This document summarizes research on radioactive contamination and natural background radiation. It finds that residents of Ramsar, Iran, which has high natural radiation areas, have higher dietary intake of radioactive isotopes like radium-226 and cesium-137 compared to global averages. Specifically, it estimates the annual dietary intake of radium-226 is 245 Bq and cesium-137 is 130 Bq for Ramsar residents, leading to higher effective radiation doses but no detectable health risks observed in the population so far.






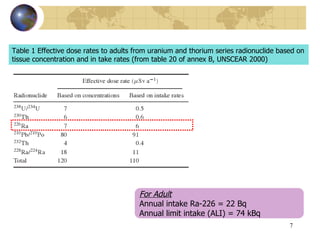

![Worldwide average effective dose Worldwide average effective dose rate from fallout radionuclide have been estimated in UNSCEAR (2000). For external irradiation, In 1999 the worldwide average was 2.90 uSv.a-1, almost entirely from 137 Cs. The worldwide average annual effective dose from natural background is 2.4 mSv, while that for all man - made sources include from nuclear accidentis about 0.8 mSv [ 1 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contaminationresearch-110125043548-phpapp01/85/Radioactive-Contamination-Research-10-320.jpg)

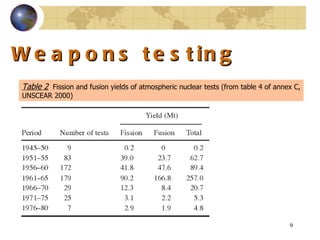
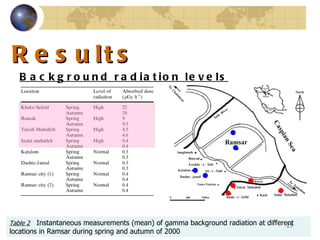
![Introduction In some areas of the world, the average annual effective dose is considerably more than the world average [ 2 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contaminationresearch-110125043548-phpapp01/85/Radioactive-Contamination-Research-12-320.jpg)
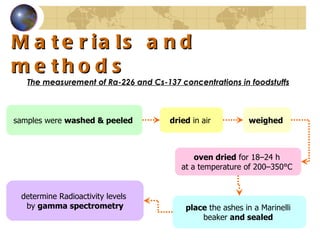
![Introduction In Ramsar, a well-known high level natural radiation area (HLNRA) in northern Iran, Talesh Mahalleh is one of the districts of the northern coastal city of Ramsar . The origin of HLNR in this area is mainly due to presence of natural radionuclides, especially Ra-226 and its decay product, in hot springs flowing into the region [ 10 ]. Radioactivity levels in local soils and the food grown in them are also high since these soils are derived from the local bedrock [ 11 ].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contaminationresearch-110125043548-phpapp01/85/Radioactive-Contamination-Research-13-320.jpg)
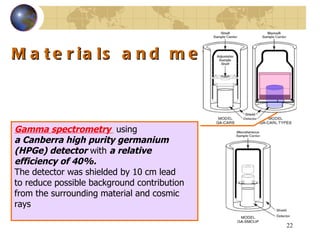
![Introduction The release of radionuclides into the environment contaminates food according to The type of soil, The chemical characteristics of soil, The physical and chemical forms of the radionuclides in the soil, Radionuclide uptake by particular plants, The level of accumulation by particular foodstuffs . Previous studies did not show any evidence of significant increase in health problems compared with that in normal background areas [ 2 , 8 , 10 , 12 , 13 ].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contaminationresearch-110125043548-phpapp01/85/Radioactive-Contamination-Research-15-320.jpg)







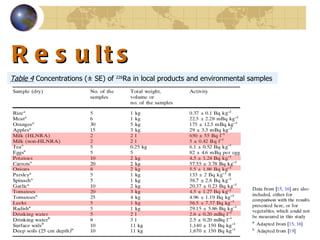
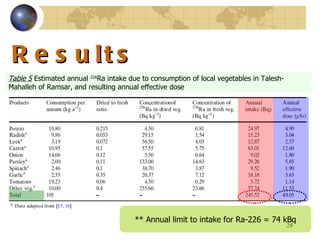
![Discussion The uptake of 226 Ra by food grown in the area under study is governed by the radium in local soil and water . Soil samples collected from the area show a high level of radionuclides [ 19 ]. A very high level of 226 Ra was also detected in milk of a sheep fed from locally obtained food and water in comparison with one fed from imported food and water from a normal area ( Table 4) ; There is evidence to support the fact that in most cases human intake of milk in the HNLRA of Ramsar is derived from cows which are fed mainly on import food and uncontaminated water; under such circumstances, it is estimated that the annual human intake of 226 Ra intake is about 250 Bq ( a figure similar to that derived from local vegetables —Table 5 ).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contaminationresearch-110125043548-phpapp01/85/Radioactive-Contamination-Research-30-320.jpg)


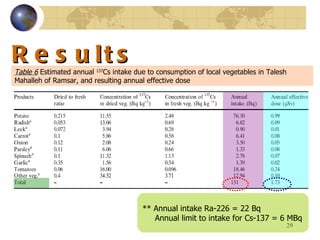
![Conclusions Contamination by 226 Ra of non - vegetable food consumed via local products, especially in Talesh Mahaleh, is about ten times higher than the world average [ 1 ]. Deposition of 137 Cs depends on the type of foodstuff and meteorological conditions, such as rainfall, which more effectively contaminates leafy vegetables. Since radionuclides of Cs may be spread over long distances and because of its relatively long half-life, it is likely that the concentration of 137 Cs in the study area is mainly as a result of Chernobyl accident, and to a lesser extent from operating nuclear reactors or nuclear weapons testing.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contaminationresearch-110125043548-phpapp01/85/Radioactive-Contamination-Research-33-320.jpg)

