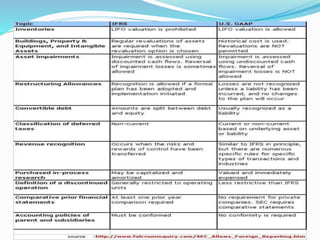
IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) are a set of accounting standards used to prepare financial statements providing a globally recognized way to communicate the financial performance of a company. India is implementing IFRS (called Ind-AS) in a phased manner starting in 2016-17. Adopting IFRS has benefits like increasing the credibility and comparability of financial statements internationally and with cross-border transactions but also challenges like amendments needed to laws, impact on financial results, and need for user awareness and training on the new standards. The conclusion is that while implementation issues exist, adopting IFRS in India is expected to be largely beneficial overall by promoting better investment decisions and increasing foreign investment.