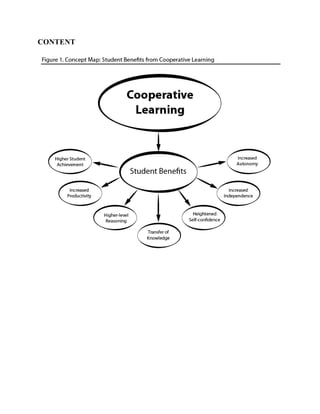
This document discusses cooperative learning with computers. It defines cooperative learning as students working together in small groups on common tasks. Cooperative learning has benefits like increasing academic performance and social skills. While an ideal ratio is one computer per student, teachers can implement cooperative learning even without enough computers. The computer is well-suited to cooperative learning activities. Key components of cooperative learning include assigning mixed-ability student groups, establishing interdependence, teaching social skills, ensuring individual accountability, and providing group processing.