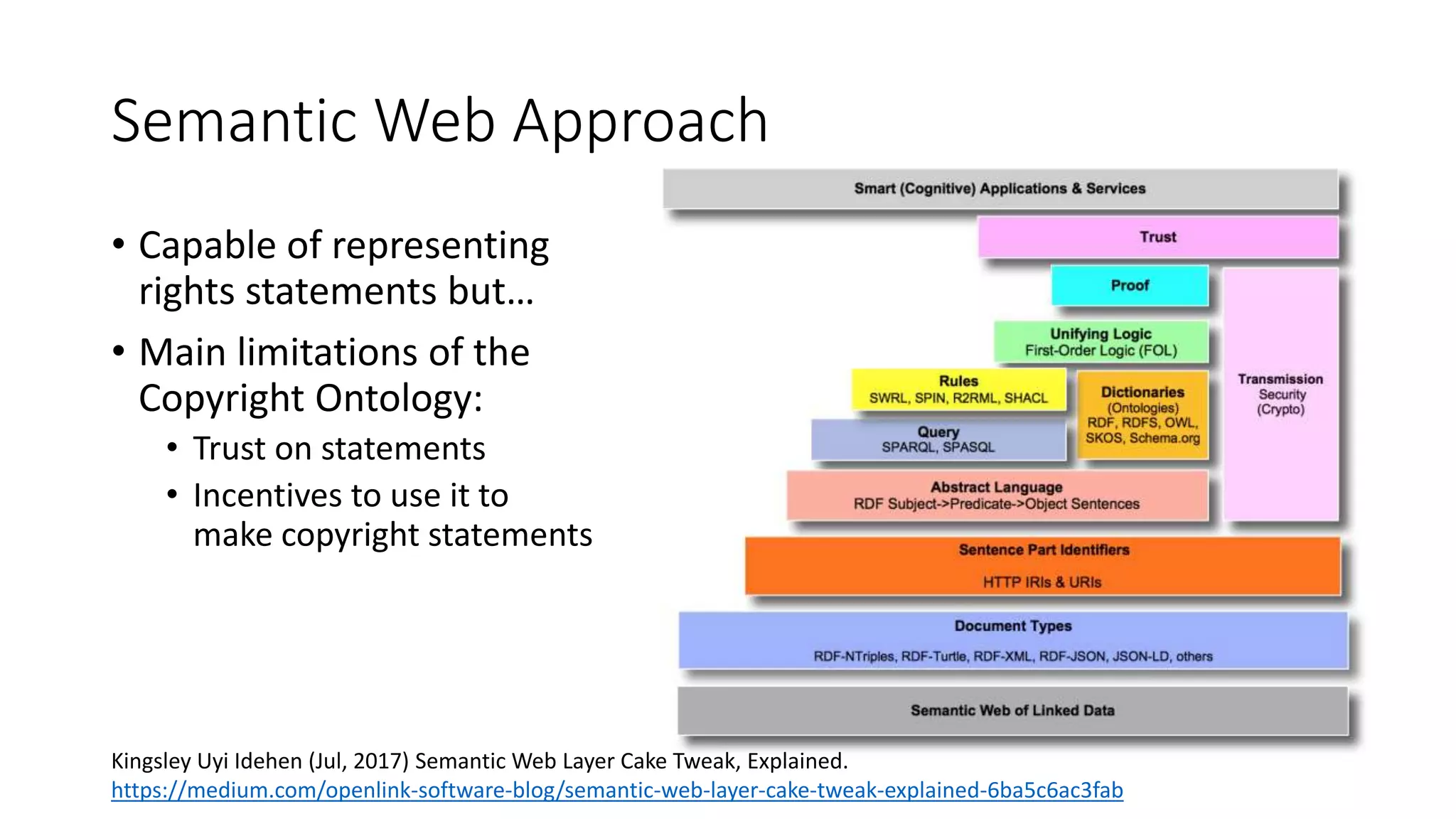
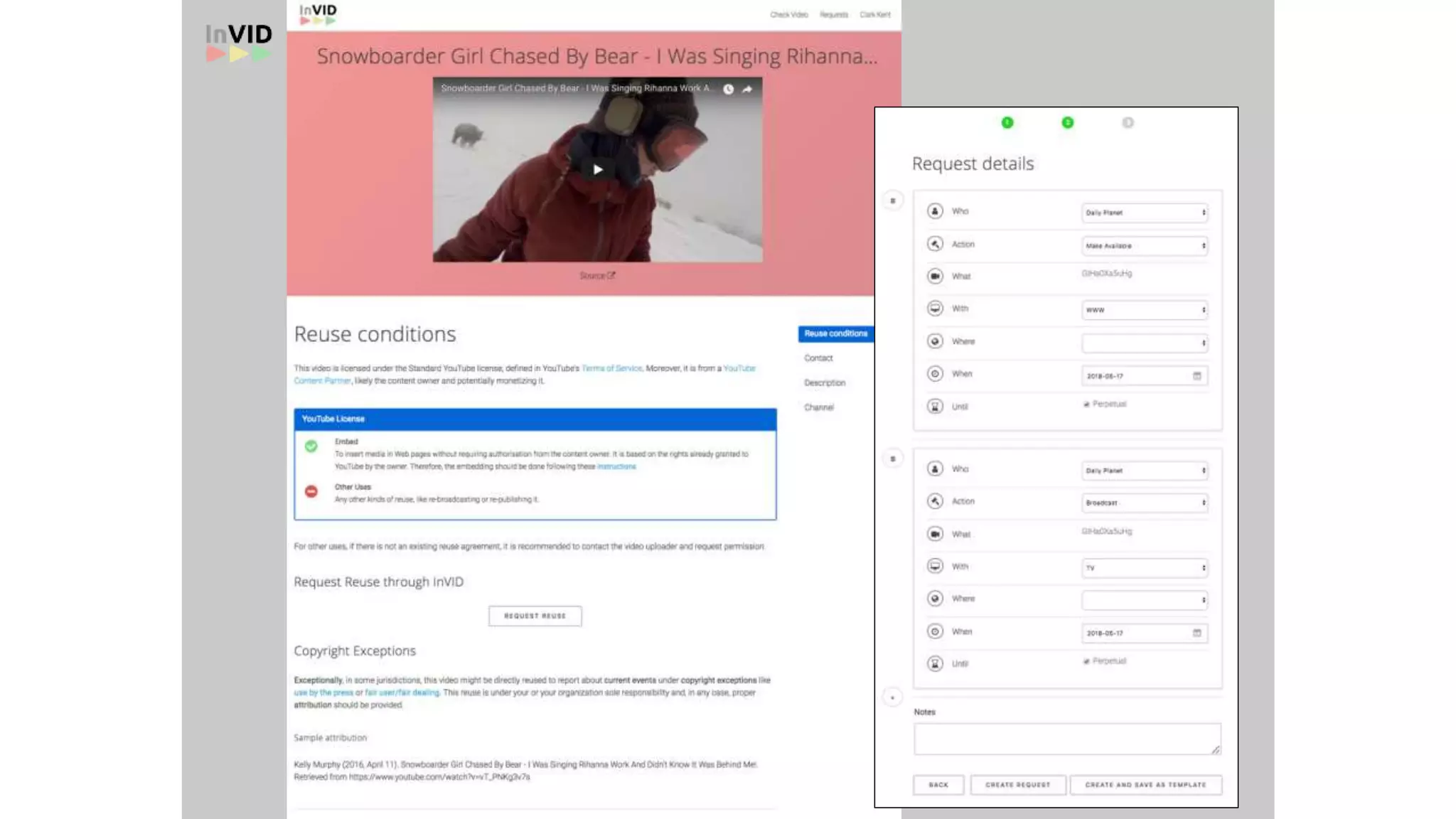
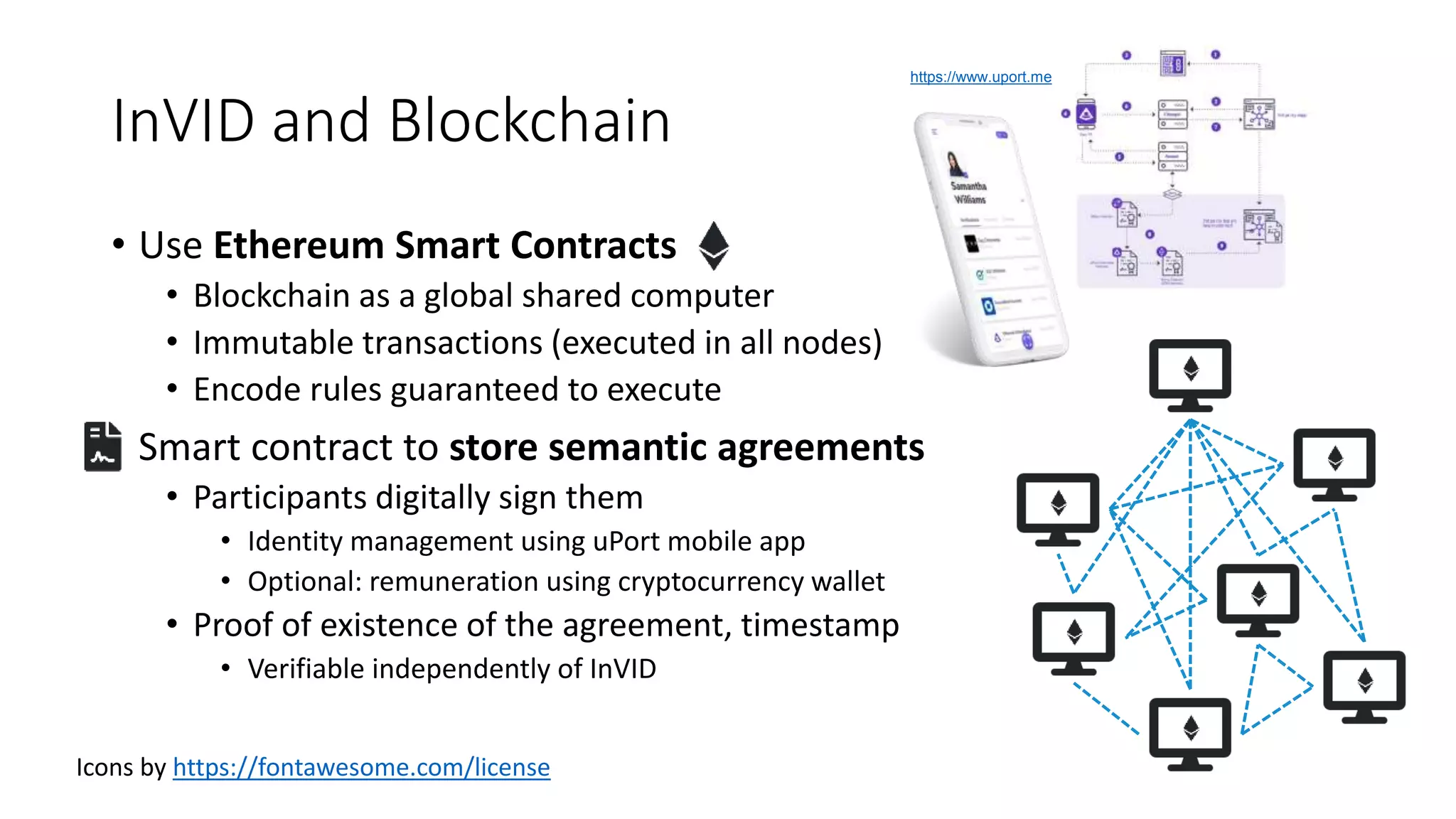
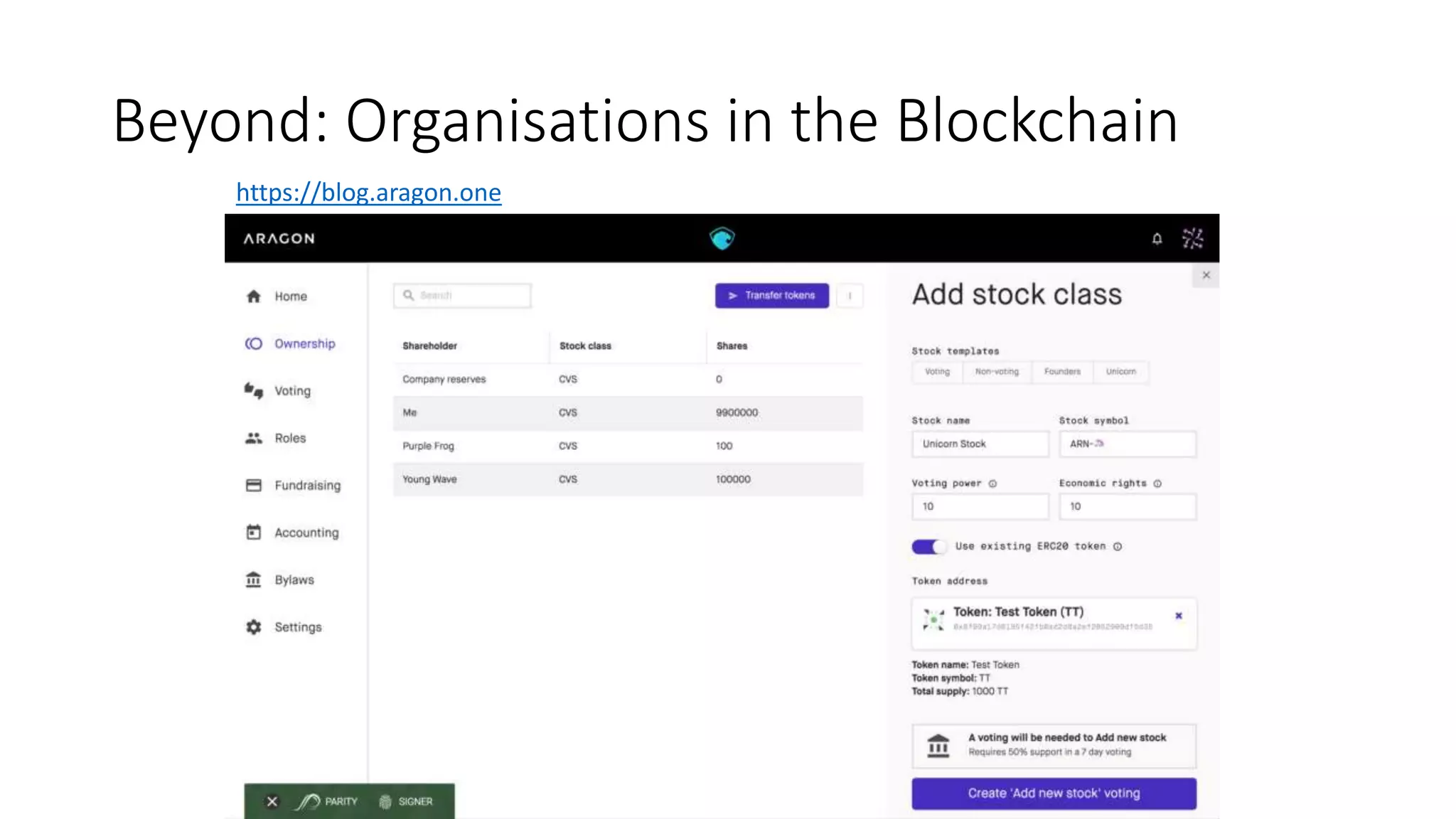
The document discusses copyright management in the context of Web 3.0, the semantic web, and blockchain technologies, emphasizing the growing importance of effective copyright management due to new business models and user-generated content. It explores the potential of semantic technologies and smart contracts for scalable and automated copyright management across digital platforms, while presenting challenges related to disputes and rights management. Additionally, it outlines a proposed copyright ontology that aims to enhance the expressiveness of rights statements and facilitate better management of copyrights in the digital age.