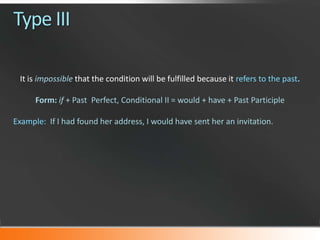
1) The document discusses different types of conditional sentences in English, known as conditional clauses or "if" clauses.
2) There are three main types of conditional sentences - Type I refers to possible future events, Type II refers to unlikely present events, and Type III refers to impossible past events.
3) Each type has a specific grammatical form, such as "if + present/will-future" for Type I and "if + past perfect/would have + past participle" for Type III.