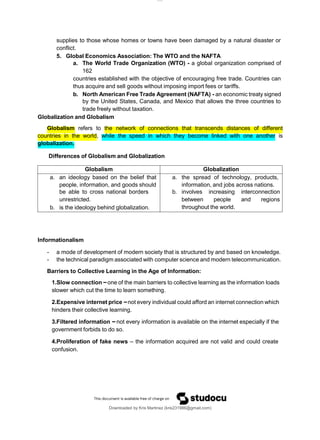
The document discusses several topics related to globalization and the global interstate system. It defines the interstate system as a theoretical system of contending and cooperating states that is the primary focus of international relations studies. It also discusses challenges to globalization like traditional difficulties, national identity movements, neoliberal economics, and global social movements. Additionally, it outlines key institutions that govern international relations such as the United Nations, International Court of Justice, NATO, and non-governmental organizations.