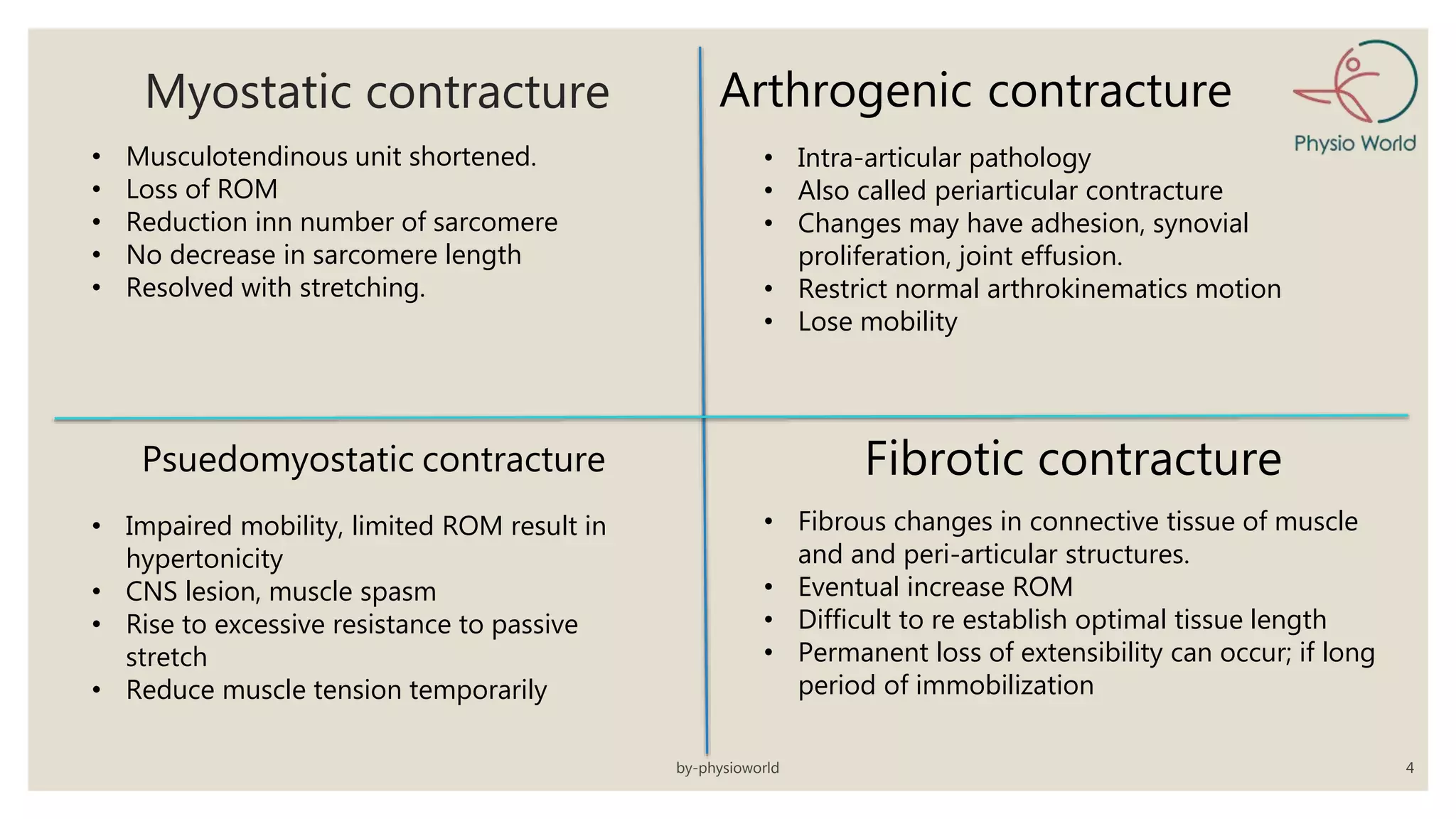
The document explains contractures as adaptive shortening of muscle-tendon units causing limited range of motion and functional impairment. It discusses various types of contractures including myostatic, arthrogenic, pseudomyostatic, and fibrotic, along with their causes such as paralysis and muscular atrophy. Therapeutic approaches for contracture management include positioning, heat application, stretching techniques, massage, and manual joint mobilization.