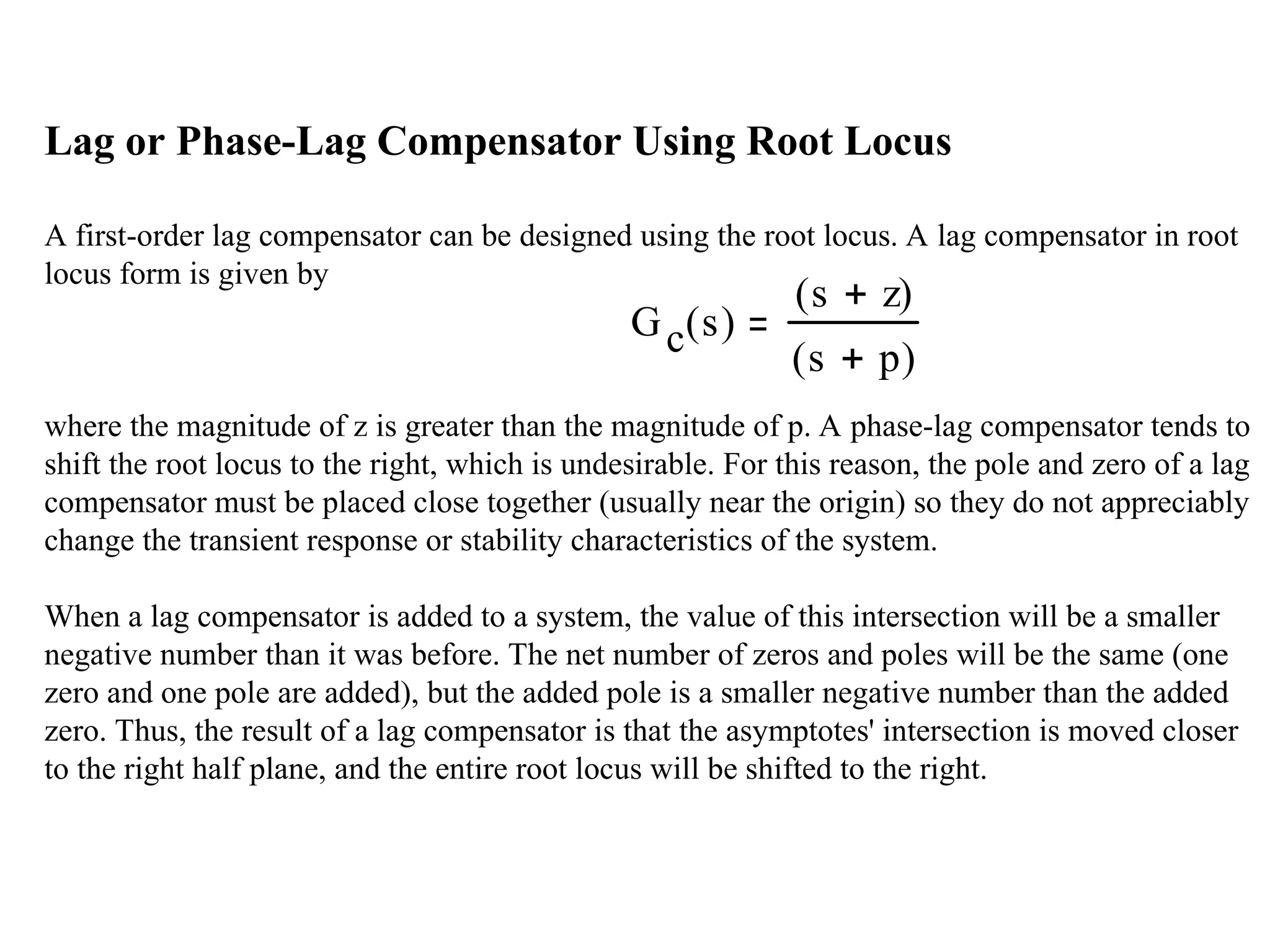
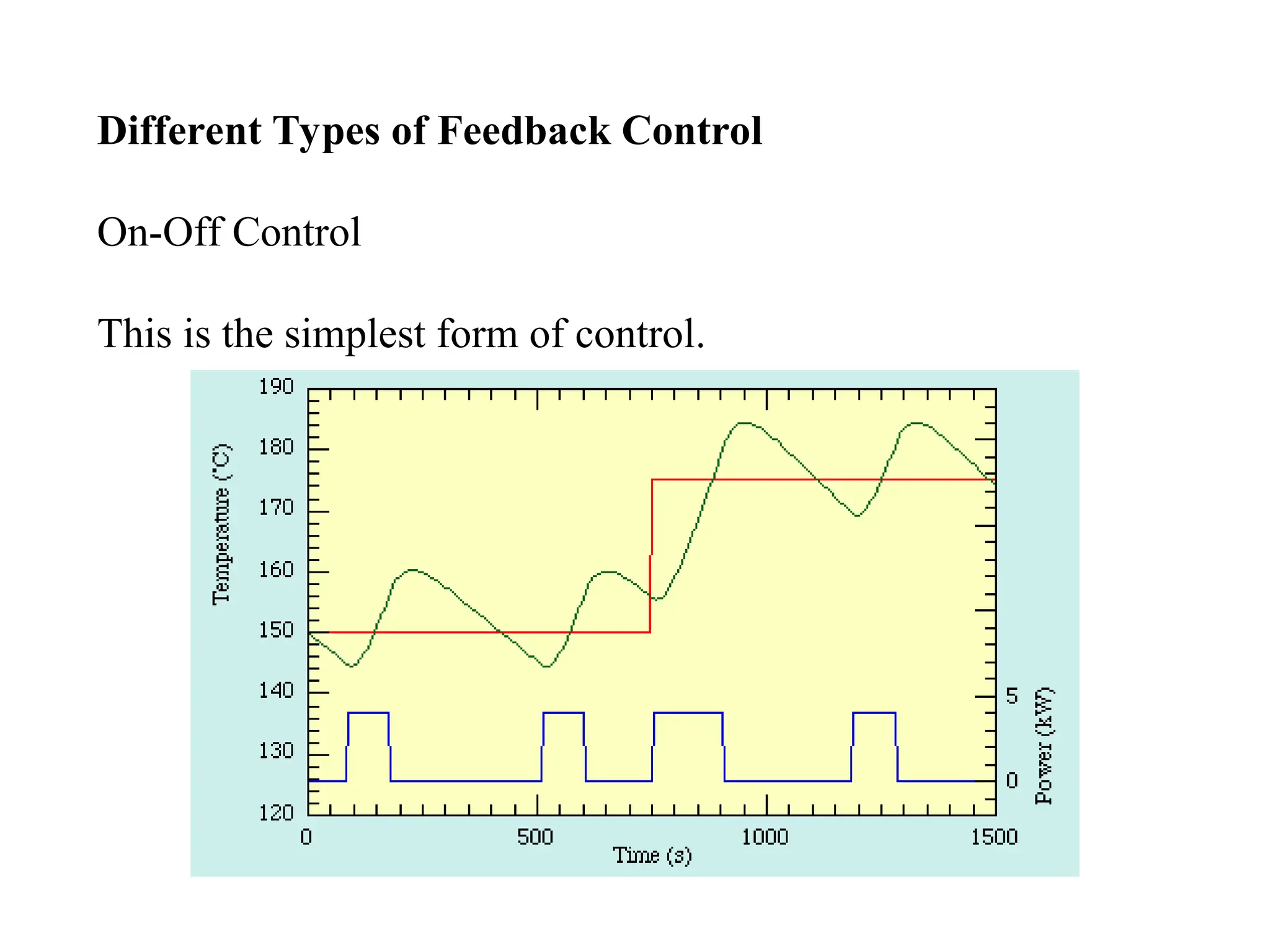
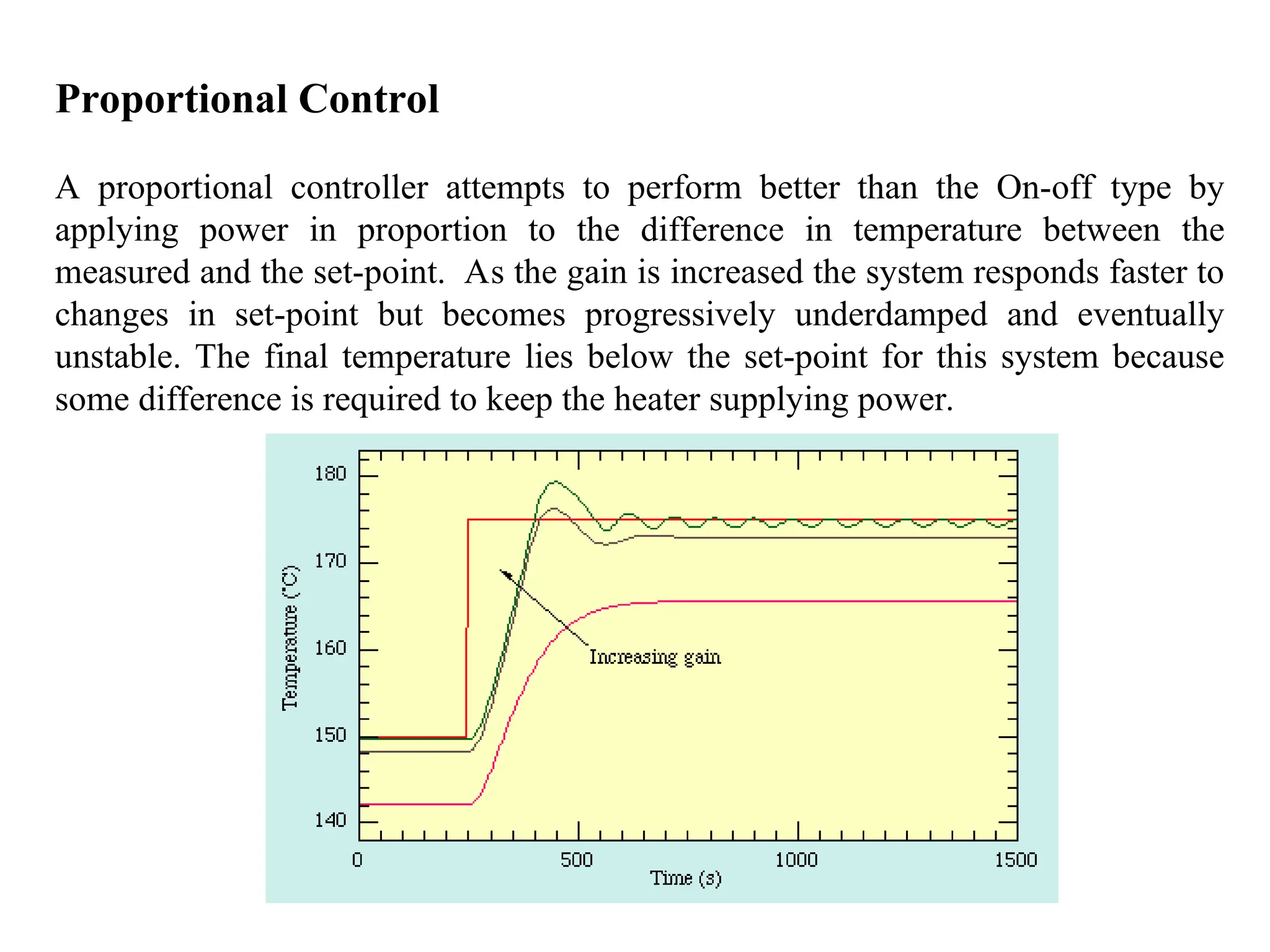
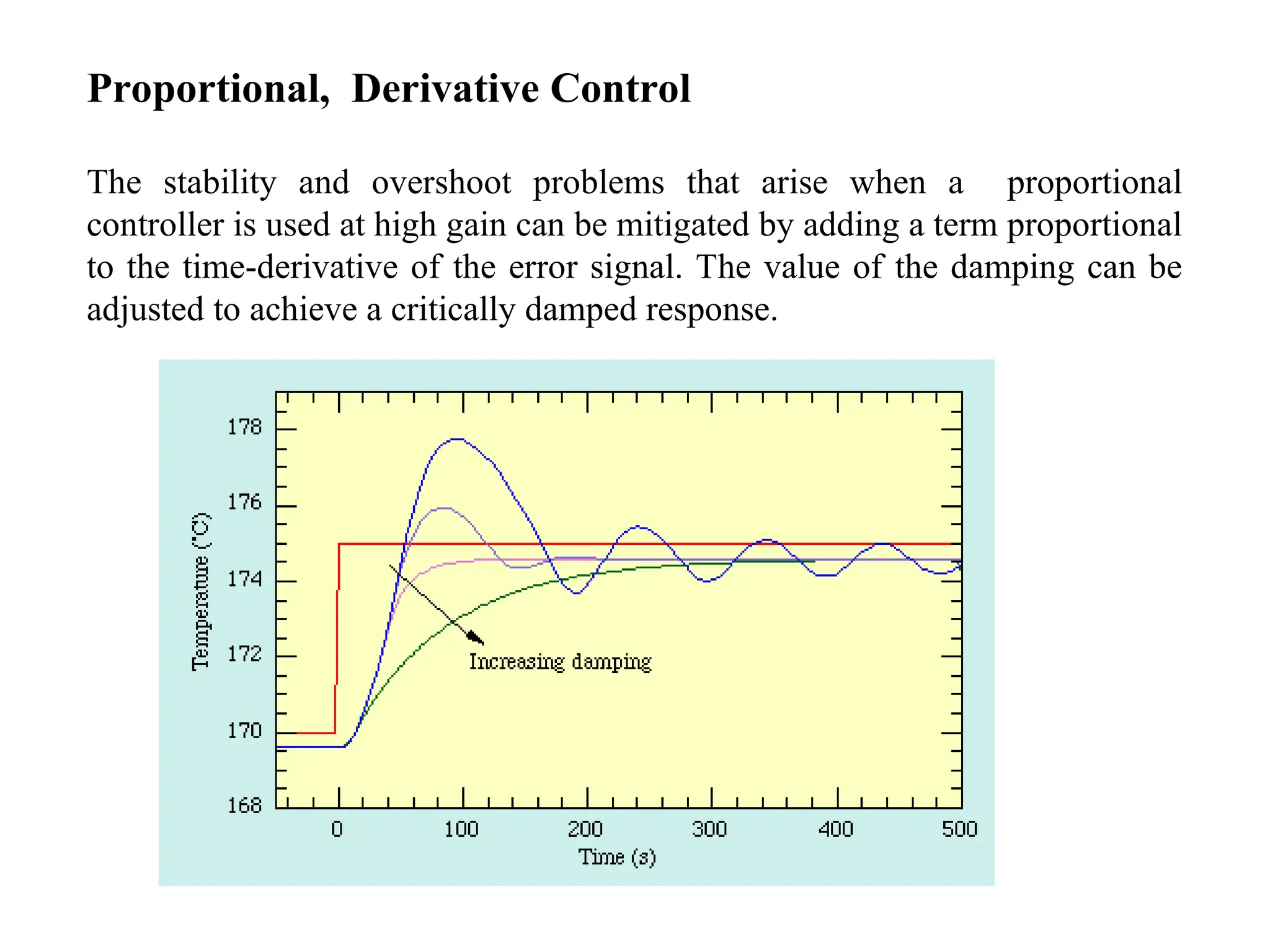
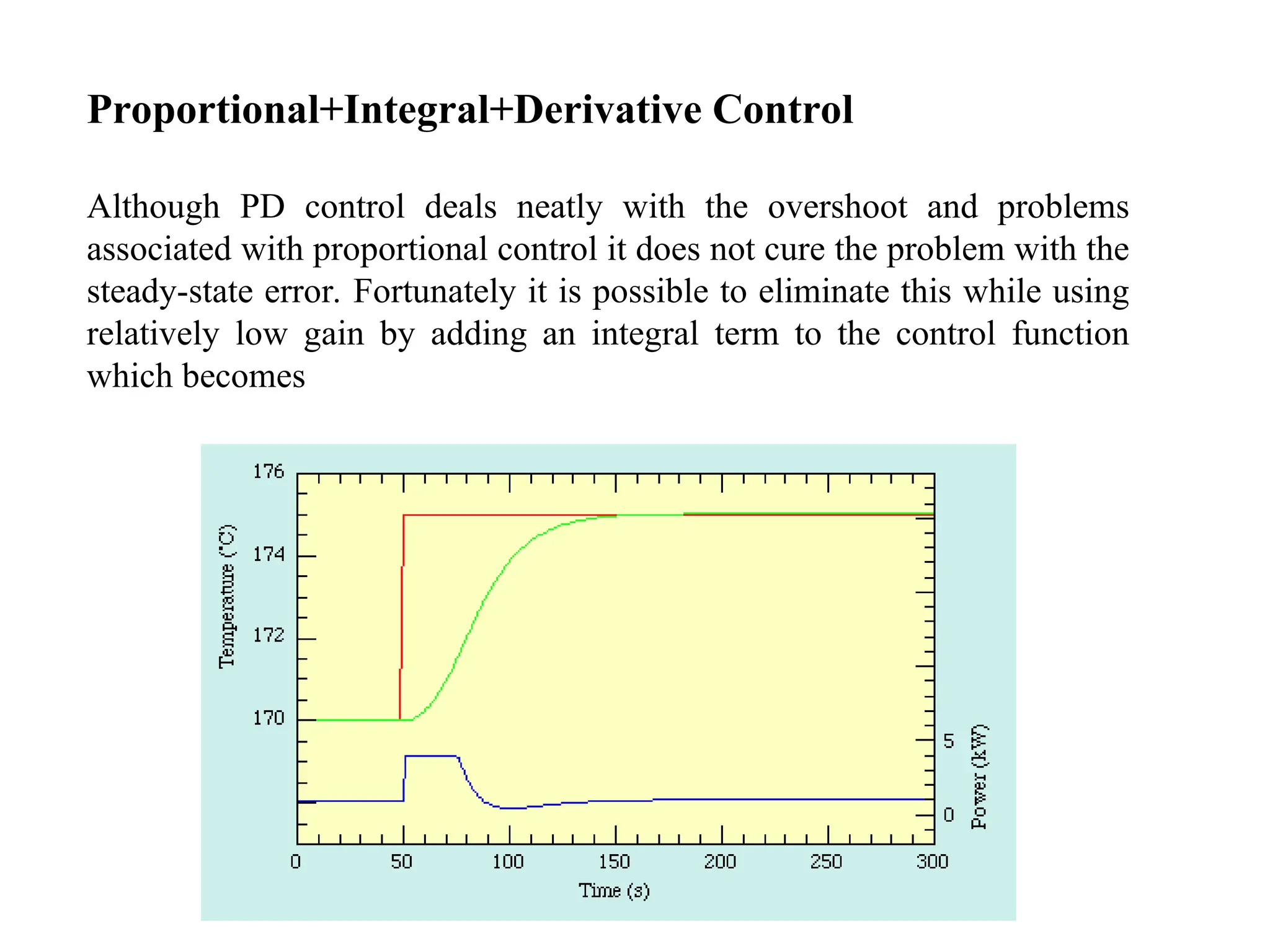
The document discusses various types of control in PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) systems, explaining how proportional control reduces rise time but can lead to steady-state errors, while derivative control mitigates overshoot and settling time. It outlines the significance of combining proportional, integral, and derivative controls for optimized system response and stability, and provides MATLAB examples for implementation. Additionally, it covers the design of lead and lag compensators through root locus techniques to adjust system stability and response speed.




![num=1;
den=[1 10 20];
step(num,den)
Open-Loop Control - Example
G s
( )
1
s
2
10s
20
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pid1-241027173047-e563d294/75/controller-details-are-given-as-power-point-10-2048.jpg)
![Proportional Control - Example
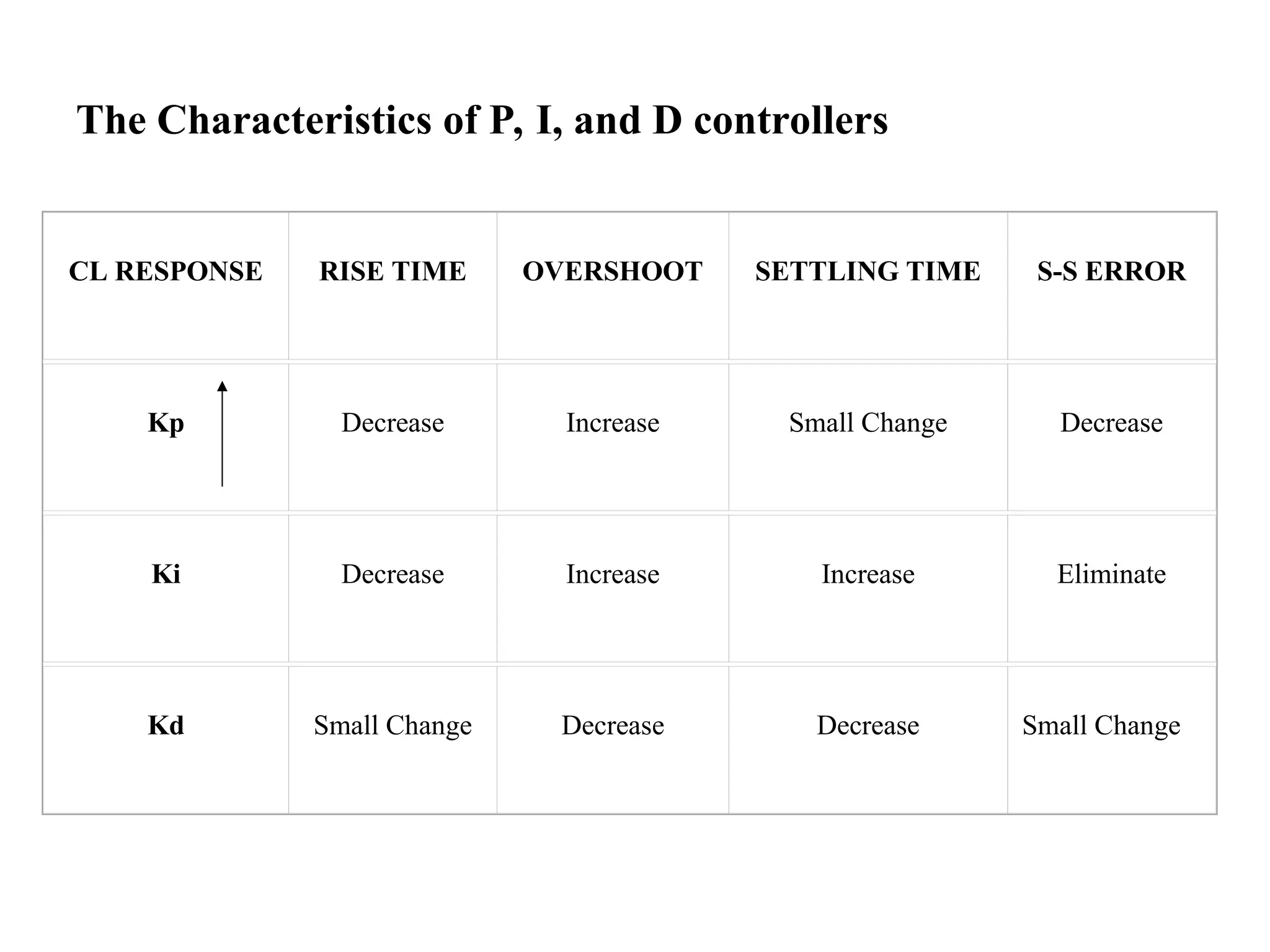
The proportional controller (Kp) reduces the rise time, increases
the overshoot, and reduces the steady-state error.
MATLAB Example
Kp=300;
num=[Kp];
den=[1 10 20+Kp];
t=0:0.01:2;
step(num,den,t)
Time (sec.)
Amplitude
Step Response
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
From: U(1)
To:
Y(1)
T s
( )
Kp
s
2
10 s
20 Kp
( )
Time (sec.)
Amplitude
Step Response
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
From: U(1)
To:
Y(1)
K=300 K=100](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pid1-241027173047-e563d294/75/controller-details-are-given-as-power-point-11-2048.jpg)
![Time (sec.)
Amplitude
Step Response
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
From: U(1)
To:
Y(1)
Kp=300;
Kd=10;
num=[Kd Kp];
den=[1 10+Kd 20+Kp];
t=0:0.01:2;
step(num,den,t)
Proportional - Derivative - Example
The derivative controller (Kd) reduces both the overshoot and the
settling time.
MATLAB Example T s
( )
Kd s
Kp
s
2
10 Kd
( ) s
20 Kp
( )
Time (sec.)
Amplitude
Step Response
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
From: U(1)
To:
Y(1)
Kd=10
Kd=20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pid1-241027173047-e563d294/75/controller-details-are-given-as-power-point-12-2048.jpg)
![Proportional - Integral - Example
The integral controller (Ki) decreases the rise time, increases both
the overshoot and the settling time, and eliminates the steady-state
error
MATLAB Example
Time (sec.)
Amplitude
Step Response
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
From: U(1)
To:
Y(1)
Kp=30;
Ki=70;
num=[Kp Ki];
den=[1 10 20+Kp Ki];
t=0:0.01:2;
step(num,den,t)
T s
( )
Kp s
Ki
s
3
10 s
2
20 Kp
( ) s
Ki
Time (sec.)
A
m
plitude
Step Response
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
From: U(1)
To:
Y(1)
Ki=70
Ki=100](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pid1-241027173047-e563d294/75/controller-details-are-given-as-power-point-13-2048.jpg)
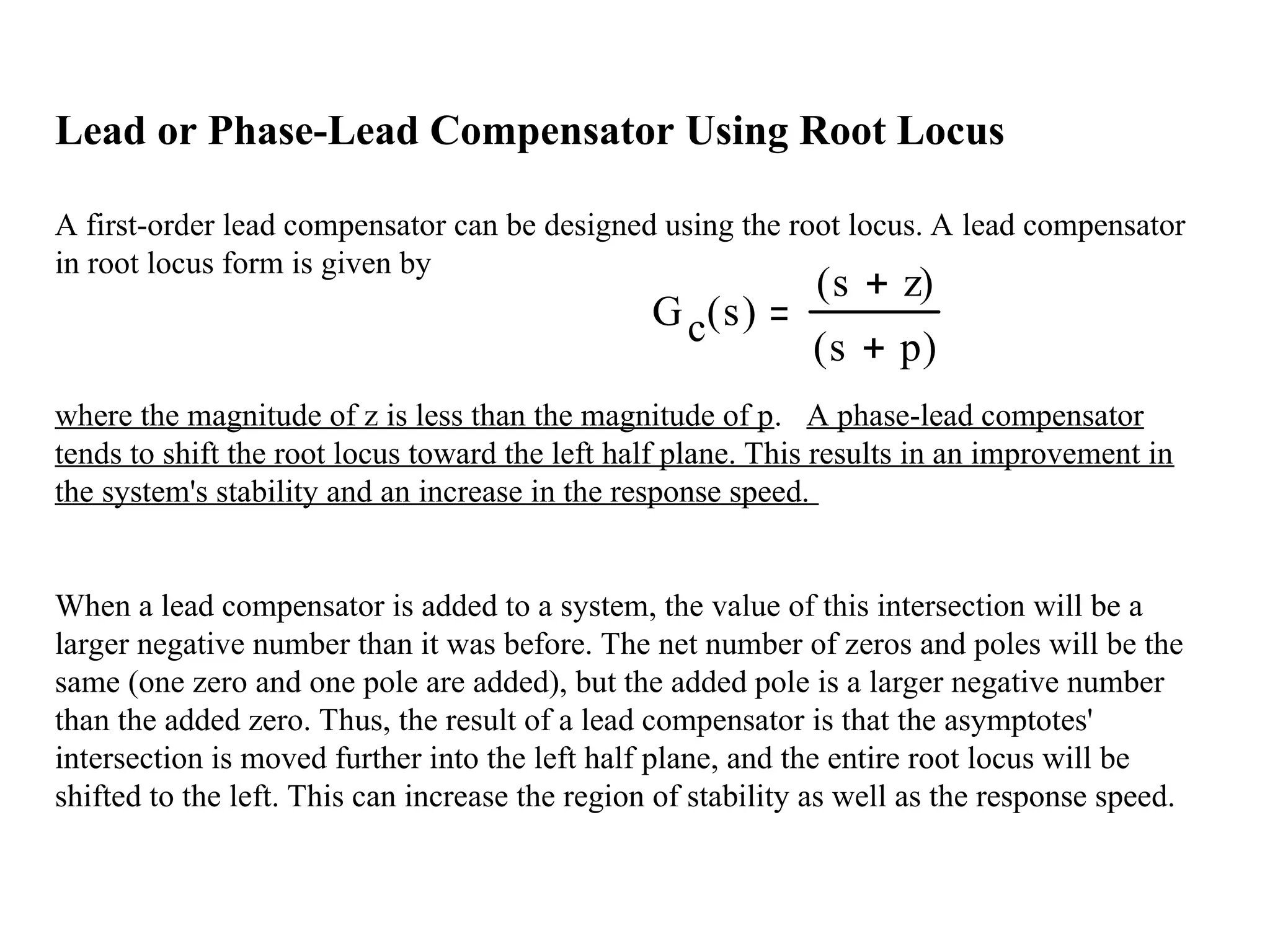
![In Matlab a phase lead compensator in root
locus form is implemented by using the transfer
function in the form
numlead=kc*[1 z];
denlead=[1 p];
and using the conv() function to implement it
with the numerator and denominator of the plant
newnum=conv(num,numlead);
newden=conv(den,denlead);
Lead or Phase-Lead Compensator Using Root Locus](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pid1-241027173047-e563d294/75/controller-details-are-given-as-power-point-16-2048.jpg)