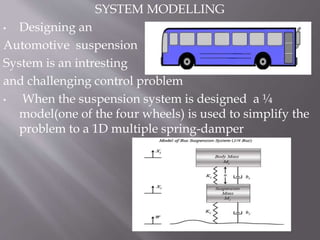
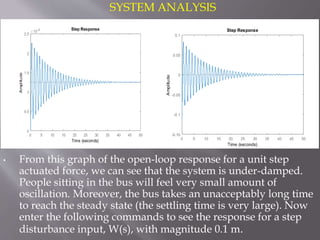
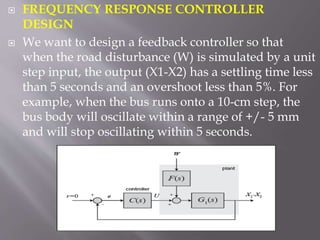
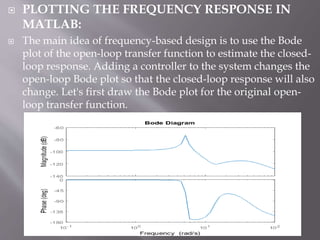
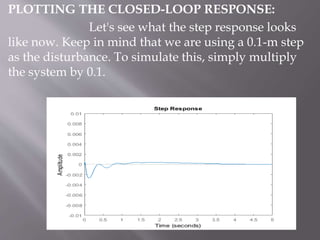
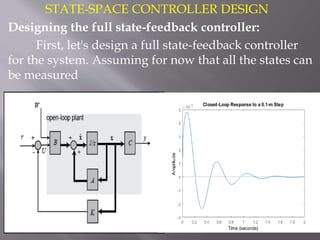
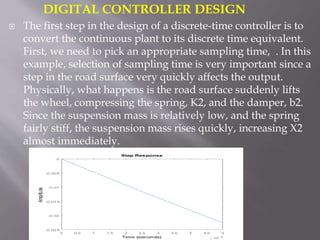
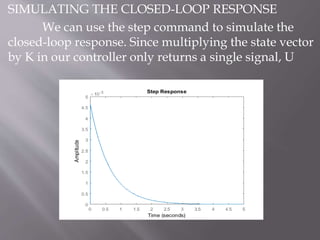
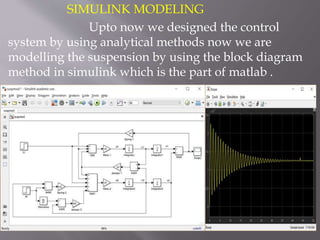
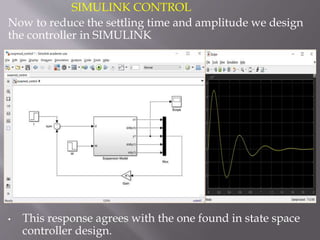
This document describes the design of a controller for an automobile suspension system using various control system methods. The objective is to reduce oscillations and settling time when the vehicle encounters bumps and potholes to improve passenger comfort. A quarter-car model is used to represent the system and analyze the open-loop response. Frequency response, state-space, and digital control design methods are applied to design controllers. Simulink modeling is also used to simulate the closed-loop response. The results show that the designed controllers reduce oscillations to below 5mm and settling time to less than 5 seconds, providing a satisfactory suspension system.