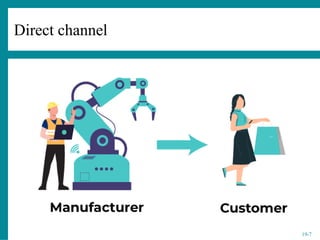
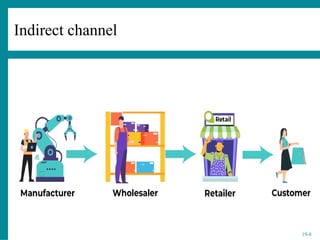
The document provides an overview of consumer behavior in electronic commerce, emphasizing factors such as psychological, social, cultural, and personal influences on purchasing decisions. It details the consumer decision-making process, various distribution channels, and the importance of store environment elements like location, layout, and in-store stimuli. Additionally, it discusses different consumer purchase modes and their implications for retail channel strategy, highlighting the critical roles of store image and store atmosphere in influencing consumer behavior.