This document discusses taking an agile approach to continuous security. It covers recent high profile attacks, surveying tools that can check for vulnerable components and exposed secrets. The goal is to automate security checks by integrating tools into the development pipeline to test for vulnerabilities during regular builds and prevent secrets from being committed to version control. This would help catch issues early and increase security through continuous and automated testing.



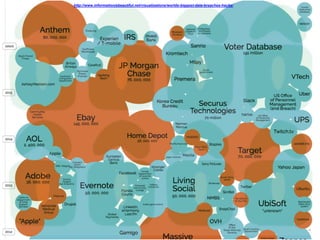









![Vulnerable Components
22
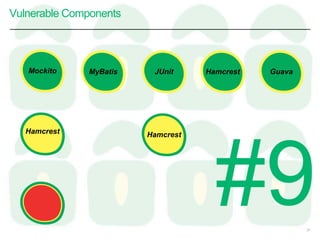
http://www.aspectsecurity.com/research-presentations/the-unfortunate-reality-of-insecure-libraries
We studied the 31 most popular
Java frameworks and security libraries
downloaded from the [maven central]
and discovered that 26% of these
have known vulnerabilities.
More than half of the Global 500
use software built using components
with vulnerable code.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/continoussecurity-tccc-160421113348/85/Continuous-Security-TCCC-20-320.jpg)