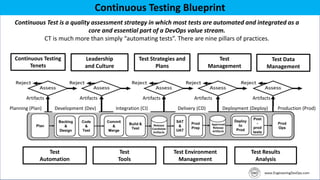
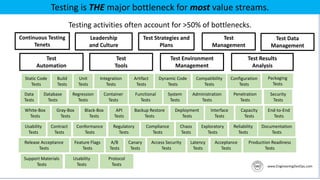
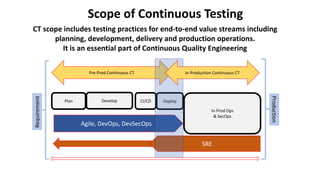
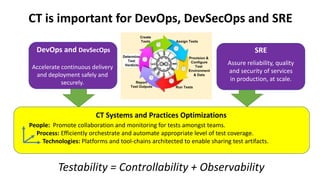
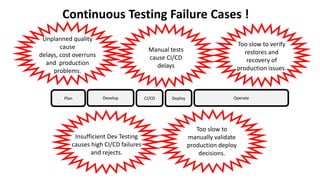
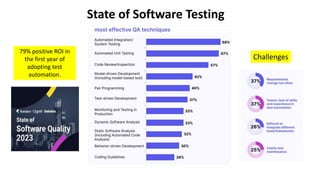
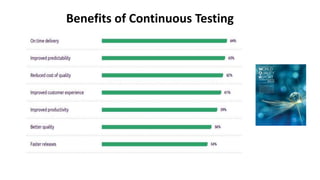
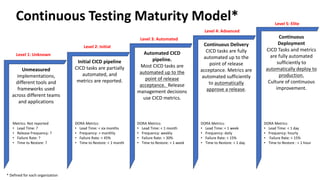
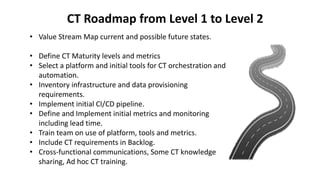
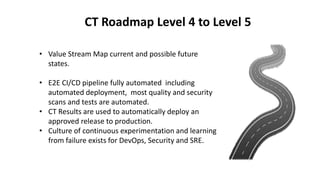
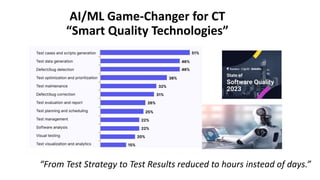
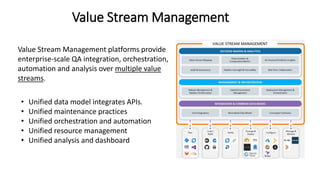
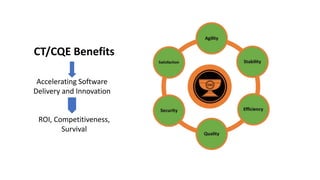
The document outlines the essential components and benefits of continuous testing within the realms of quality engineering, DevOps, DevSecOps, and SRE. It presents a maturity model for continuous testing practices, emphasizing the need for automated testing and collaboration across teams to enhance software delivery and minimize bottlenecks. Key takeaways include the significant ROI from test automation and the role of continuous testing as fundamental to achieving quality in software development processes.