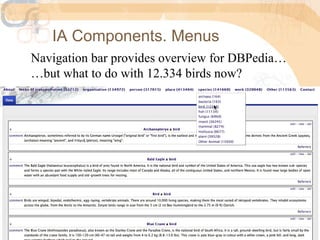
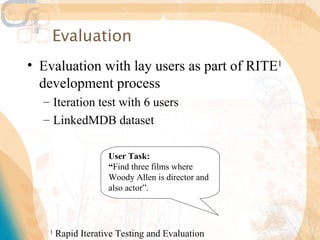
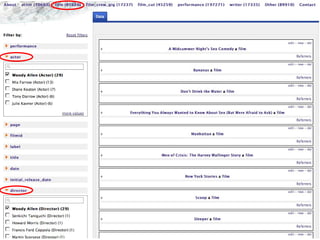
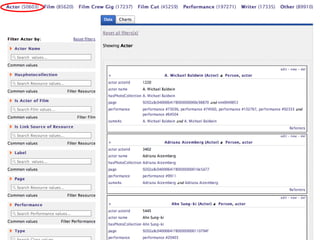
The document discusses methods for enhancing user interaction with linked data through user interface design, focusing on facets, menus, and pivoting strategies. It highlights user evaluations that indicated challenges lay users face when navigating complex data structures and emphasizes the importance of contextual aids. Proposals for improving usability include creating dynamic facets, preserving filters during navigation, and facilitating query construction without technical knowledge.

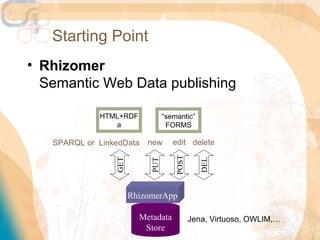


![Proposal
Ontologies and dataset structure
Information
Architecture
Components
[Morville]
Interaction Overview Menus, Sitemaps,…
Patterns for Zoom & Filter Facets
Data Analysis
[Shneiderman]
Details Lists, Maps, Timelines…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rhizomer-ild12-120528061618-phpapp01/85/Facets-and-Pivoting-for-Flexible-and-Usable-Linked-Data-Exploration-5-320.jpg)