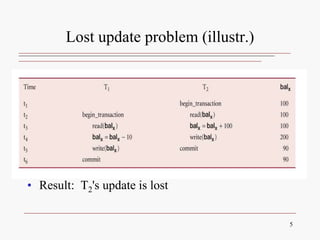
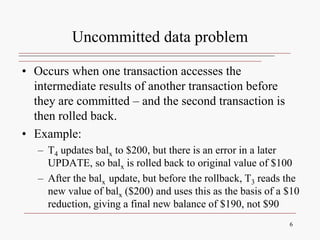
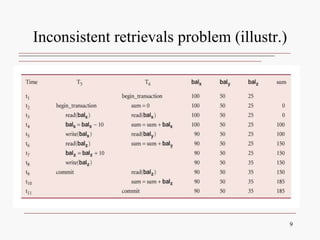
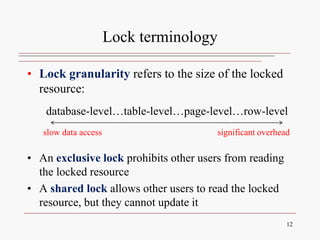
This document discusses database concurrency control and the need to prevent interference when multiple users access a database simultaneously. It describes three potential problems that can occur without concurrency control: lost updates, uncommitted data, and inconsistent retrievals. Examples are provided to illustrate each problem. The document also discusses schedulers and locking methods like two-phase locking that can be used to ensure serializable execution and prevent conflicts between concurrent transactions. Deadlocks are identified as a potential issue, and techniques for controlling deadlocks like prevention, detection, and avoidance are outlined. Timestamping is also presented as an alternative concurrency control method.