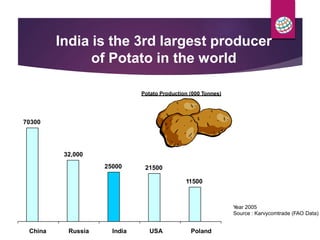
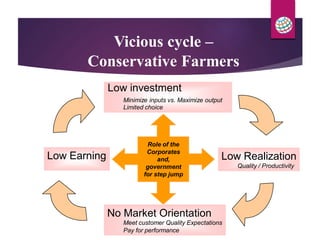
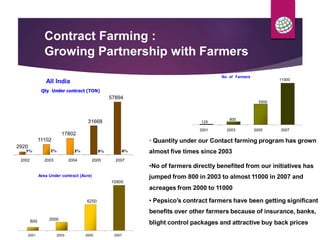
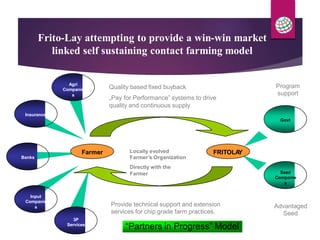
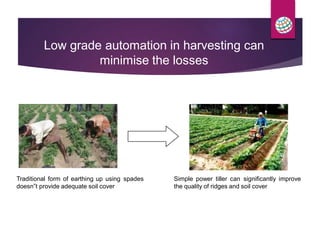
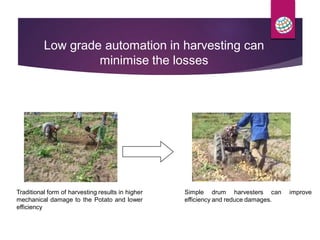
PepsiCo has a contract farming program in India to source potatoes. It partners with over 11,000 farmers and has increased the quantity sourced under contract from 800 tons in 2003 to over 11,000 tons in 2007. The program provides farmers with access to new varieties, agronomic practices, and insurance to increase their yields and incomes. PepsiCo also faces challenges in ensuring consistent supply of high quality potatoes needed for its processing. It is working with farmers on improved practices for land preparation, planting, harvesting, and post-harvest handling and storage to reduce losses and meet its quality standards.