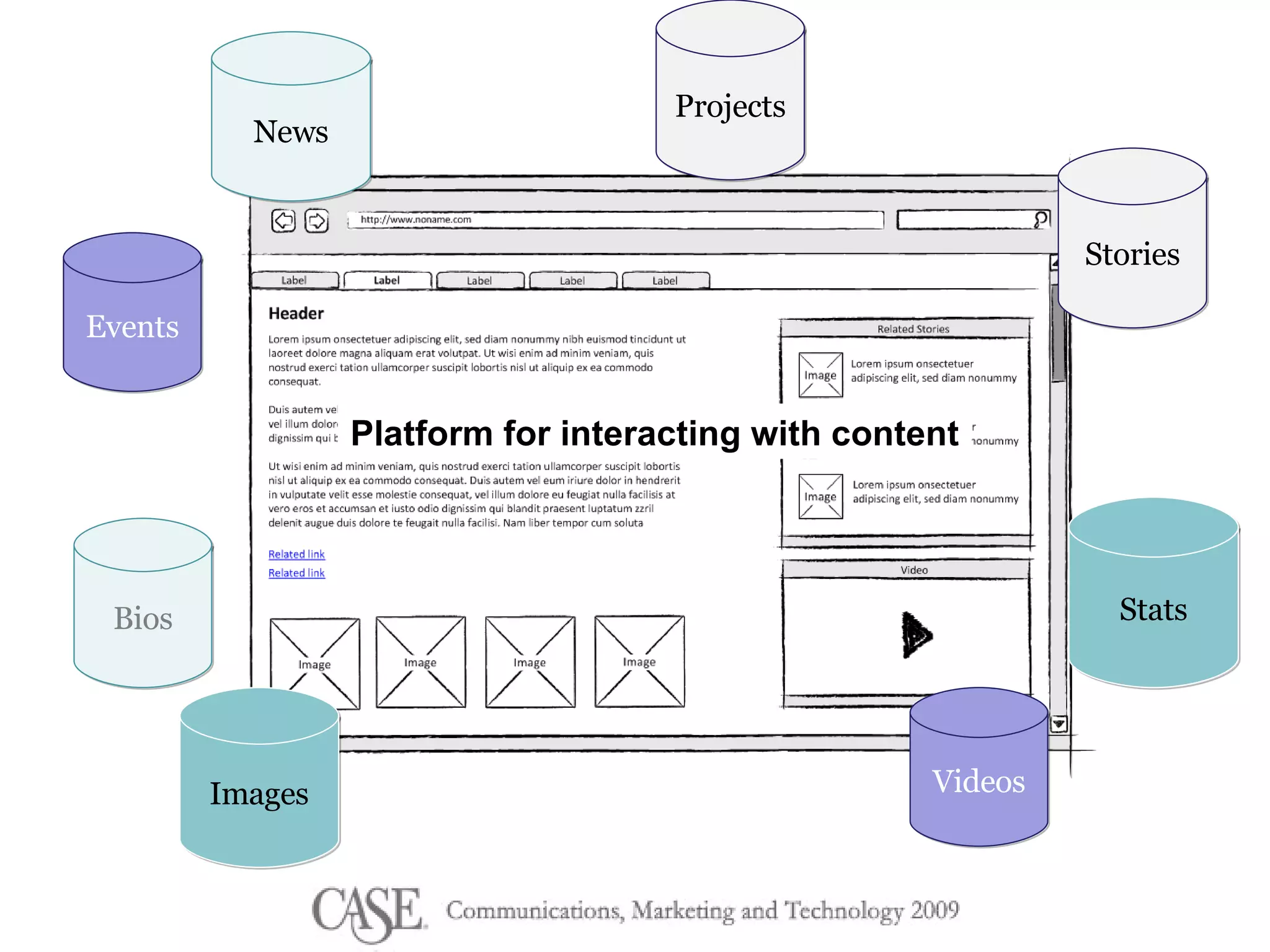
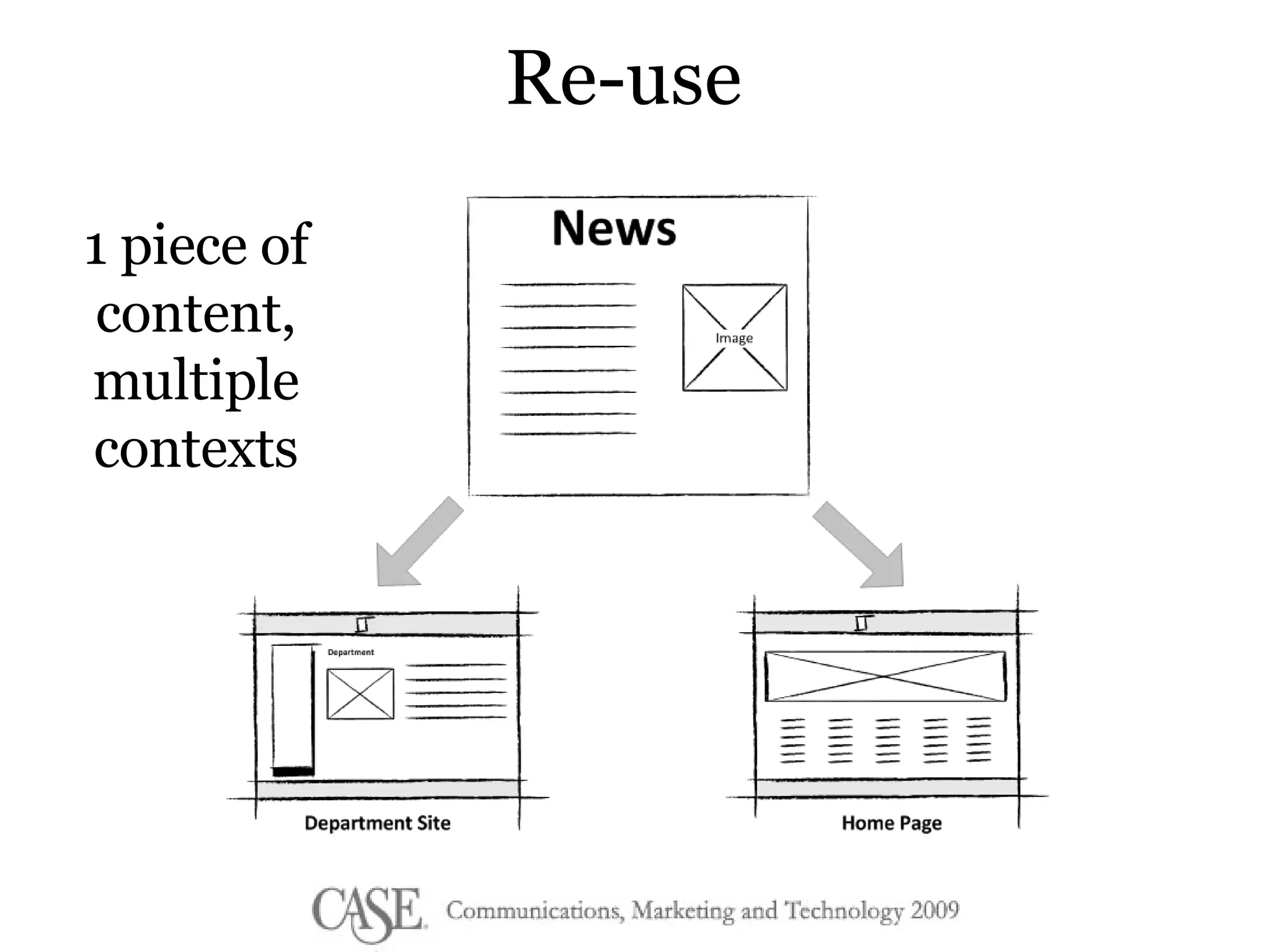
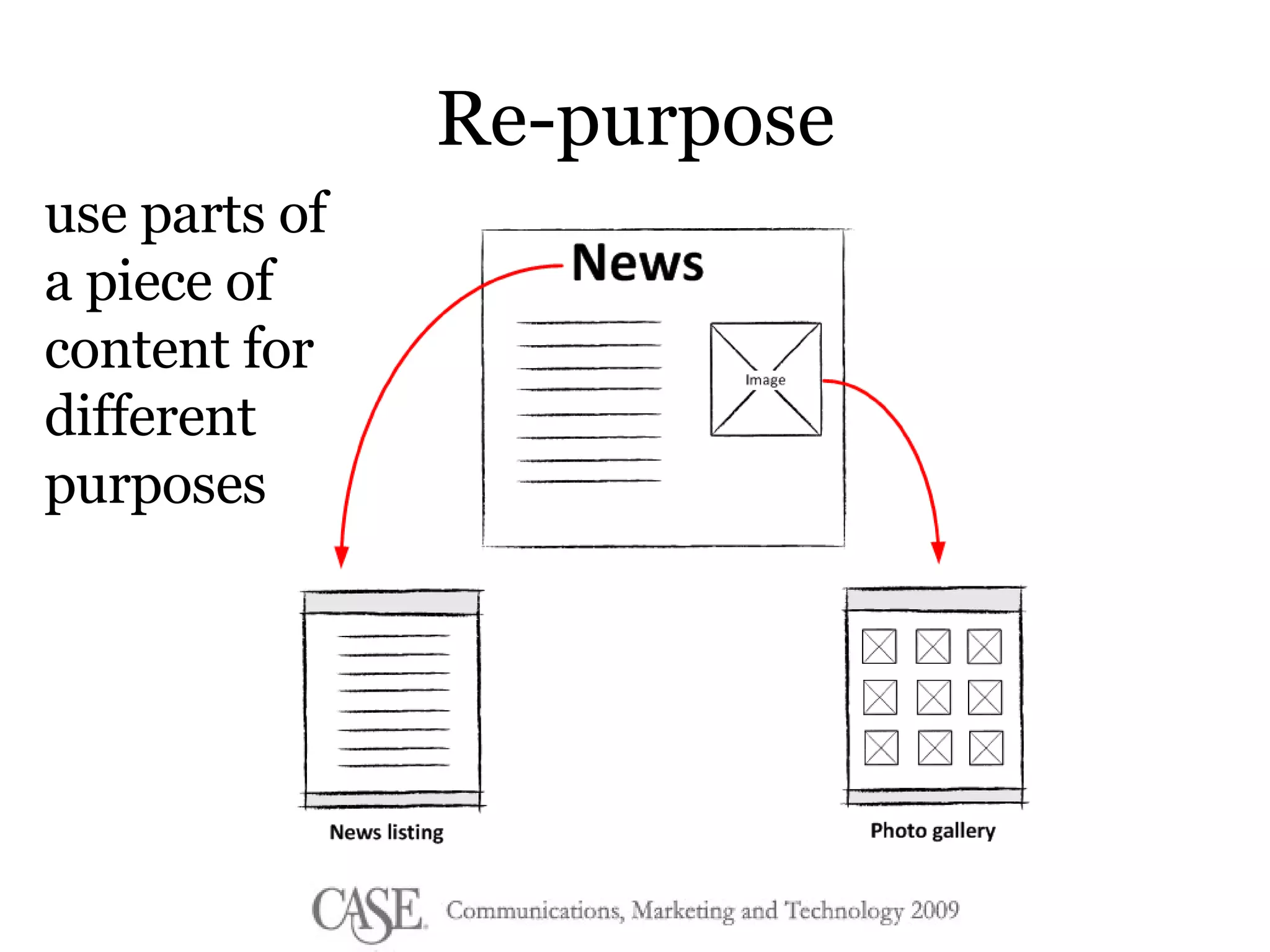
The document discusses the evolution of college websites and the importance of implementing a content management system (CMS) to ease content creation and management. It emphasizes the benefits and cautions of content reuse and the need for structured content to improve consistency and accessibility while addressing the challenges of unstructured content. The author encourages a shift in mindset towards content creation and collaboration, suggesting starting small and fostering a culture of contribution.



























![Questions? Contact me: [email_address] www.twitter.com/jtoddb 404-551-3915](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contentmanagement101-090417100334-phpapp01/75/Content-Management-101-38-2048.jpg)