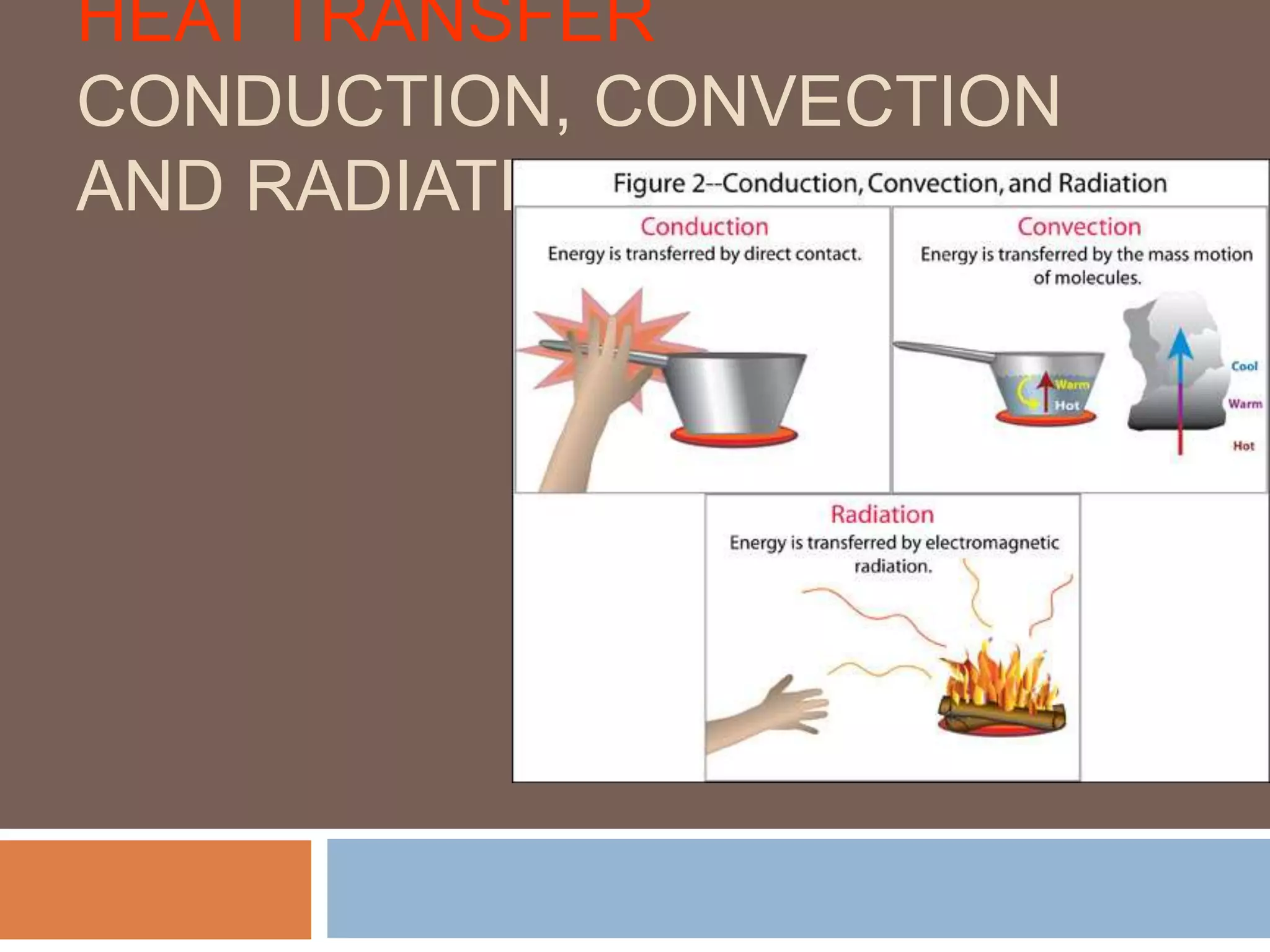
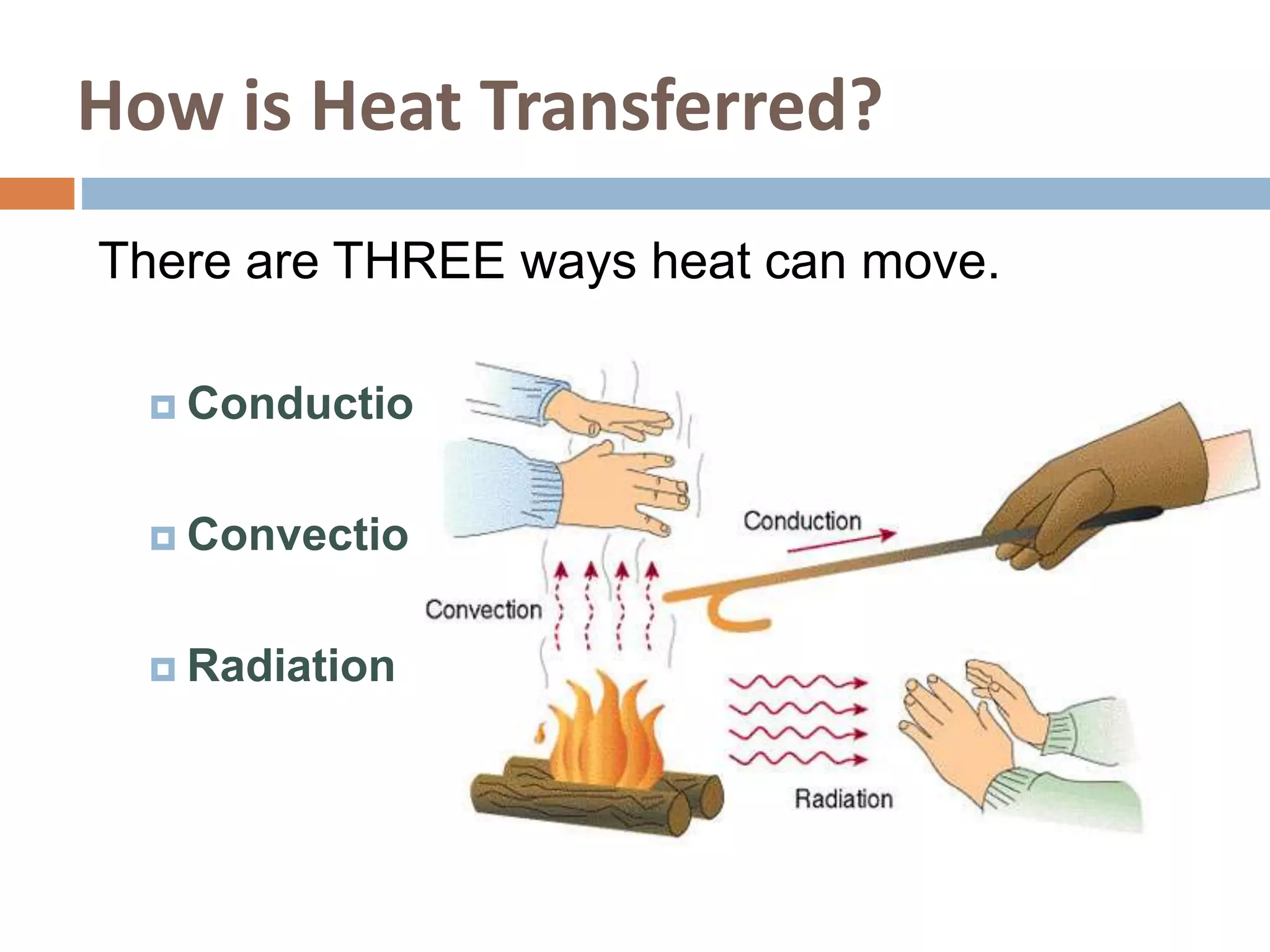
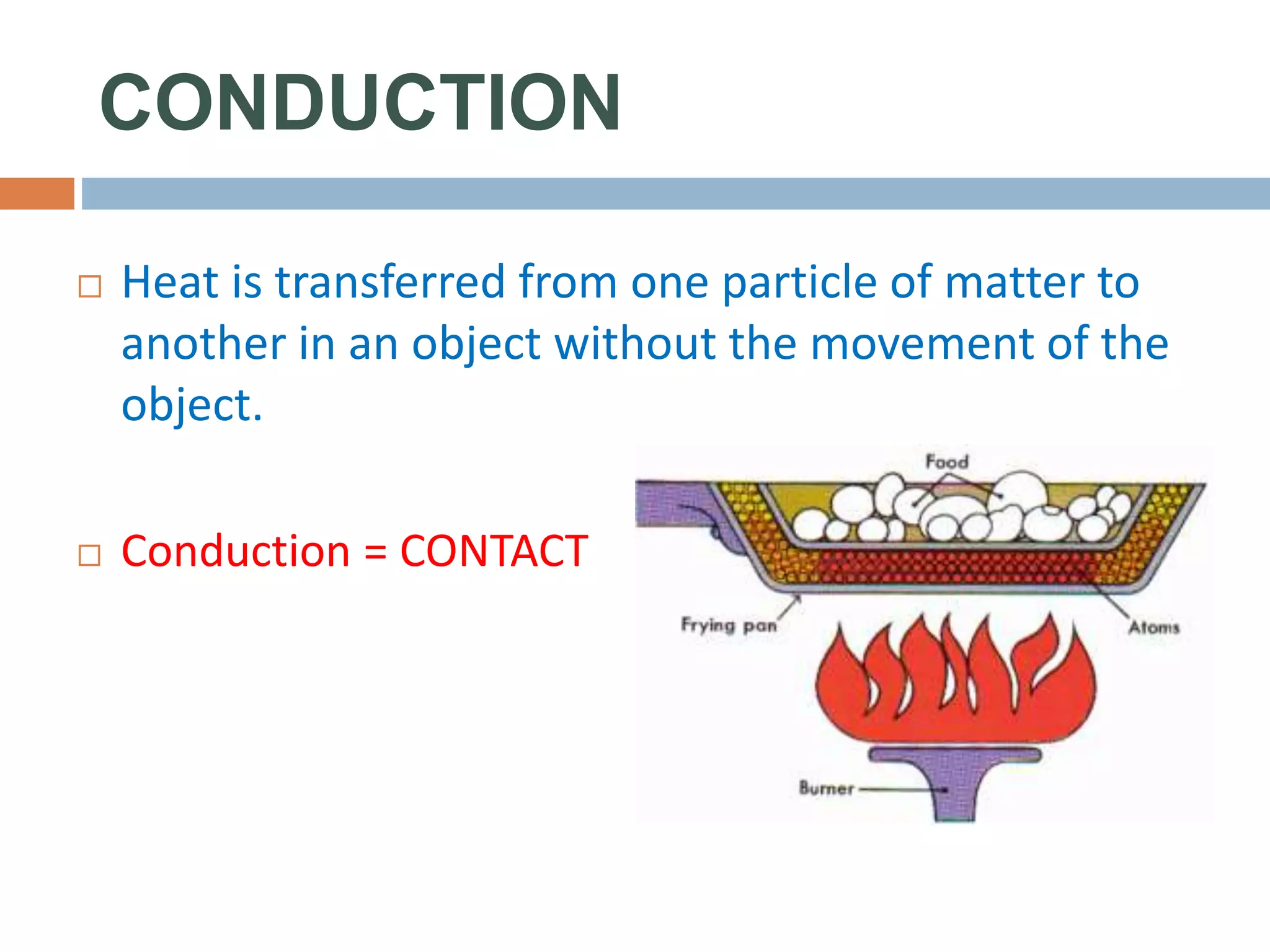
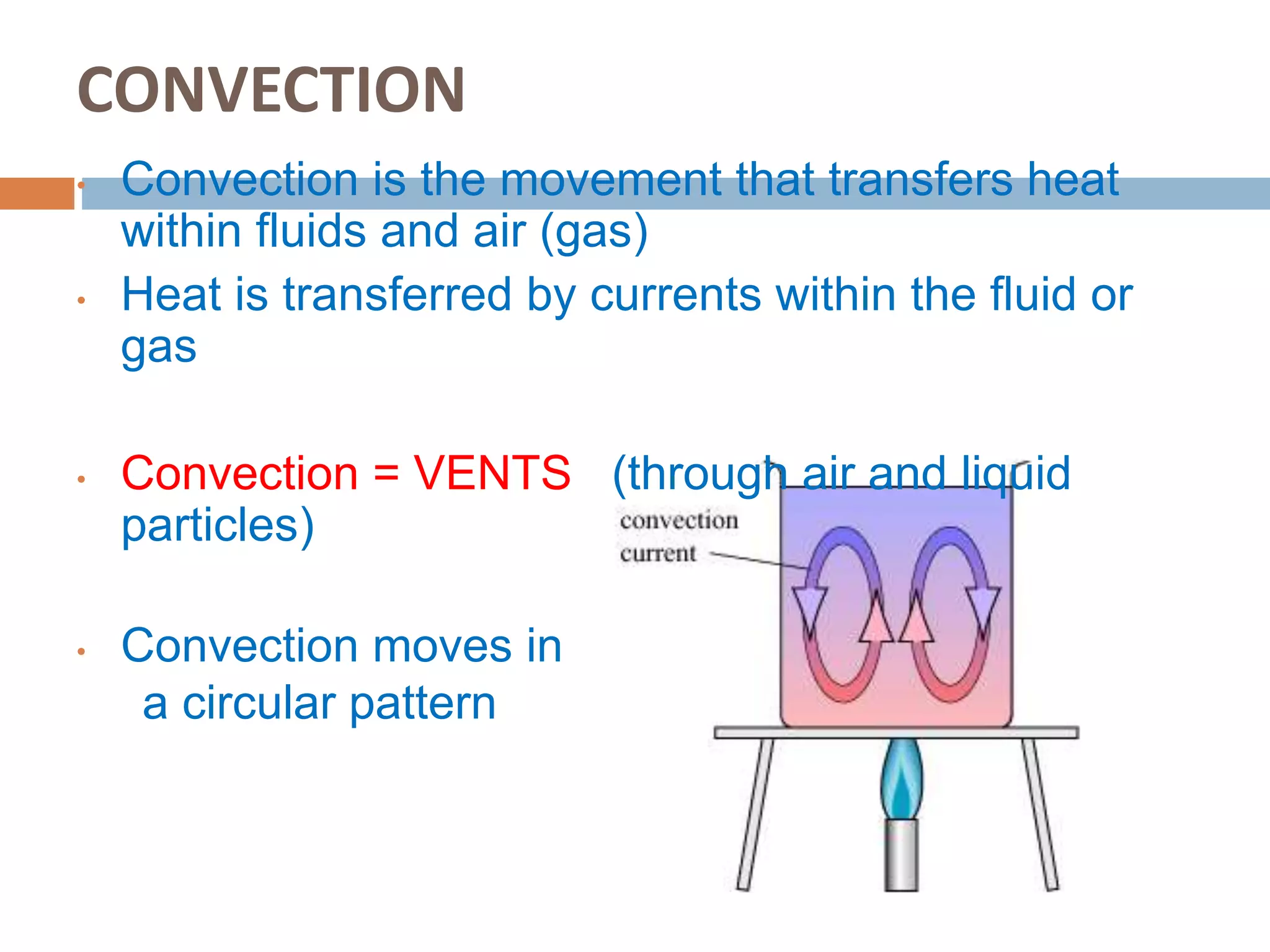
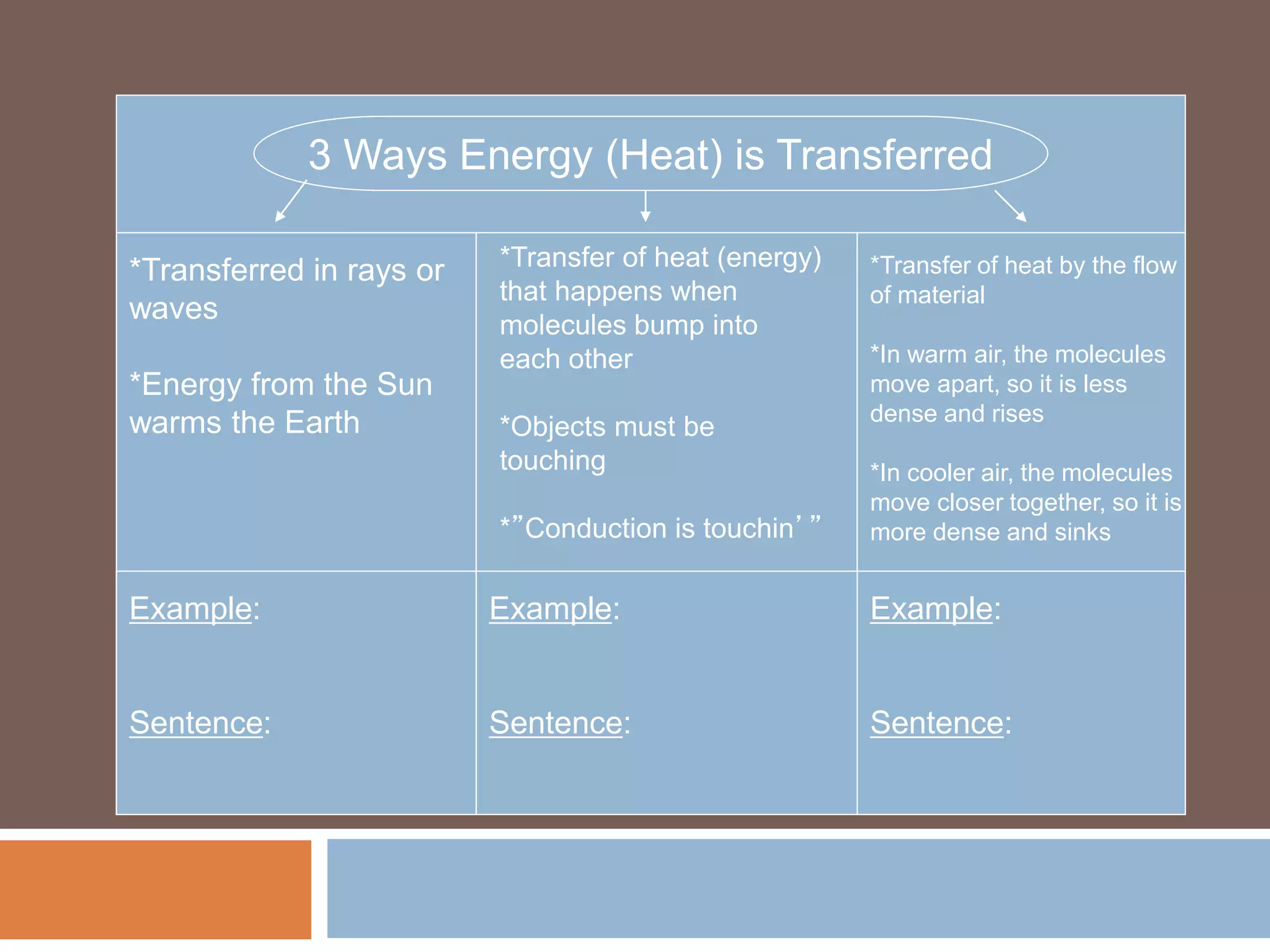
There are three main ways that heat is transferred: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction involves the transfer of heat through direct contact between objects. Convection involves the transfer of heat by the circulation of fluids like air and water. Radiation transfers heat through electromagnetic waves and does not require direct contact between the objects.