Embed presentation
Downloaded 10 times




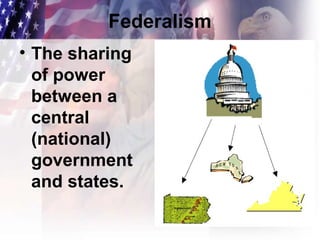
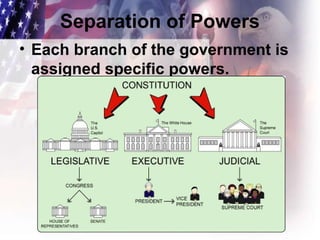


This document outlines several key constitutional principles: limited government which restricts total power for any authority figure and requires all to obey the law; republicanism where the people elect representatives to hold power; and checks and balances which prevents any one branch of government from becoming too powerful. It also discusses federalism as the sharing of power between national and state governments, separation of powers which assigns specific powers to each branch, and popular sovereignty where ultimate political power rests with the people who exercise it through voting. Additionally, it defines individual rights as personal liberties people are born with that cannot be taken away, protected by the Bill of Rights.







