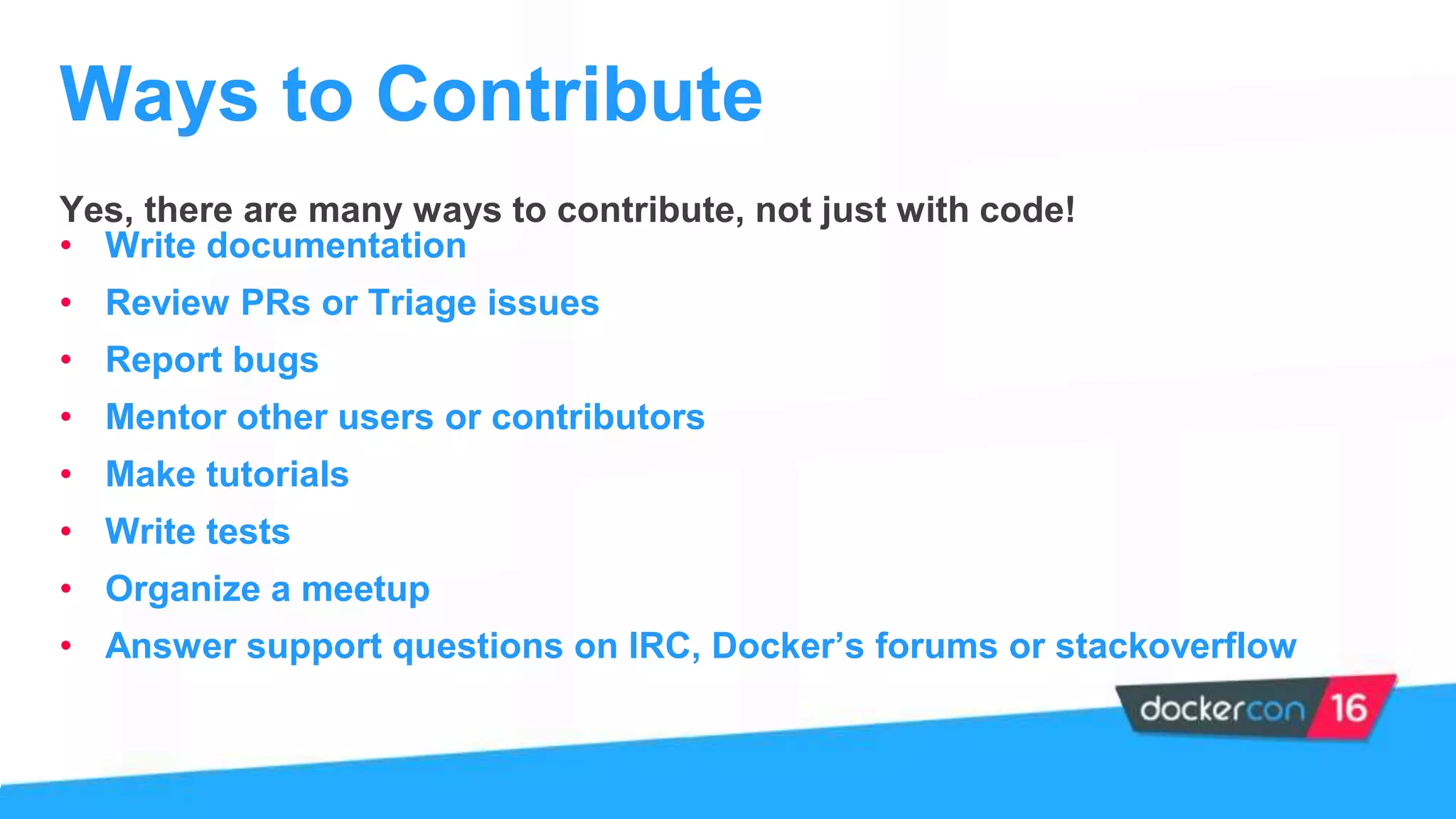
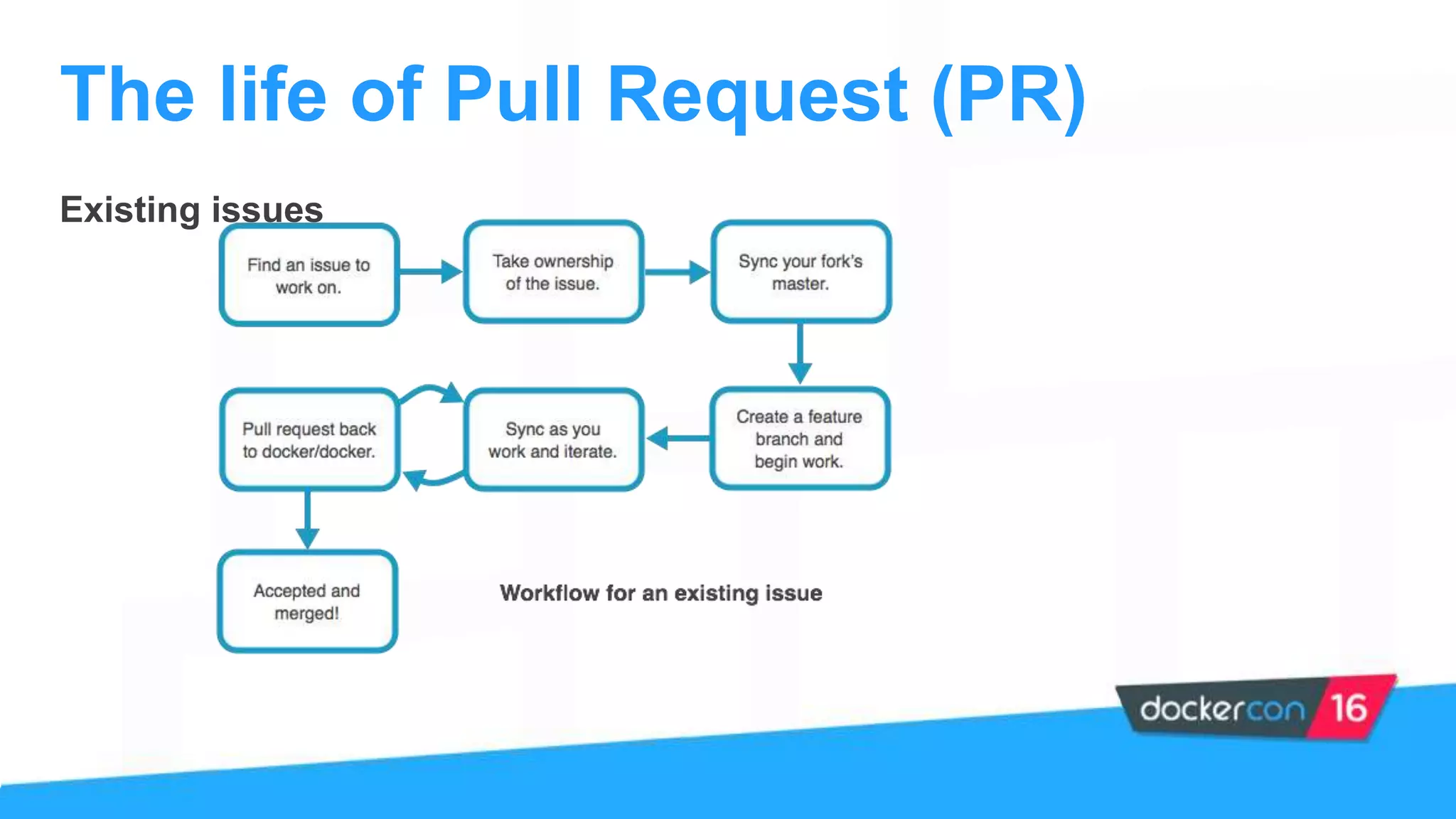
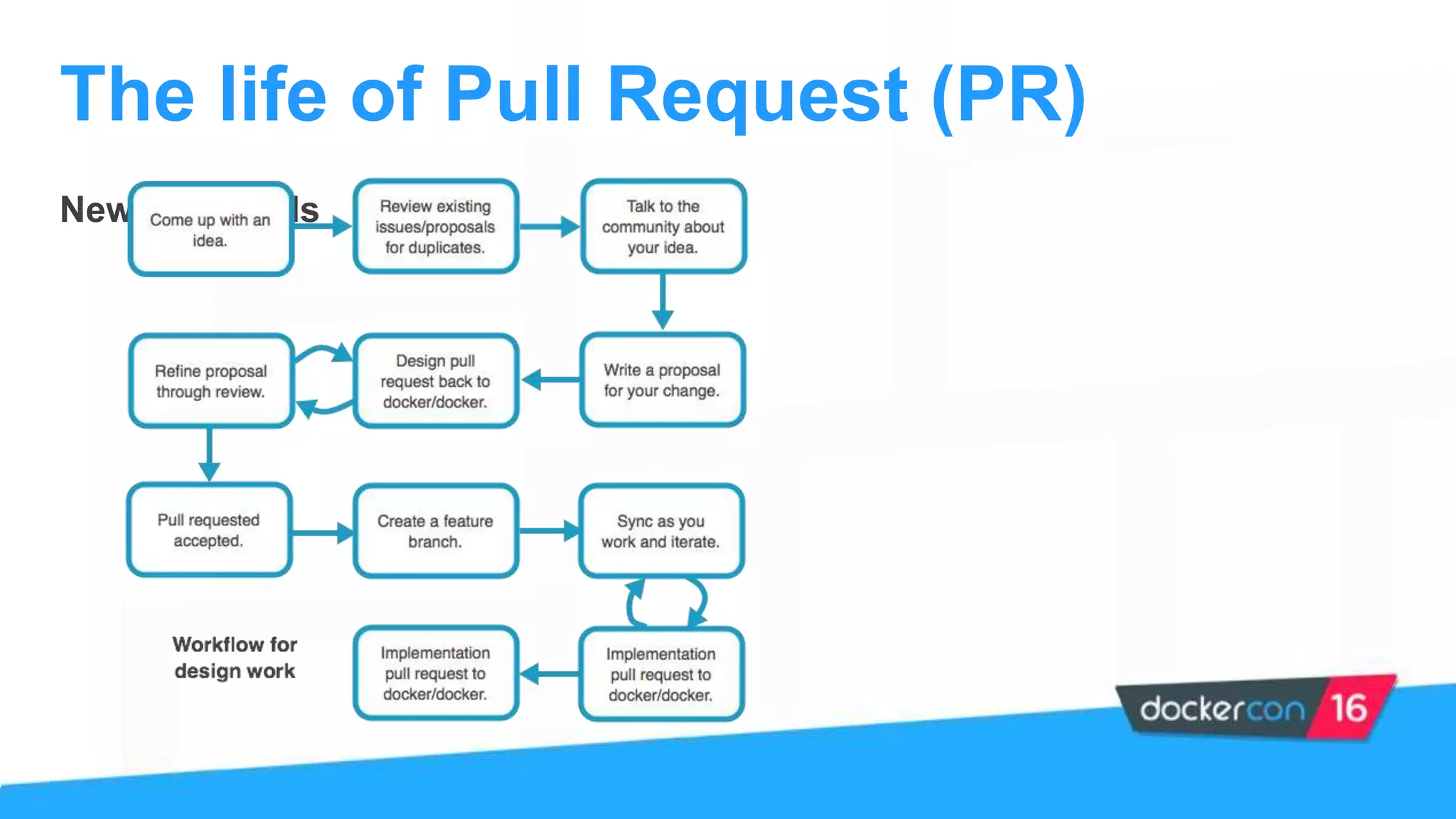
The document provides an overview of the Docker project, highlighting its structure, contributions, and ways to get involved with projects like Kitematic, Compose, and Machine. It outlines the role of maintainers, the process of contributing, and offers steps for new contributors to follow. Additionally, it mentions the importance of community engagement and resources for learning more about Docker.