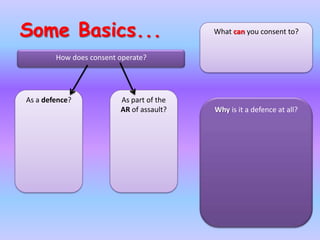
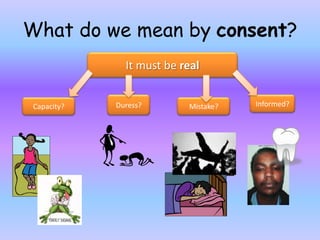
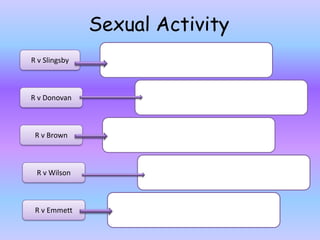
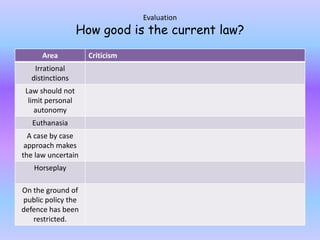
The document discusses the law around consent as a defense for offenses against the person. It provides an overview of key cases that have established rules and exceptions regarding consent. It also presents a hypothetical scenario from another jurisdiction to analyze whether consent could be a valid defense for intentionally causing harm. The document aims to assess students' existing knowledge and guide them in improving essay responses through highlighting cases, legal rules, and evaluating the development and impact of reforms.