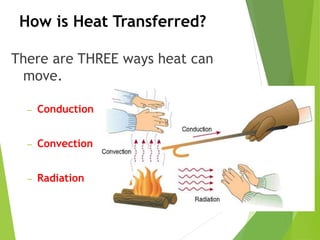
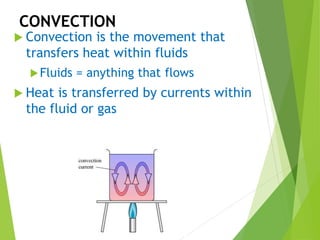
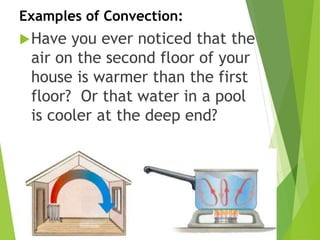
This document discusses the three main methods of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction involves the direct transfer of thermal energy between particles in direct contact with one another. Convection involves the transfer of heat by fluid currents within gases or liquids. Radiation involves the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves and does not require direct contact between the warm object and cooler object. Examples are provided for each type of heat transfer.