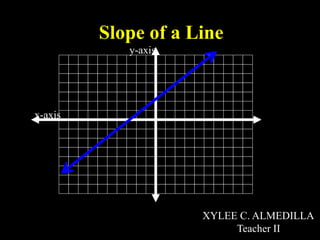
This document discusses the concept of slope of a line. It begins by defining key terms like the x-axis, y-axis, and slope. It then shows how to calculate slope using the rise over run formula. Several examples are worked out step-by-step, such as finding the slope between points (-3,6) and (5,2). Real-world applications of slope are discussed. Students are expected to understand how to describe trends using slope, calculate slope, and relate slope to real life.