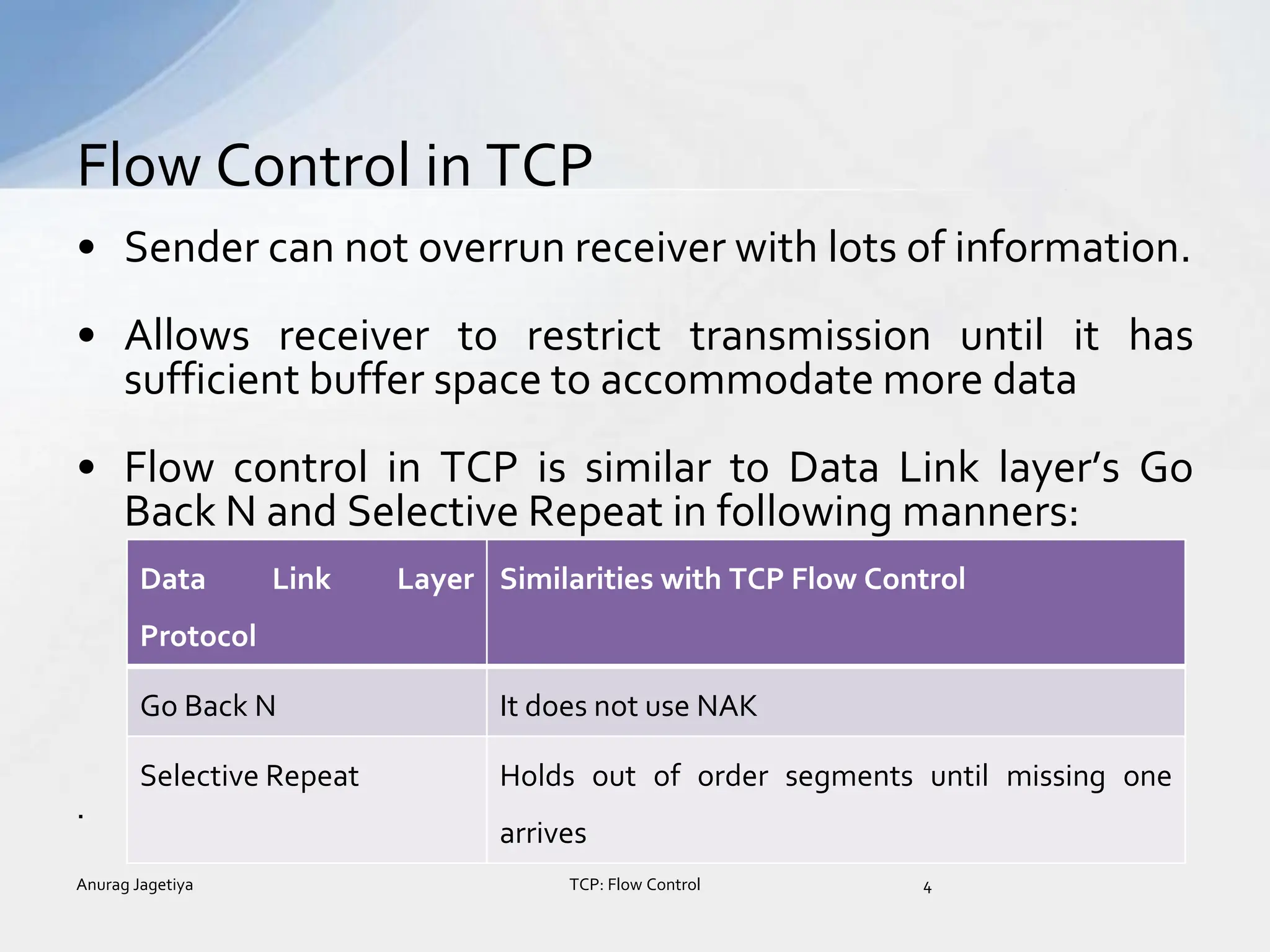
The document discusses flow control in TCP. It explains that TCP uses a sliding window mechanism for flow control to balance the sender's transmission rate with the receiver's reception rate. The size of the sliding window is determined by the receiver's advertised window size and the congestion window size. TCP provides reliable, in-order delivery of data segments through error control methods like checksums, acknowledgements, and retransmissions. It also addresses problems like delayed ACKs, silly window syndrome, and solutions to improve TCP transmission efficiency.


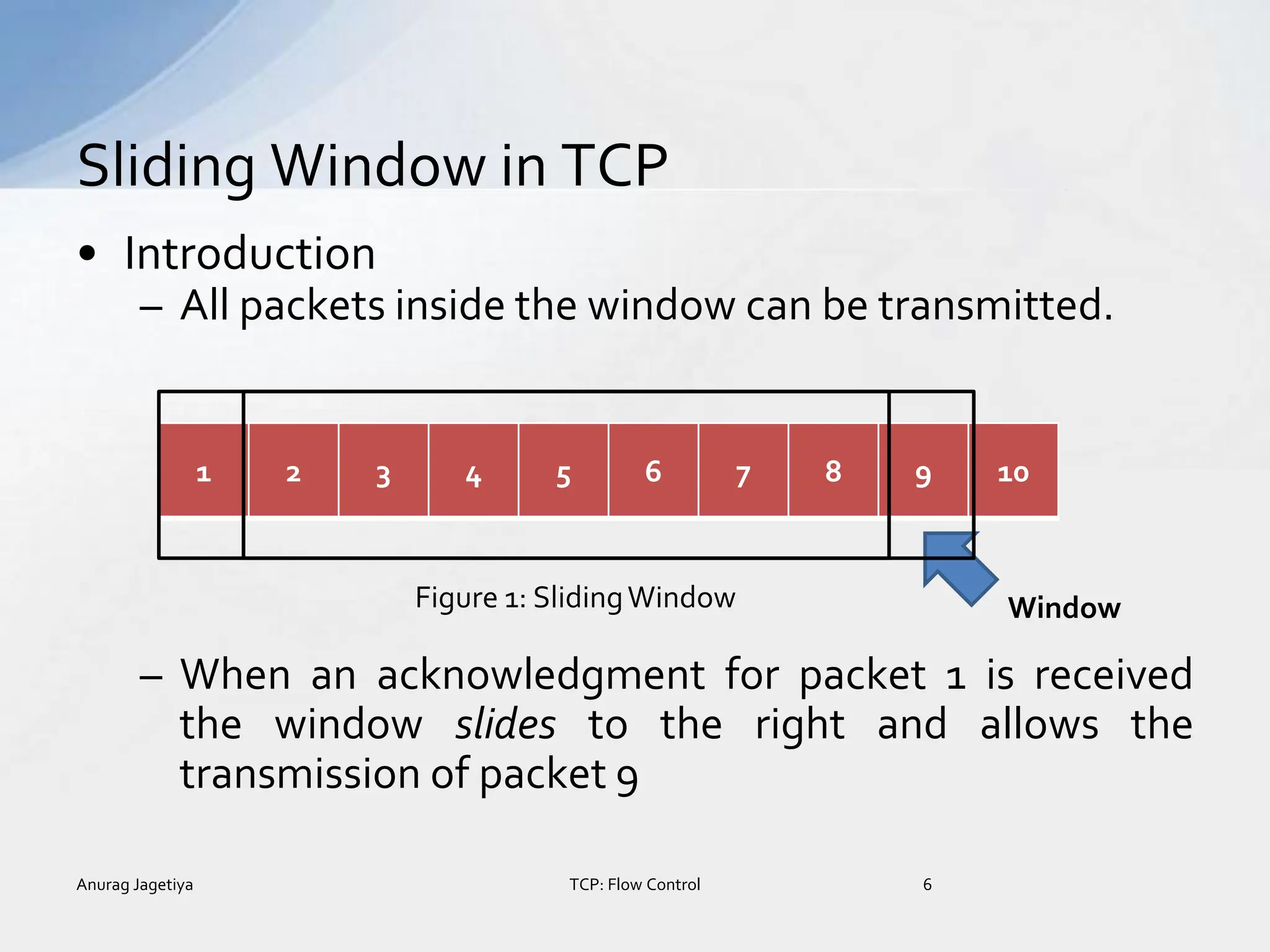
![• Conceptually partitions the window into three
classes:
– Sent and acknowledged [left side, out side the window]
– Being Transmitted [inside the window]
– Waiting to be transmitted [right side, out side the window]
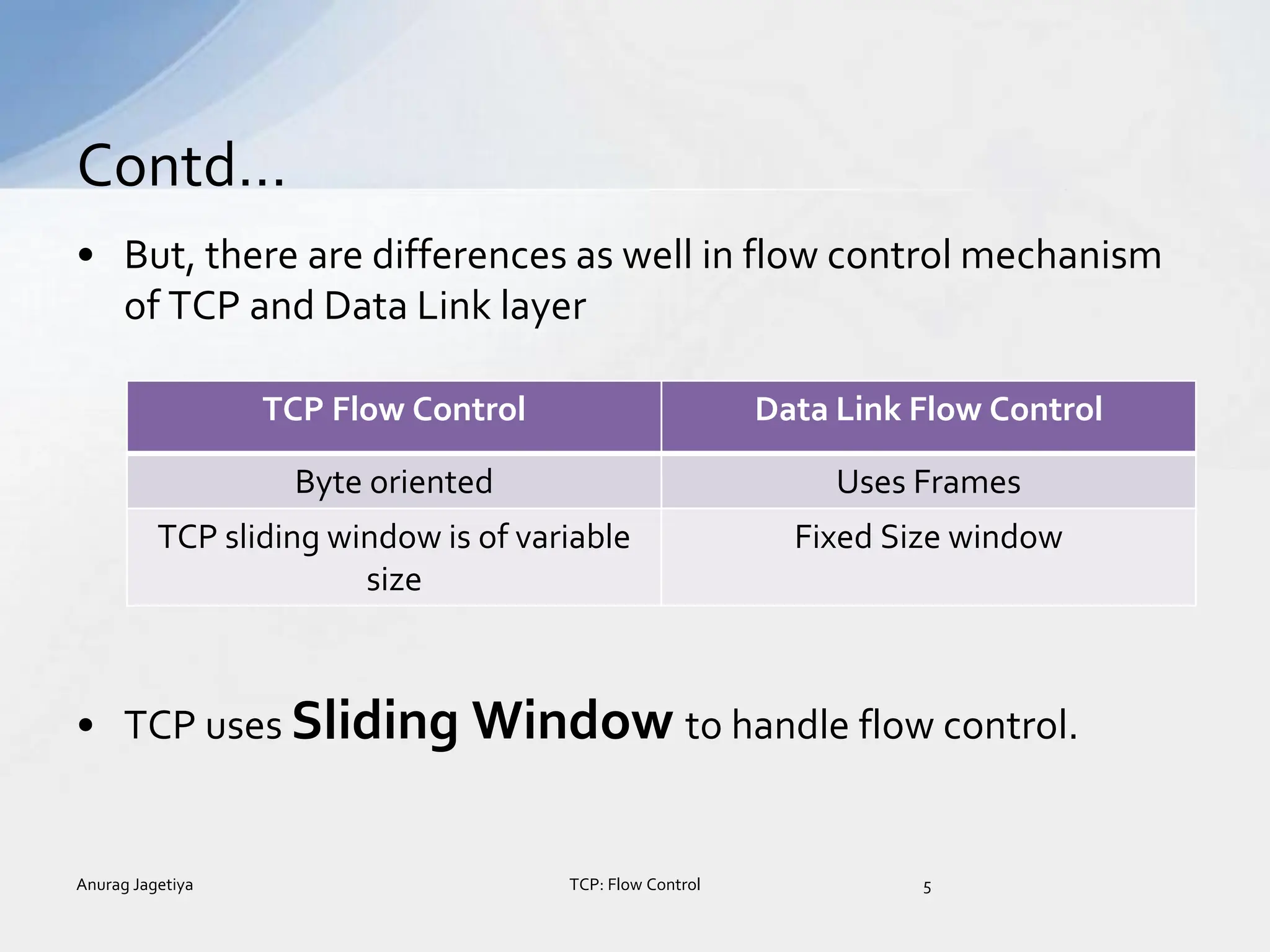
Contd..
Anurag Jagetiya 7
TCP: Flow Control
Figure 2: SlidingWindow Representation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tcpflowcontrolanurag-150513130509-lva1-app68921-240313092122-e49d2d60/75/tcpflowcontrolanurag-150513130509-lva1-app6892-1-pptx-7-2048.jpg)
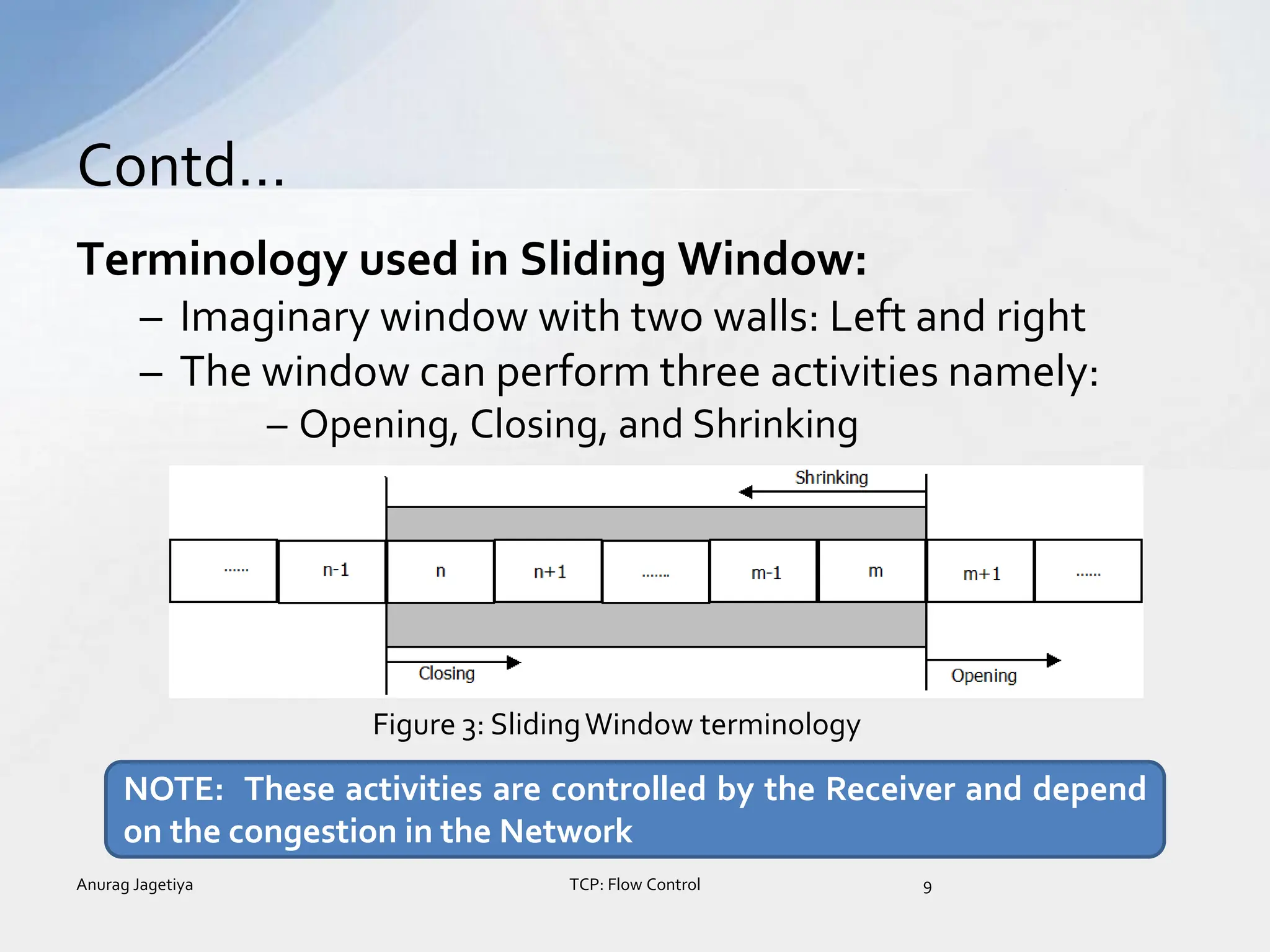
![• Opening a window
– Moving the right wall to the right
– Allows more new bytes in the buffer that are eligible for
sending
• Closing a window
– Moving left wall to right
– Some bytes have been acknowledged
• Shrinking a window
– Moving right wall to left.
– Removing eligibility of some packets.
– [Warning: Strongly discouraged and not allowed in some
implementation ]
Contd…
Anurag Jagetiya 10
TCP: Flow Control
NOTE: Left wall cannot move to left, as this will revoke some of
previously sent Acknowledges (ACKs)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tcpflowcontrolanurag-150513130509-lva1-app68921-240313092122-e49d2d60/75/tcpflowcontrolanurag-150513130509-lva1-app6892-1-pptx-10-2048.jpg)


![Example of Flow Control
Anurag Jagetiya 14
TCP: Flow Control
In this
example, It is
assumed that
there is only
unidirectional
communicatio
n between
client and
server
Figure 4:
Flow Control [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tcpflowcontrolanurag-150513130509-lva1-app68921-240313092122-e49d2d60/75/tcpflowcontrolanurag-150513130509-lva1-app6892-1-pptx-14-2048.jpg)


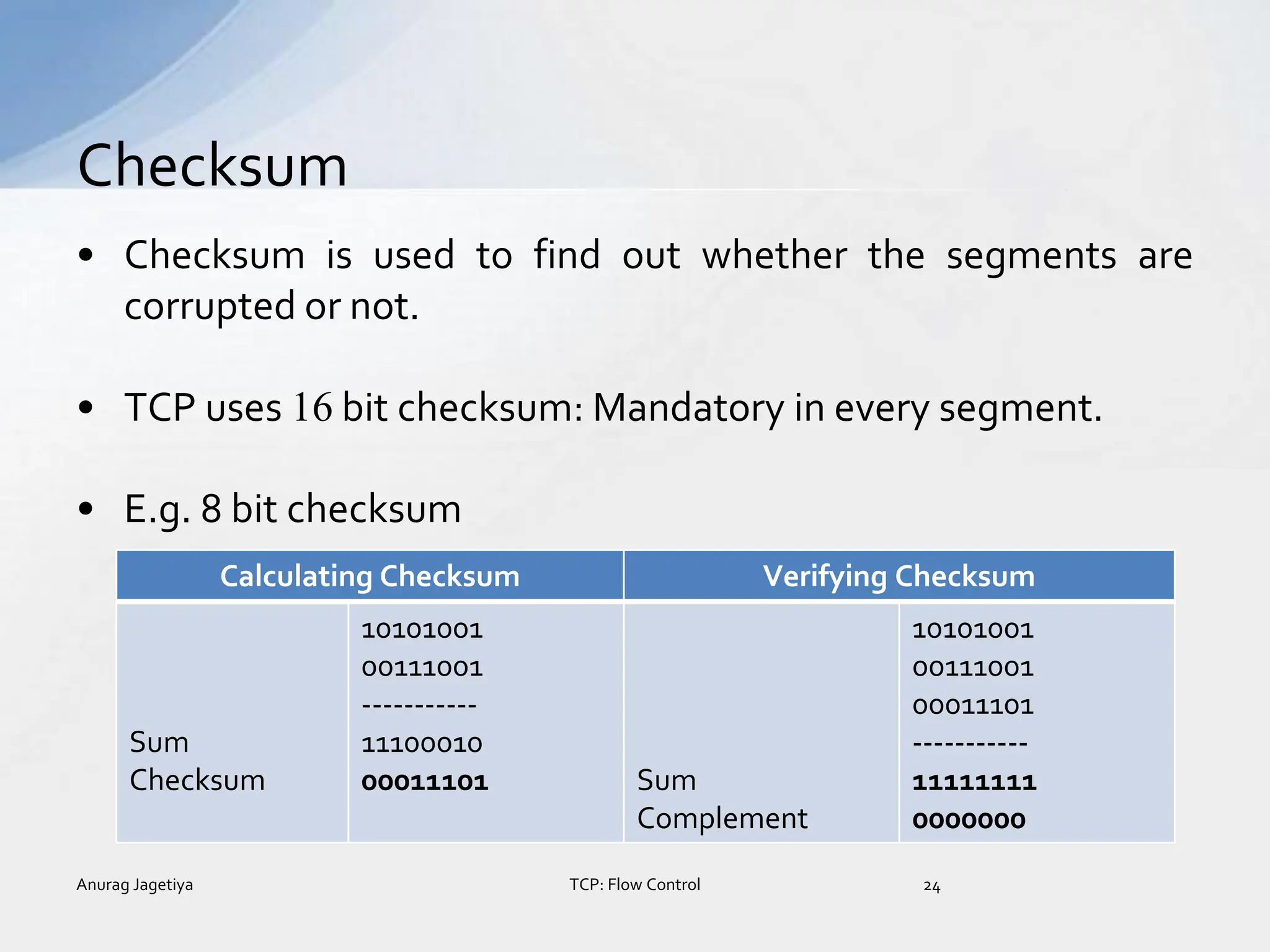
![• In the given figure:
• The receiving TCP announces a window size of 1 byte.
• The sending TCP sends only 1 byte.
Contd…
Anurag Jagetiya 19
TCP: Flow Control
Figure 5: Receiver’s Silly
Window [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tcpflowcontrolanurag-150513130509-lva1-app68921-240313092122-e49d2d60/75/tcpflowcontrolanurag-150513130509-lva1-app6892-1-pptx-19-2048.jpg)


![• NET-SEAL
[Teaching Computer NETwork Through
Simulation Experiment and Animation Library]
Simulation of TCP Flow Control
Anurag Jagetiya 22
TCP: Flow Control](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tcpflowcontrolanurag-150513130509-lva1-app68921-240313092122-e49d2d60/75/tcpflowcontrolanurag-150513130509-lva1-app6892-1-pptx-22-2048.jpg)

![• Round Trip Time measurement
– The RTT is based on time difference between segment
transmission and ACK.
– But, TCP does not ACK each segment Each connection
has only one timer.
Retransmission (Contd…)
Anurag Jagetiya 27
TCP: Flow Control
Segment 1
Segment 4
ACK for Segment 1
Segment 2
Segment 3
ACK for Segment 2 + 3
Segment 5
ACK for Segment 4
ACK for Segment 5
RTT
#1
RTT
#2
RTT
#3
Figure 6: RTT [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tcpflowcontrolanurag-150513130509-lva1-app68921-240313092122-e49d2d60/75/tcpflowcontrolanurag-150513130509-lva1-app6892-1-pptx-27-2048.jpg)
![Example of Fast Retransmission
Anurag Jagetiya 31
TCP: Flow Control
Figure 7: 3 ACK [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tcpflowcontrolanurag-150513130509-lva1-app68921-240313092122-e49d2d60/75/tcpflowcontrolanurag-150513130509-lva1-app6892-1-pptx-31-2048.jpg)