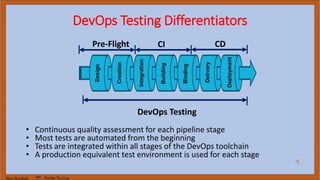
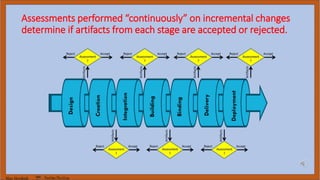
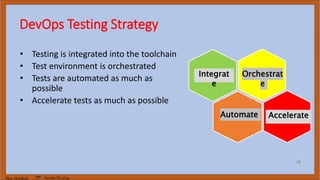
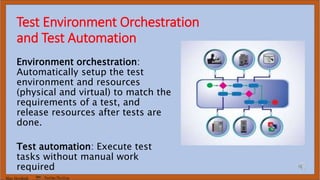
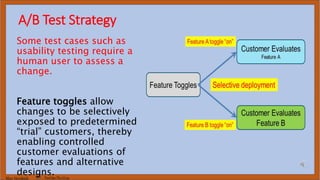
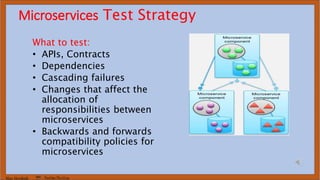
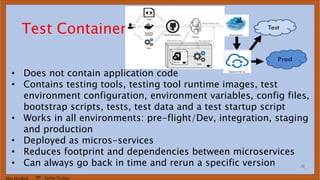
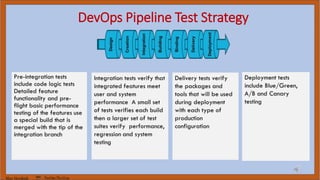
The document discusses DevOps test engineering, emphasizing its importance in ensuring continuous testing and quality across the software development pipeline. It outlines various strategies, best practices, and benefits of DevOps testing, such as automation and integrated test environments. Additionally, it explores different testing methodologies, including canary and blue-green testing, along with the potential consequences of inadequate testing practices.