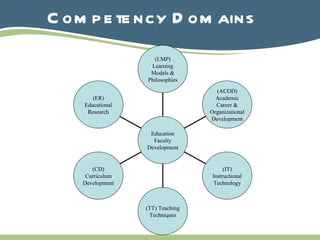
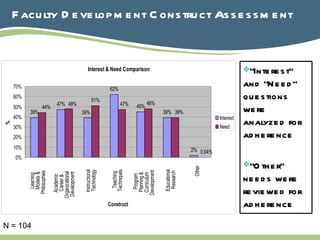
The document discusses the conceptualization of education faculty development for hospital-based faculty, emphasizing the need for innovative approaches to prepare future healthcare professionals. It highlights the importance of developing faculty expertise across various domains such as educational research, curriculum development, and instructional technology. Additionally, it suggests conducting further needs assessments and research to enhance faculty development practices and understand the medical education continuum.
![Conceptualizing Education Faculty Development for Hospital-Based Faculty Elisabeth E. Bennett, PhD Director, Education Research and Development, Baystate Health Assistant Professor, Tufts University School of Medicine [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bennettefd3-10v2-110906085512-phpapp01/75/Conceptualizing-Education-Faculty-Development-1-2048.jpg)