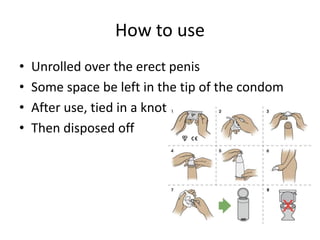
Male condoms are sheath-shaped barrier devices used during sex to reduce pregnancy and STI risk. Ancient Egyptians and Europeans historically used animal skins and linen for protection, while modern condoms are typically made of latex or polyurethane. Condoms are applied over an erect penis, leaving space at the tip, and disposed after use tied in a knot. They provide contraception and STI prevention with minimal side effects, though correct usage is important to avoid breakage.