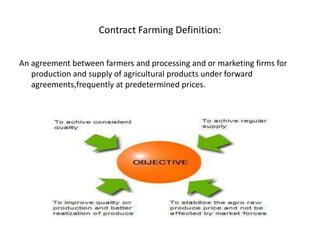
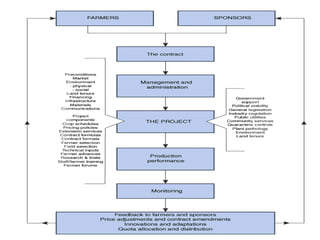
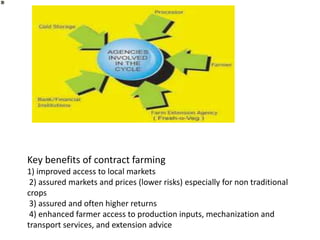
Contract farming is an agreement between farmers and processing or marketing firms where farmers agree to produce and supply agricultural products under forward contracts, often at predetermined prices. Key benefits include assured markets and prices to reduce risks for farmers, access to inputs, mechanization, and advice. It also ensures quality and timely delivery for contract partners while improving local infrastructure. However, issues can arise if contract terms are not respected, such as side selling by farmers or companies refusing to buy agreed quantities at prices.