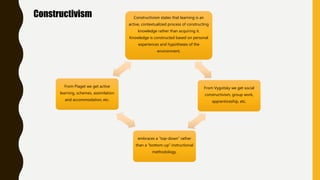
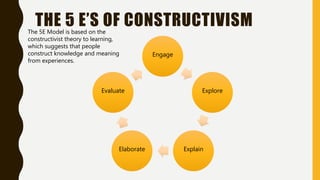
Jean Piaget was a developmental psychologist who developed the theory of constructivism. He proposed that individuals construct new knowledge through experiences of accommodation and assimilation. Constructivism suggests that learning is an active process where learners build understanding based on their experiences. The 5E model is based on constructivism and includes the steps of engage, explore, explain, elaborate, and evaluate. In the classroom, constructivism is implemented through engaging activities, exploration of topics by students, collaborative work, application of concepts to the real world, and ongoing assessment of understanding.