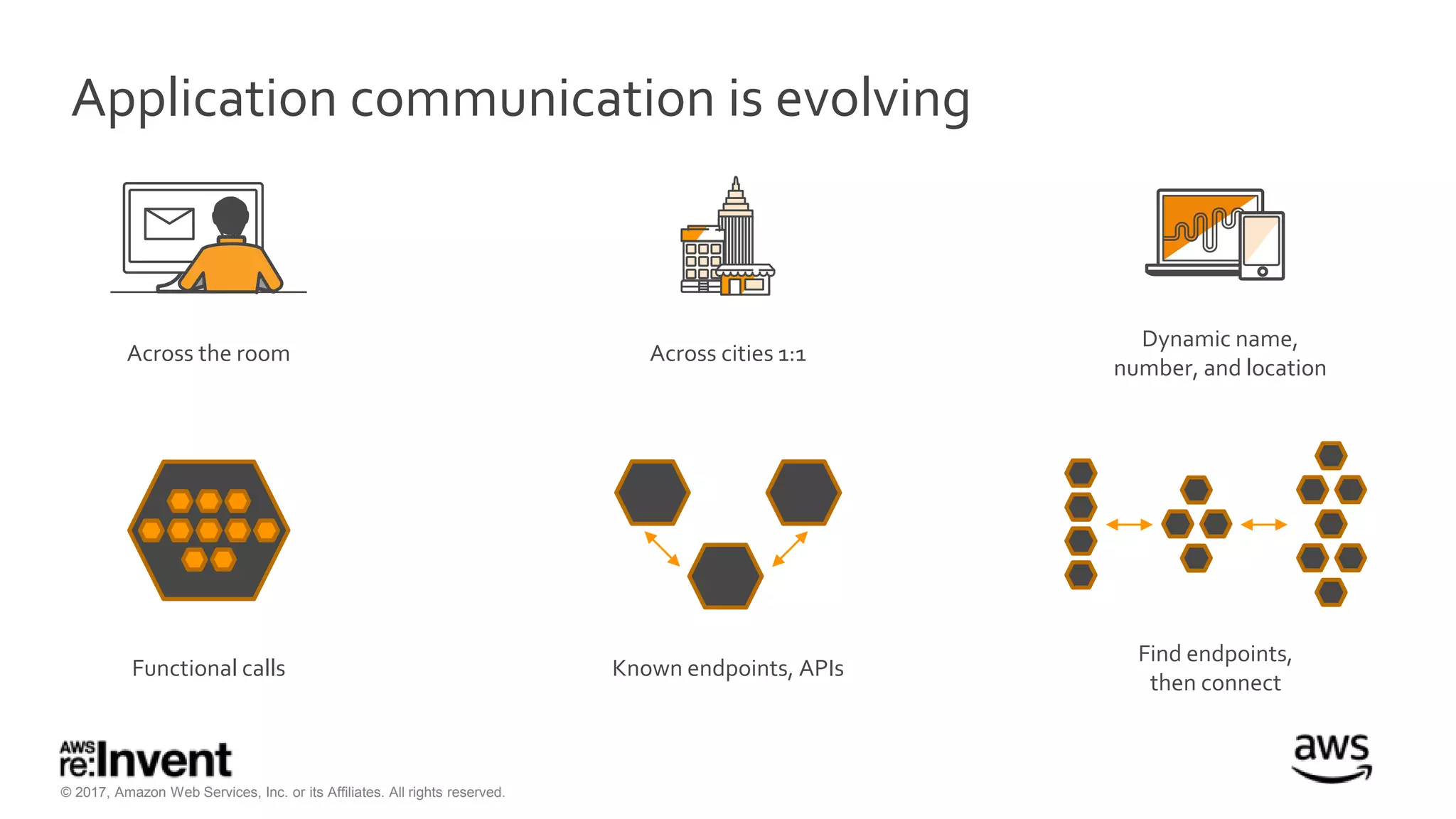
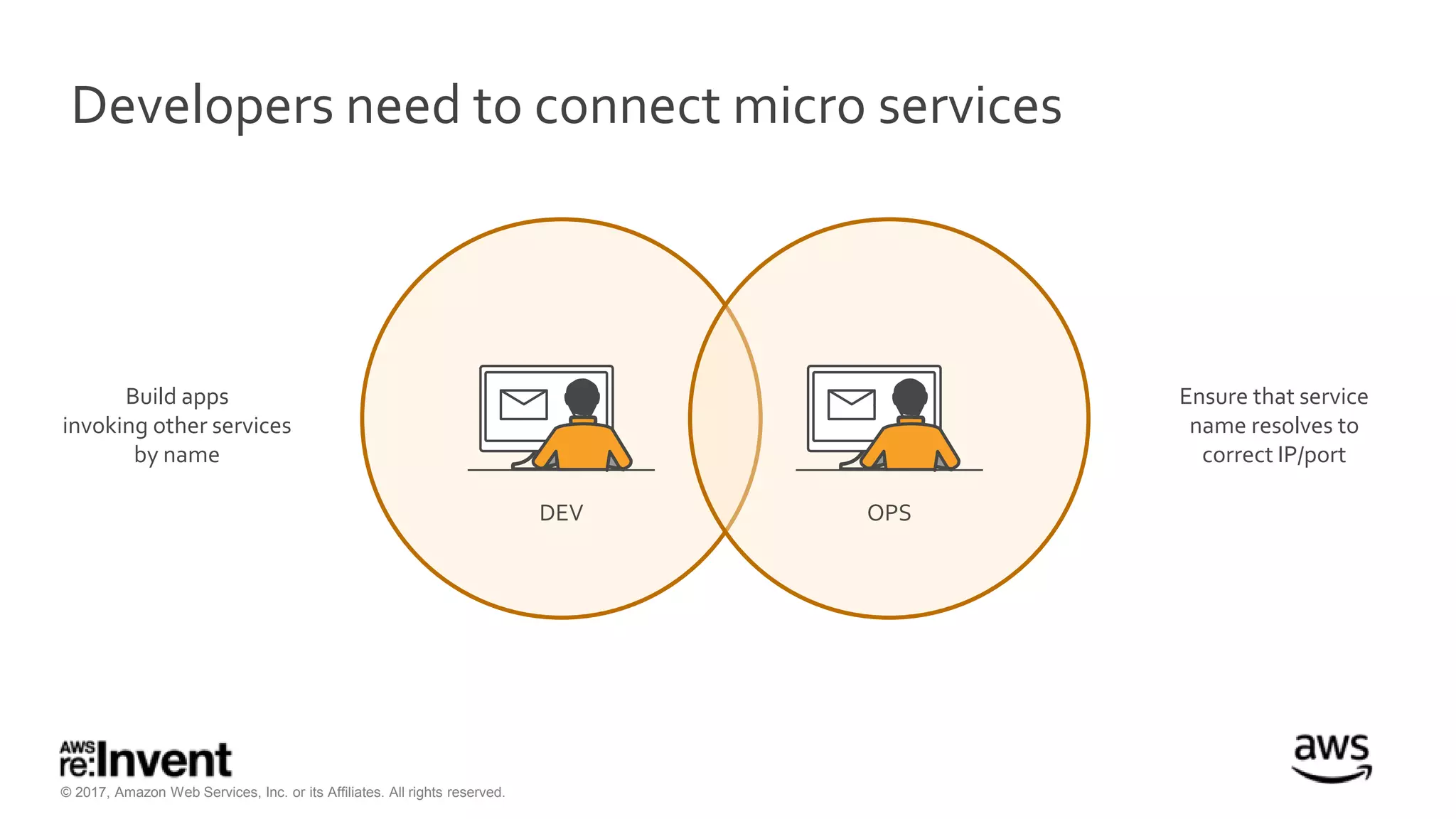
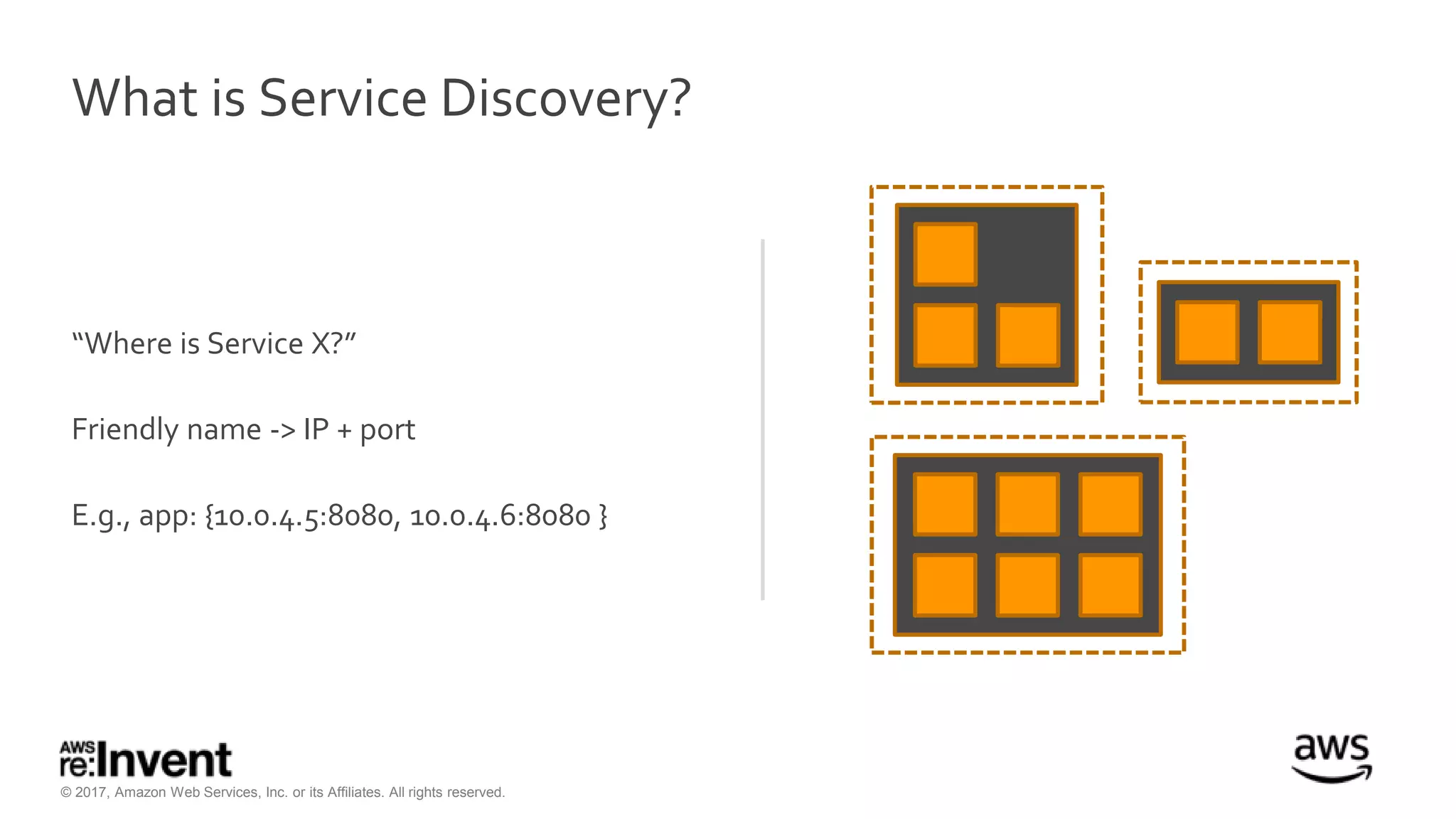
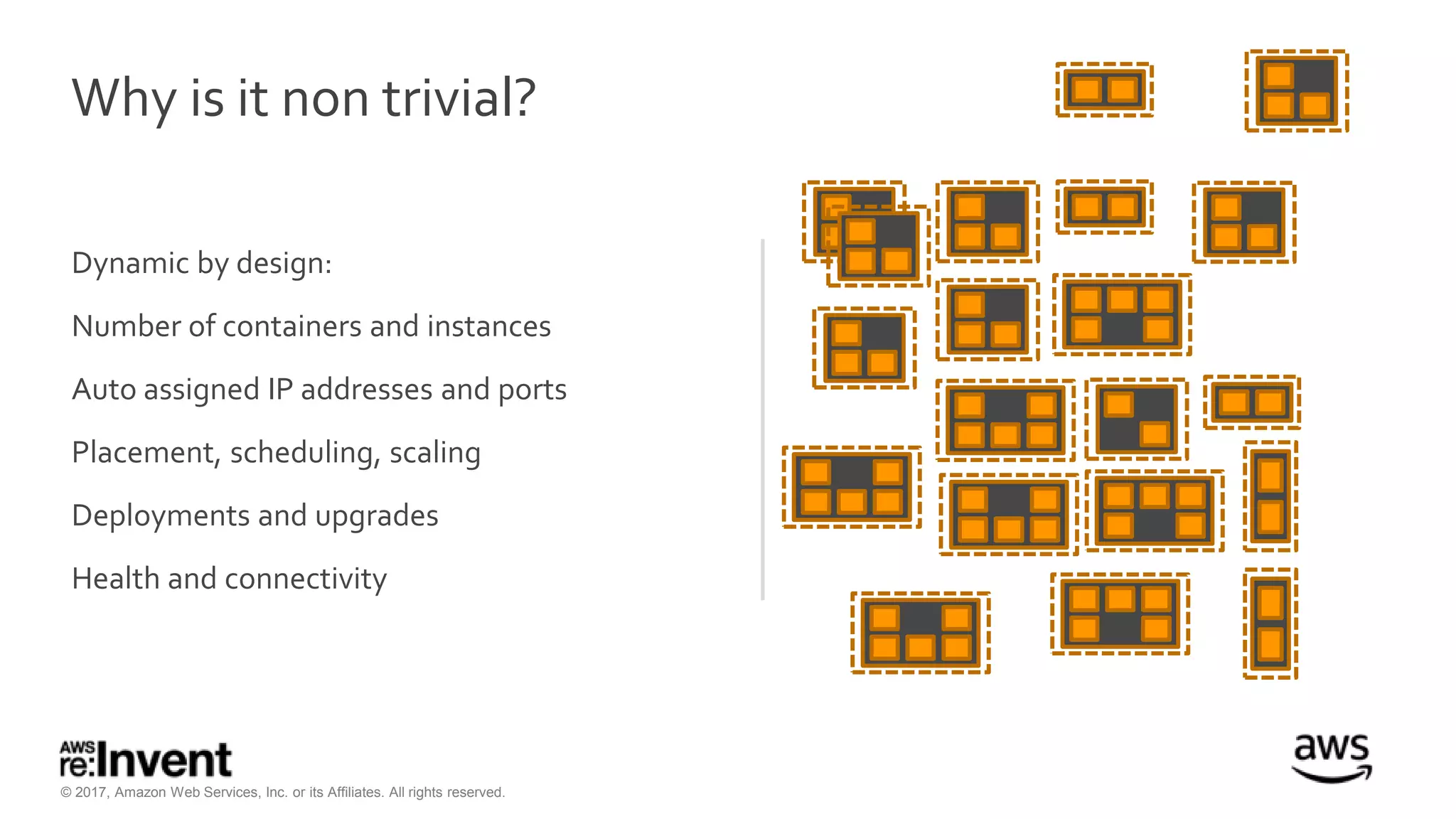
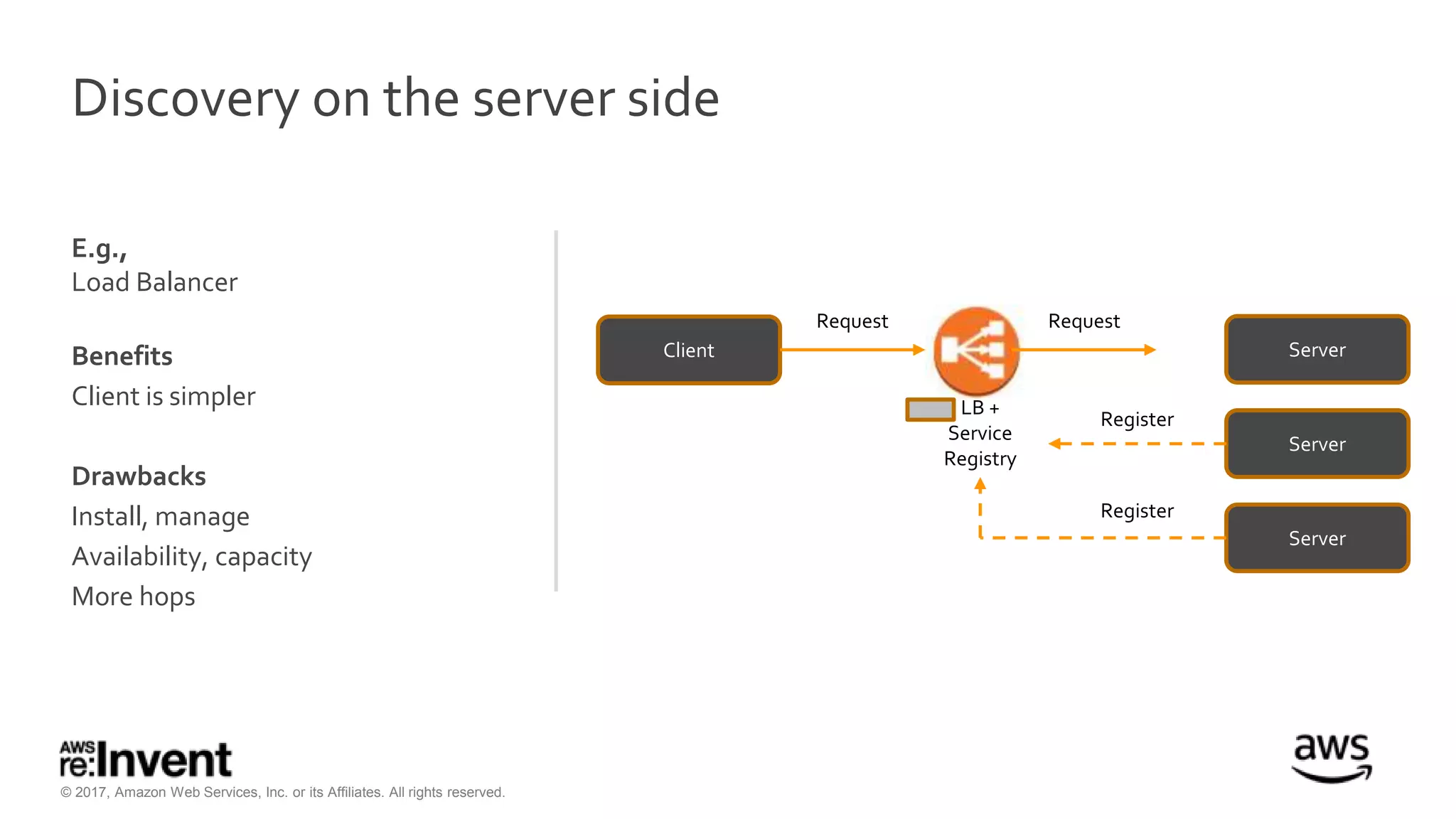
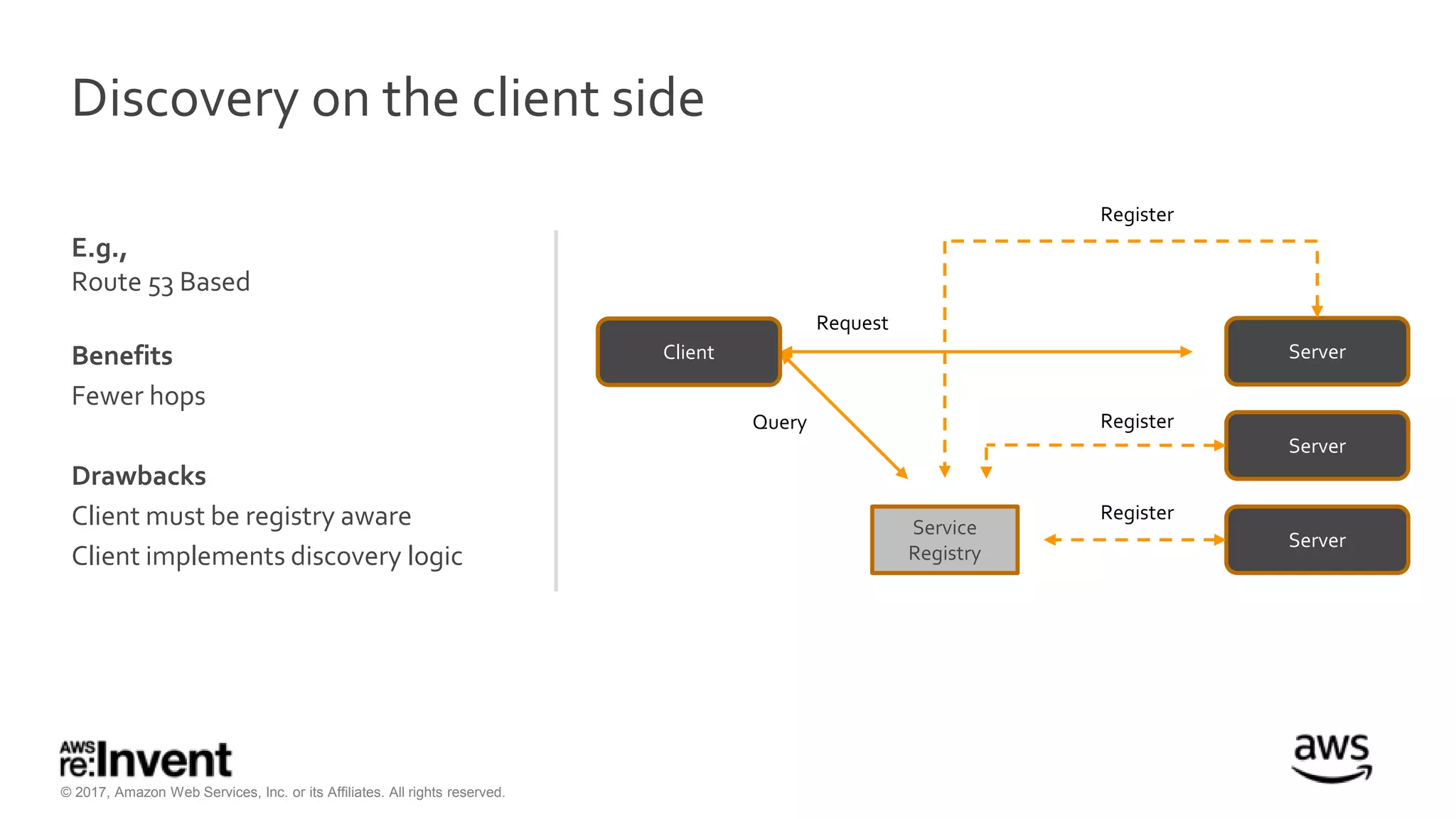
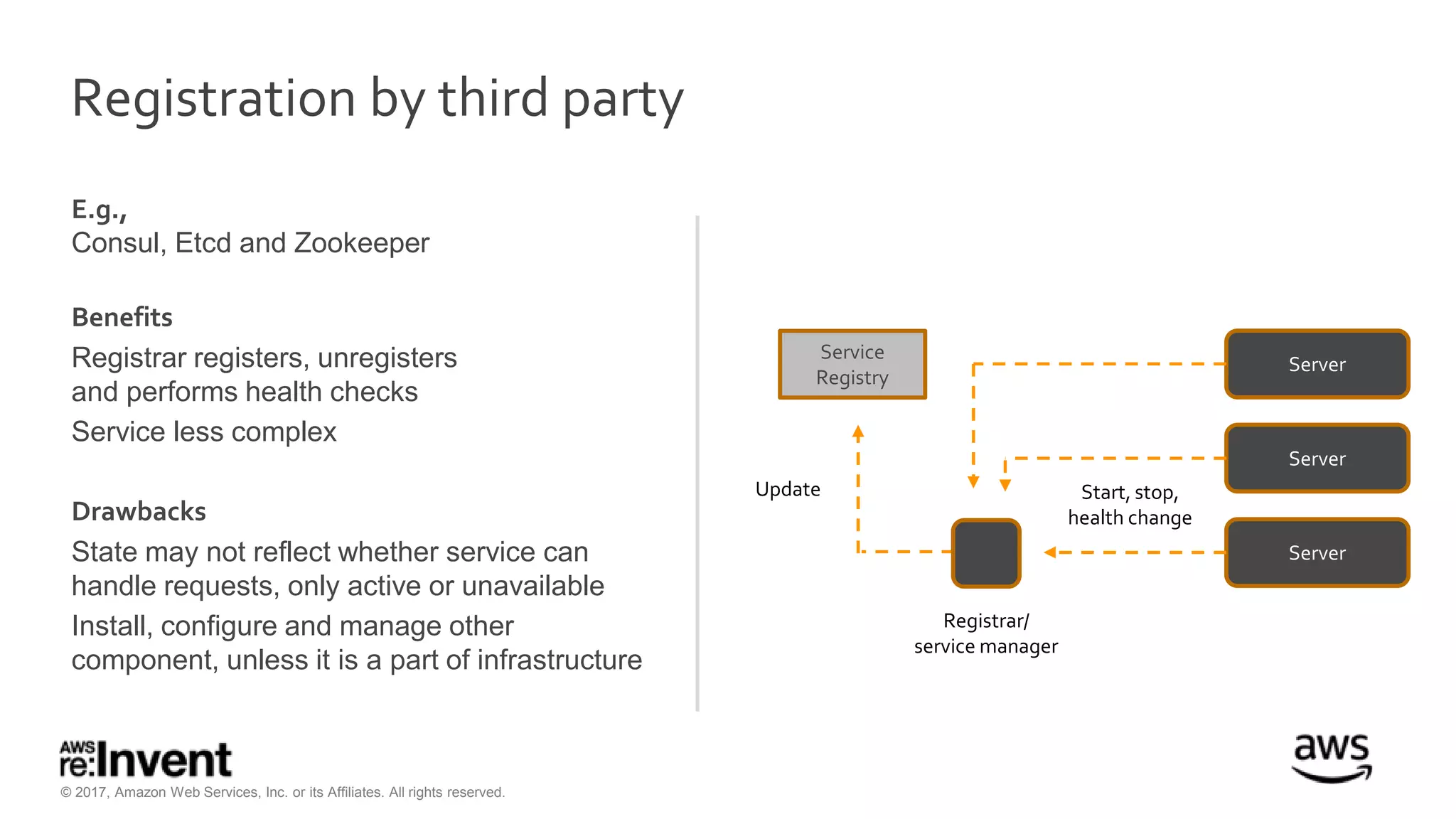
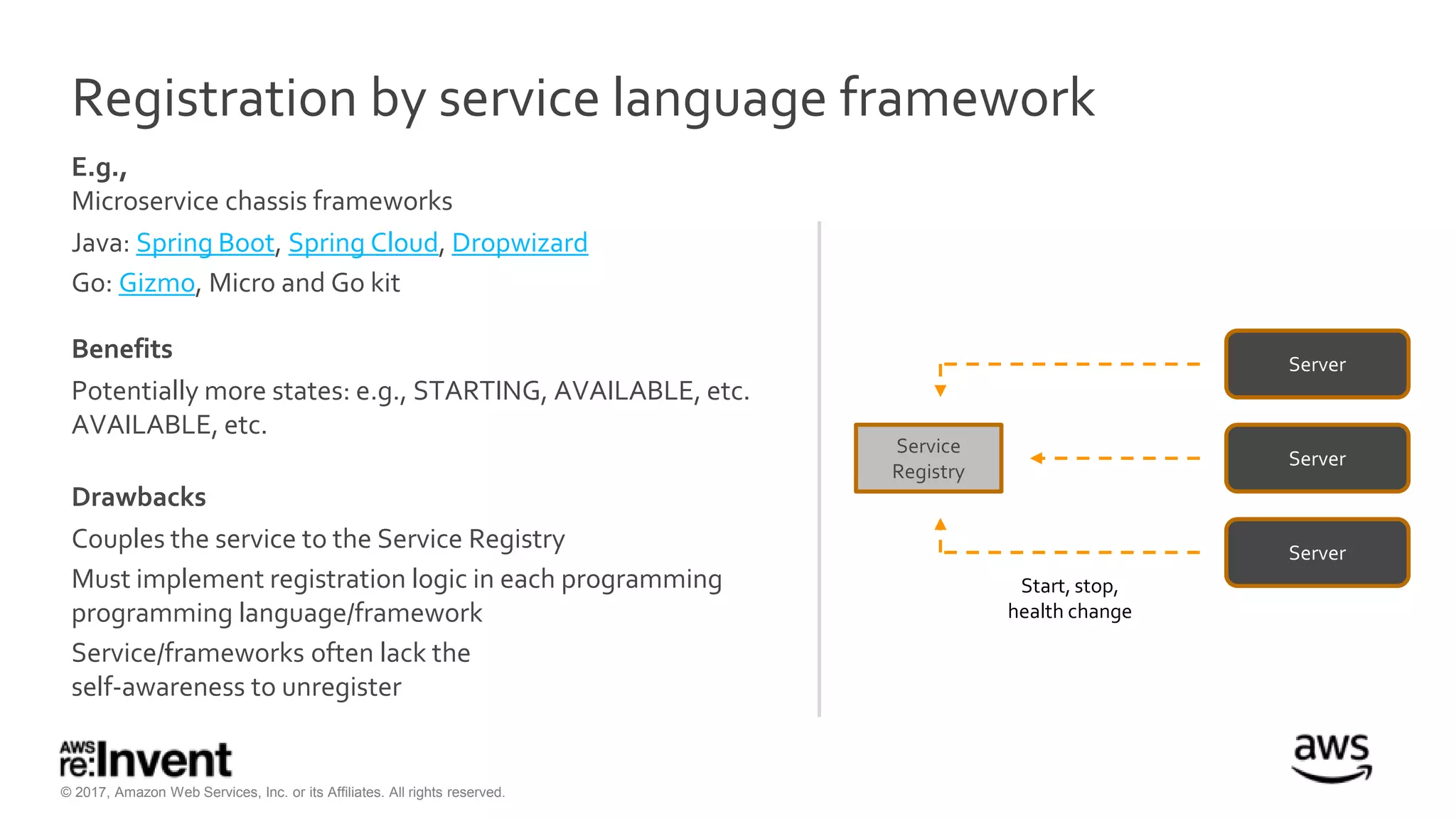
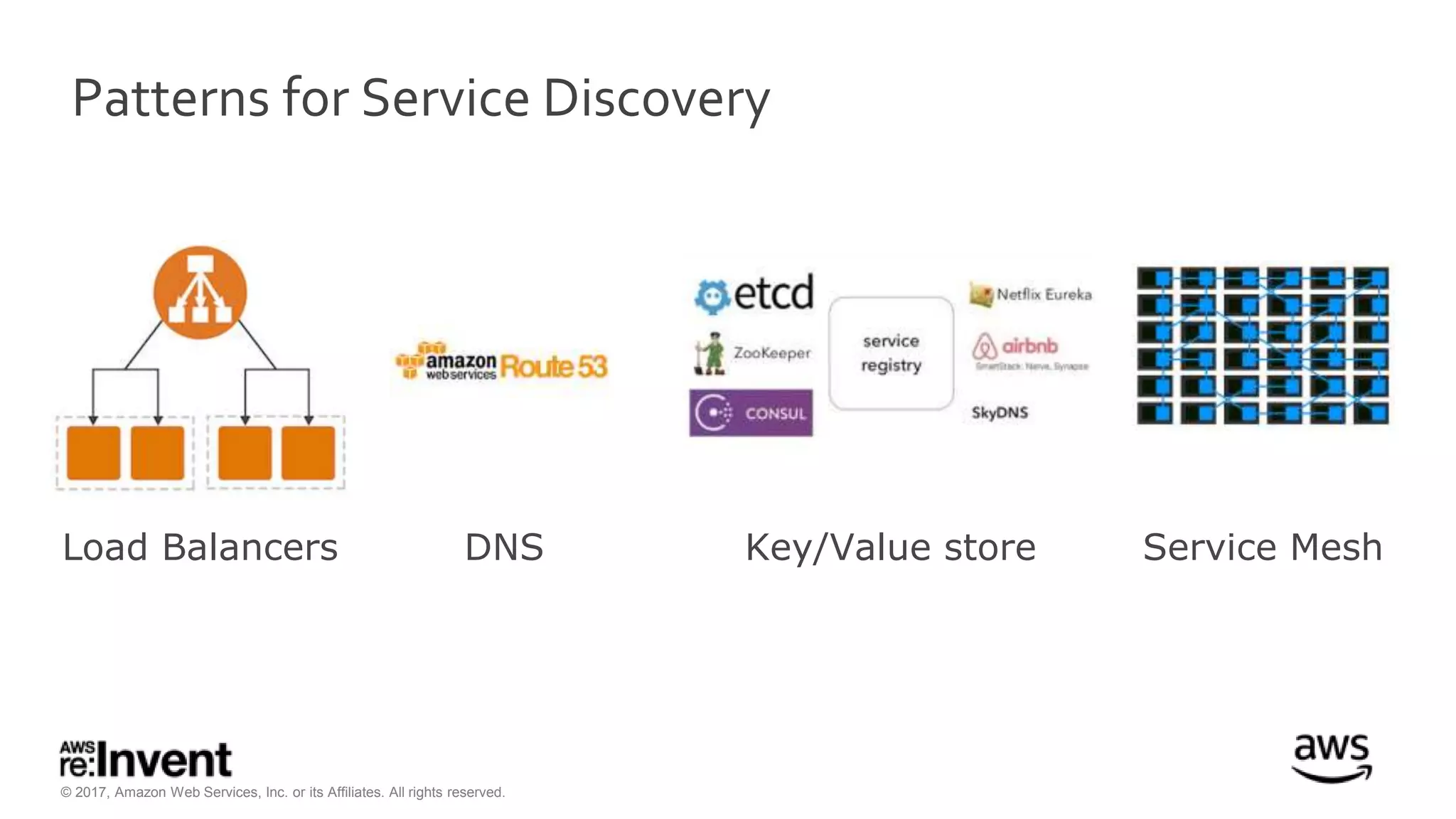
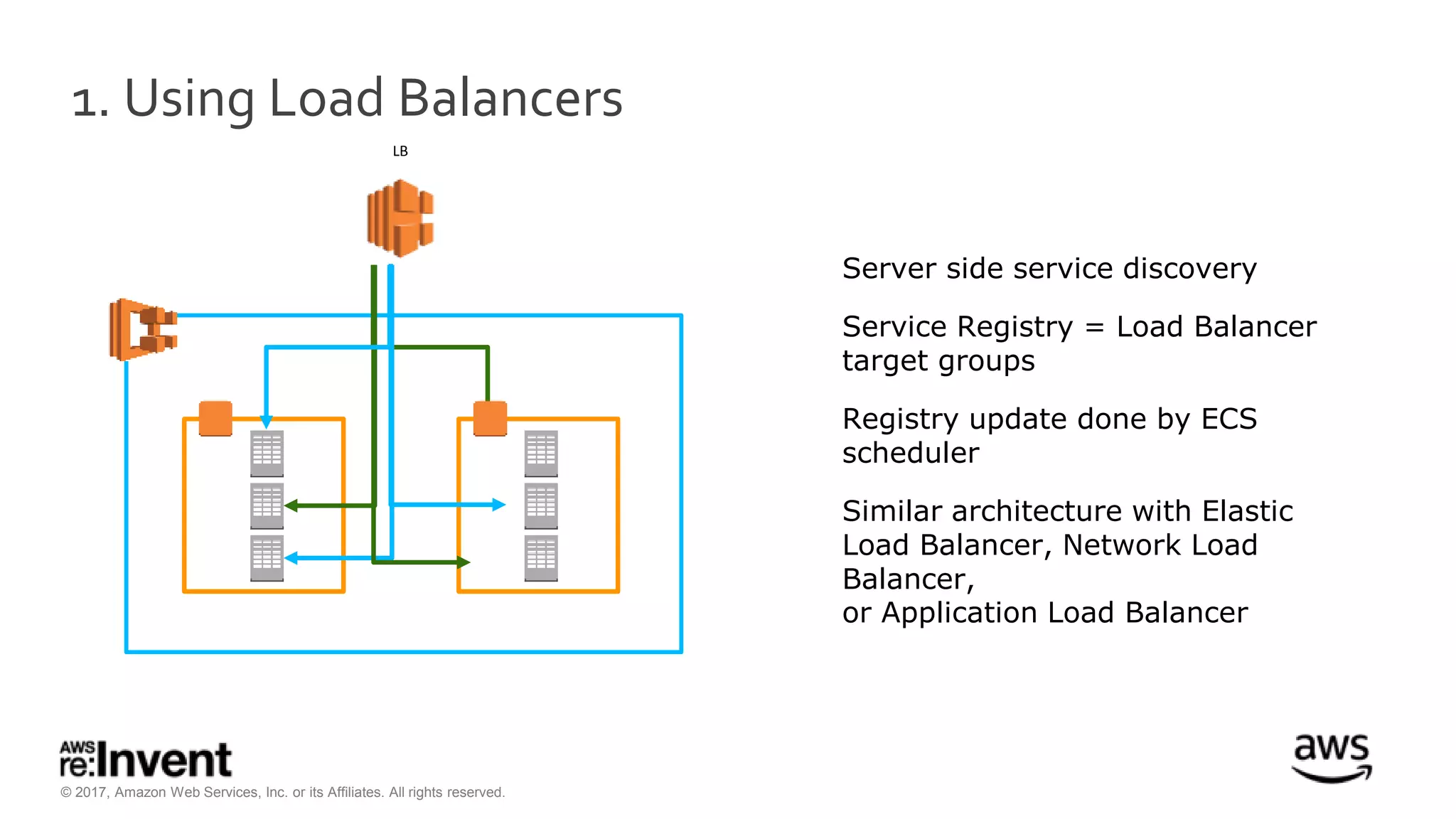
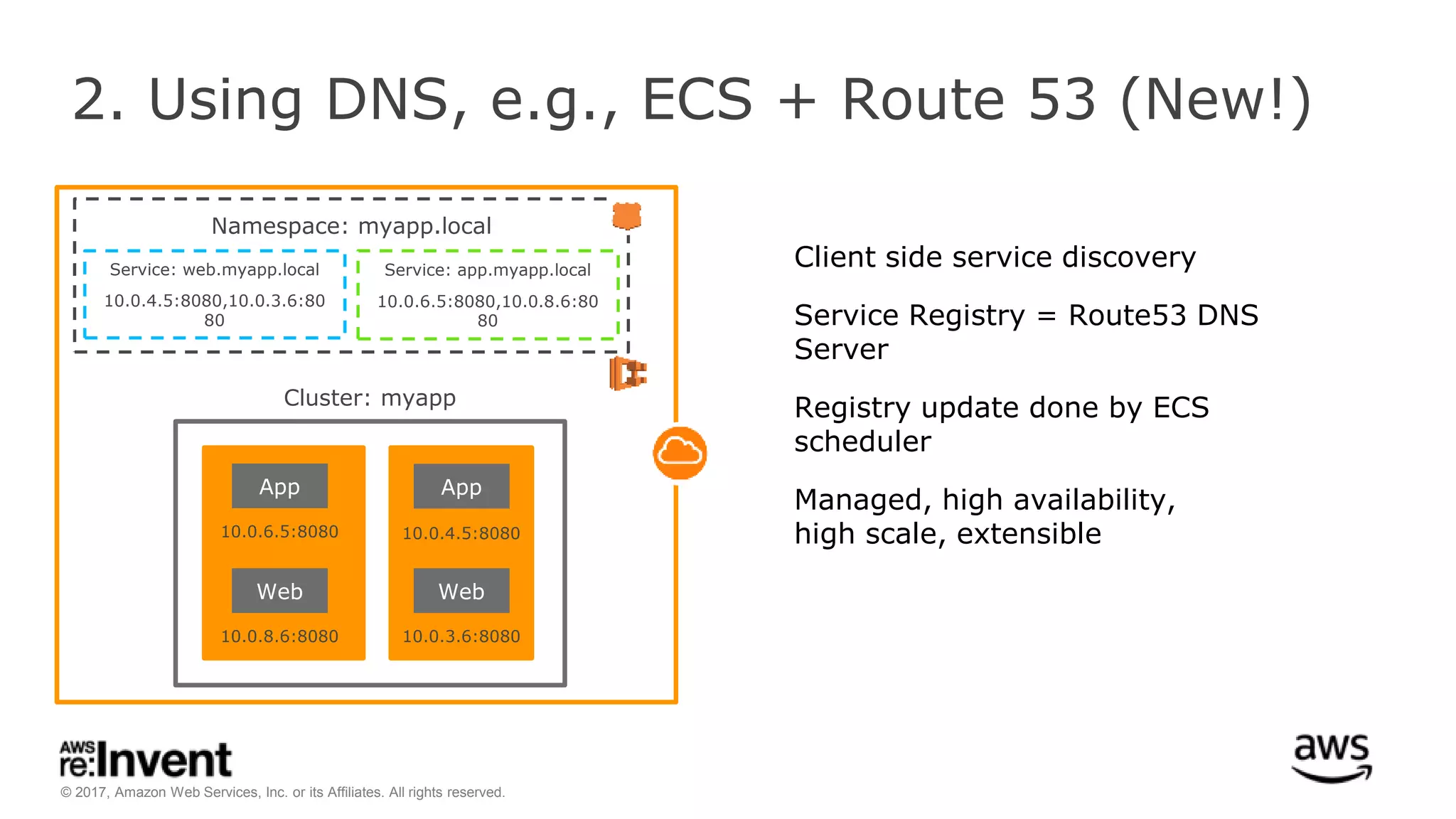
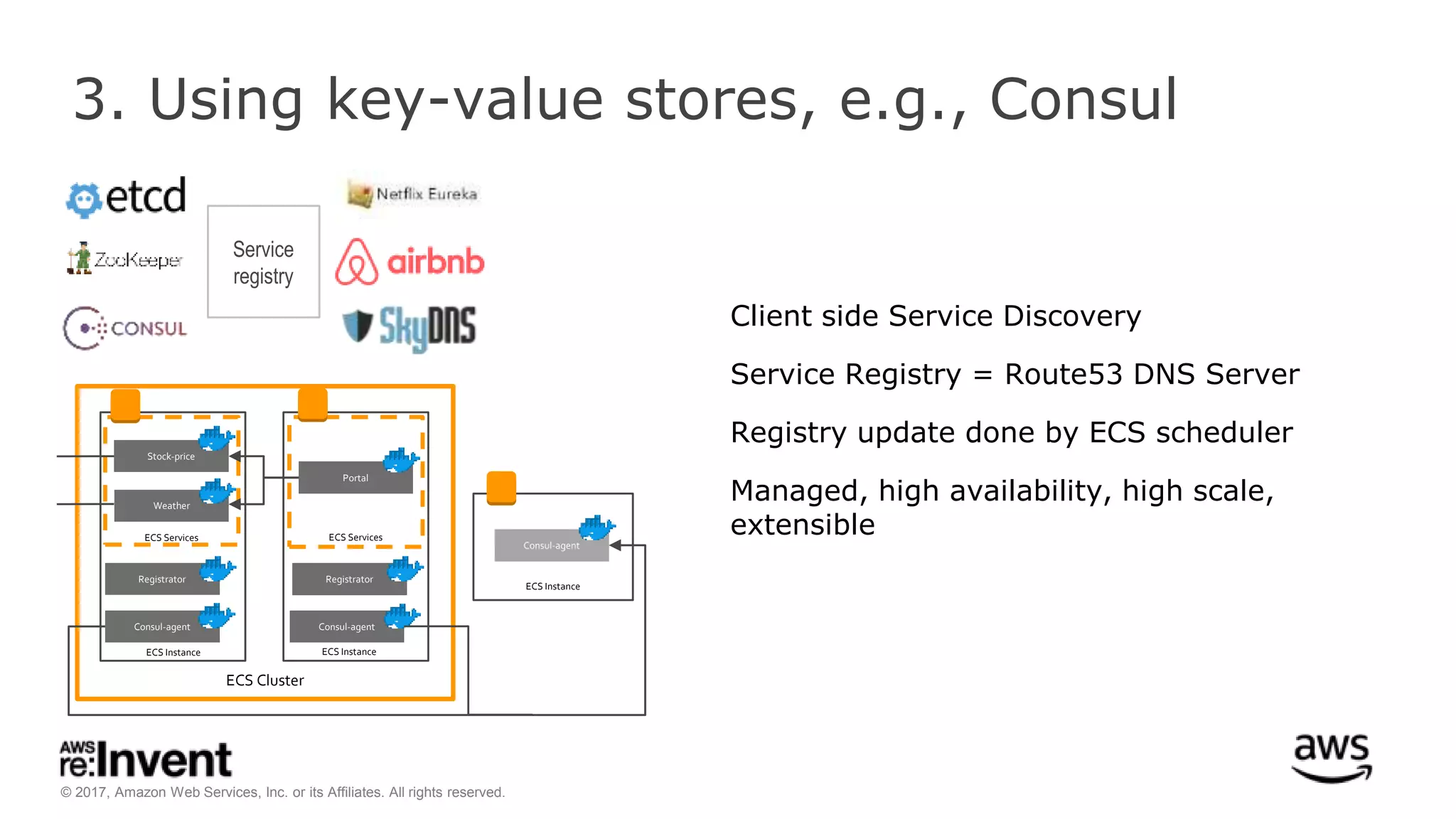
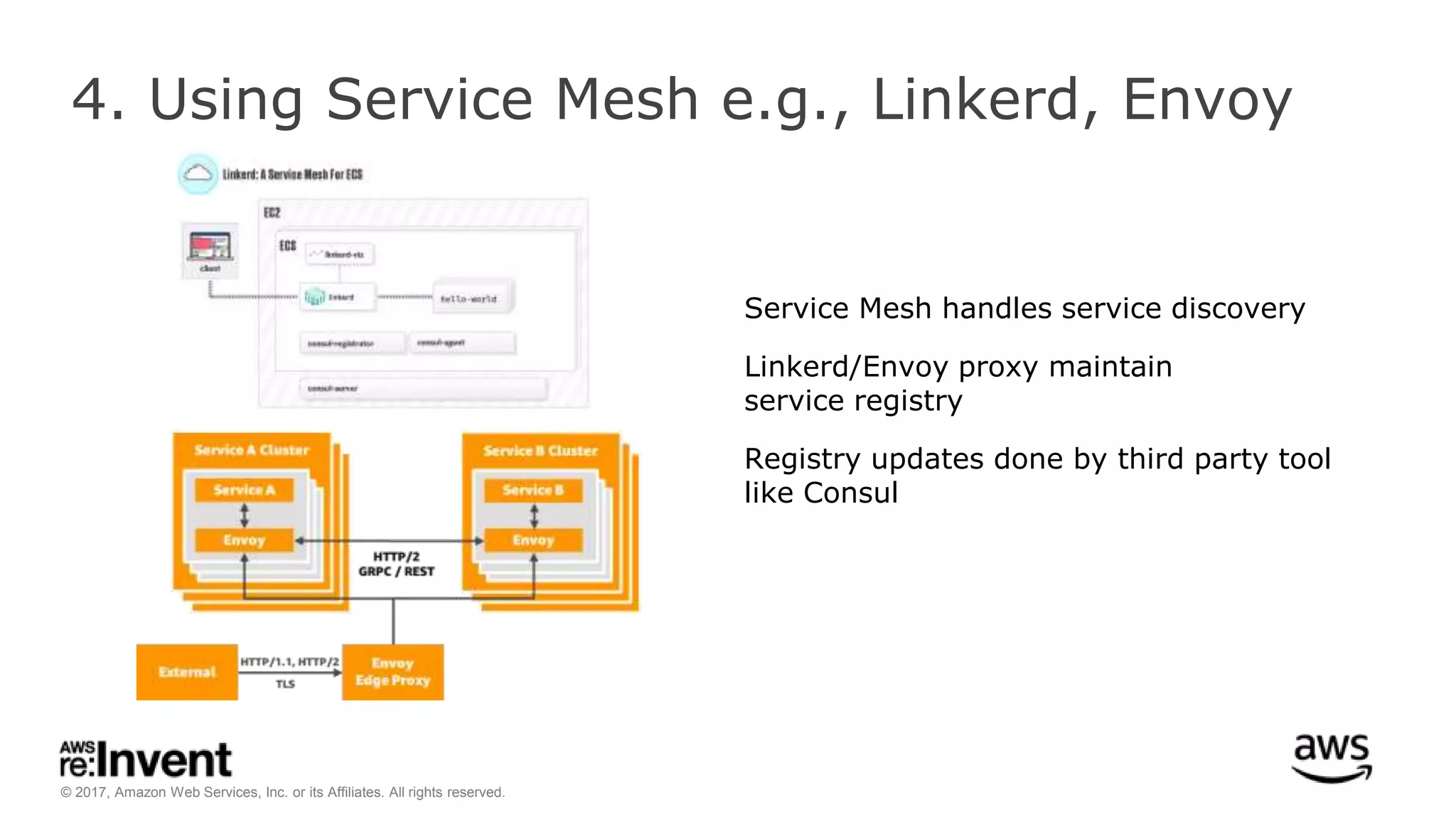
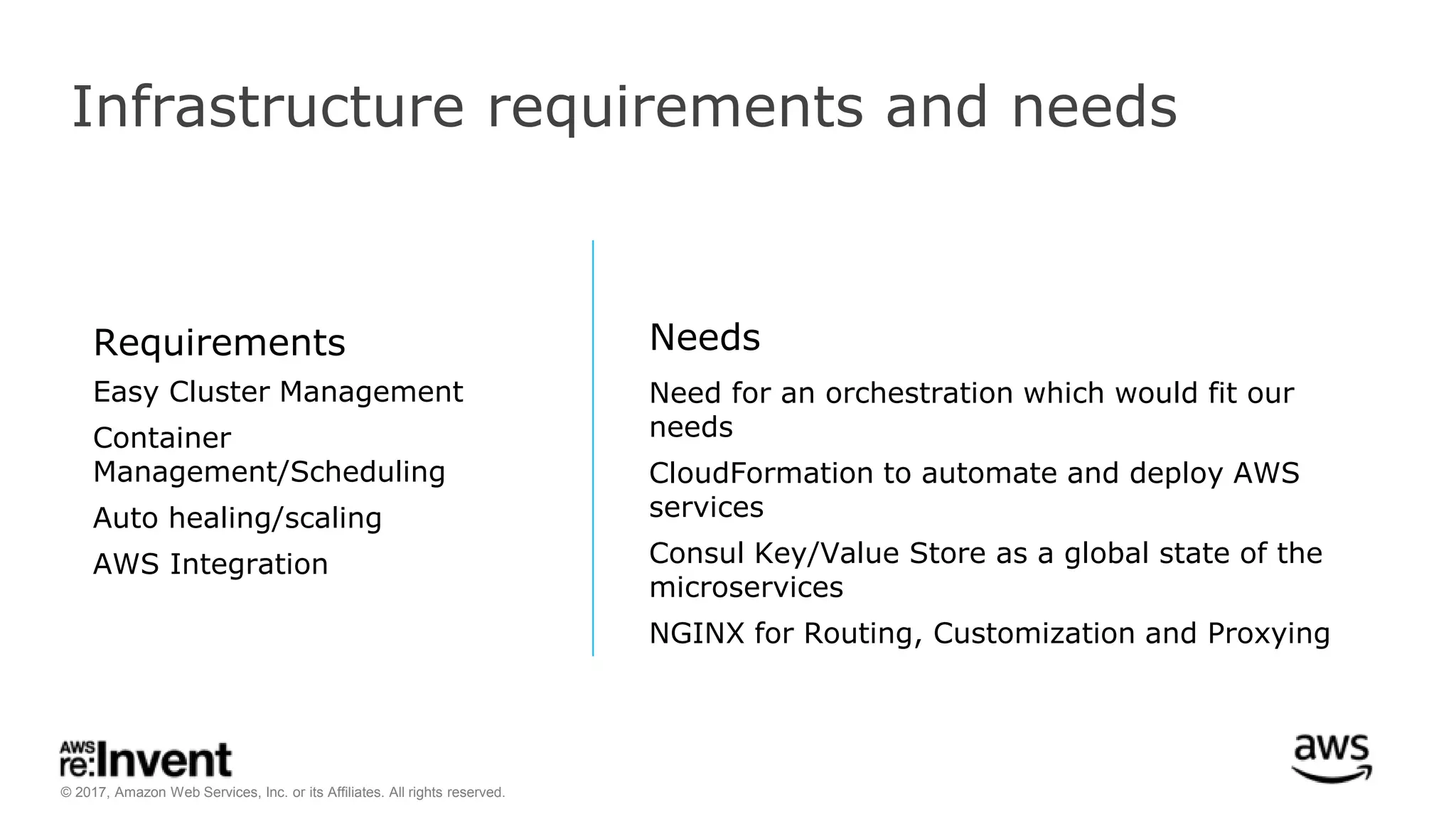
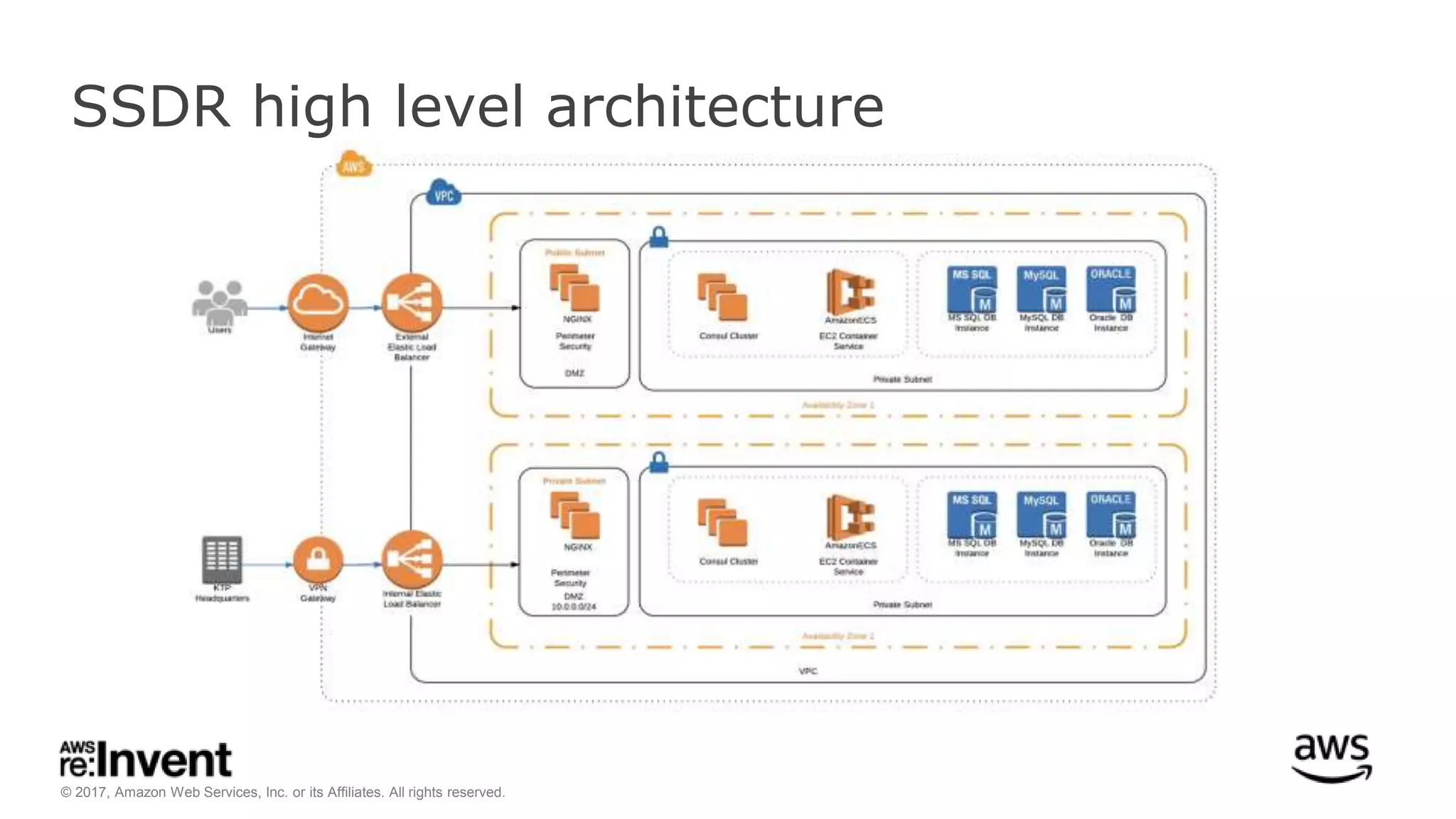
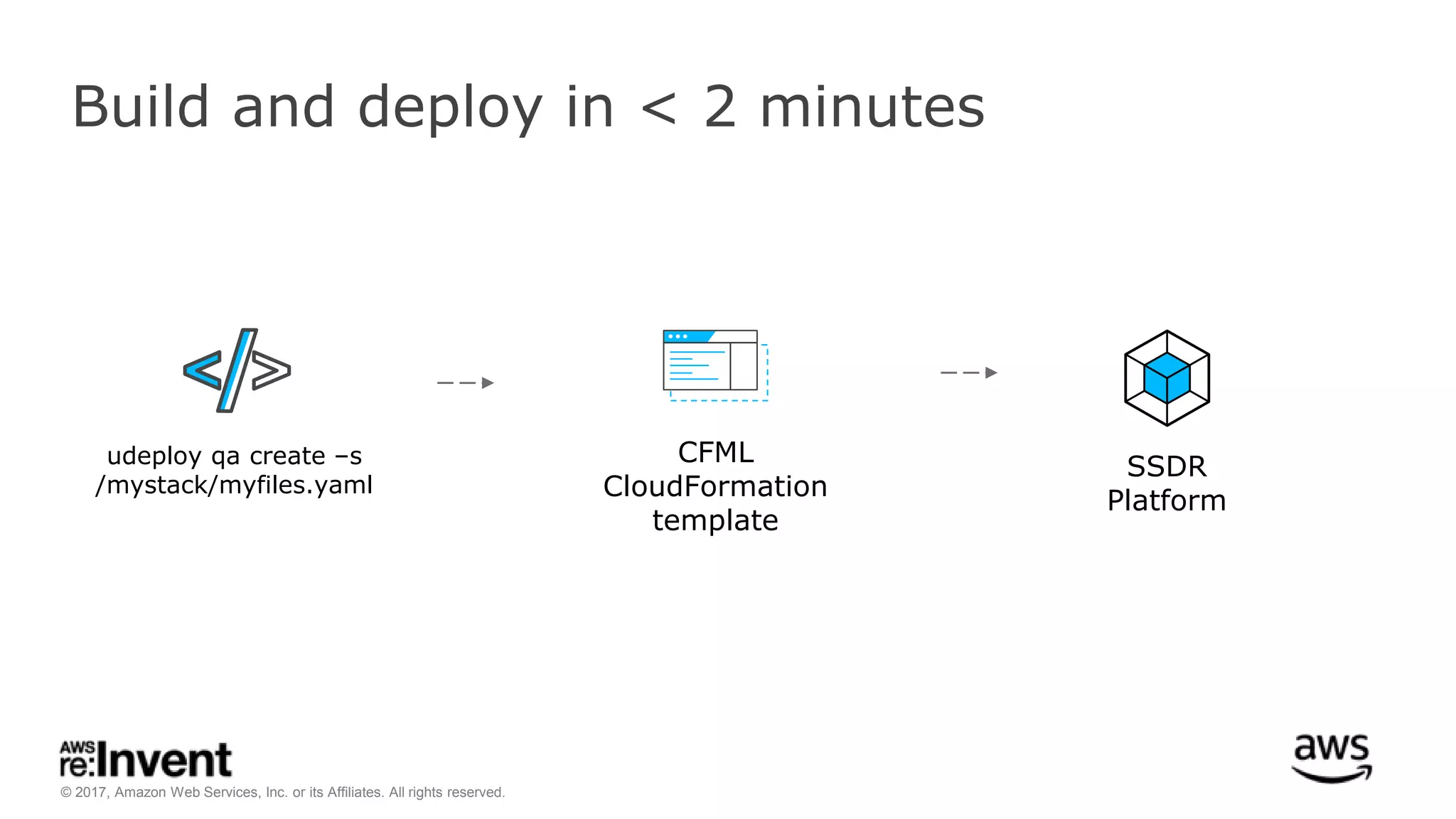
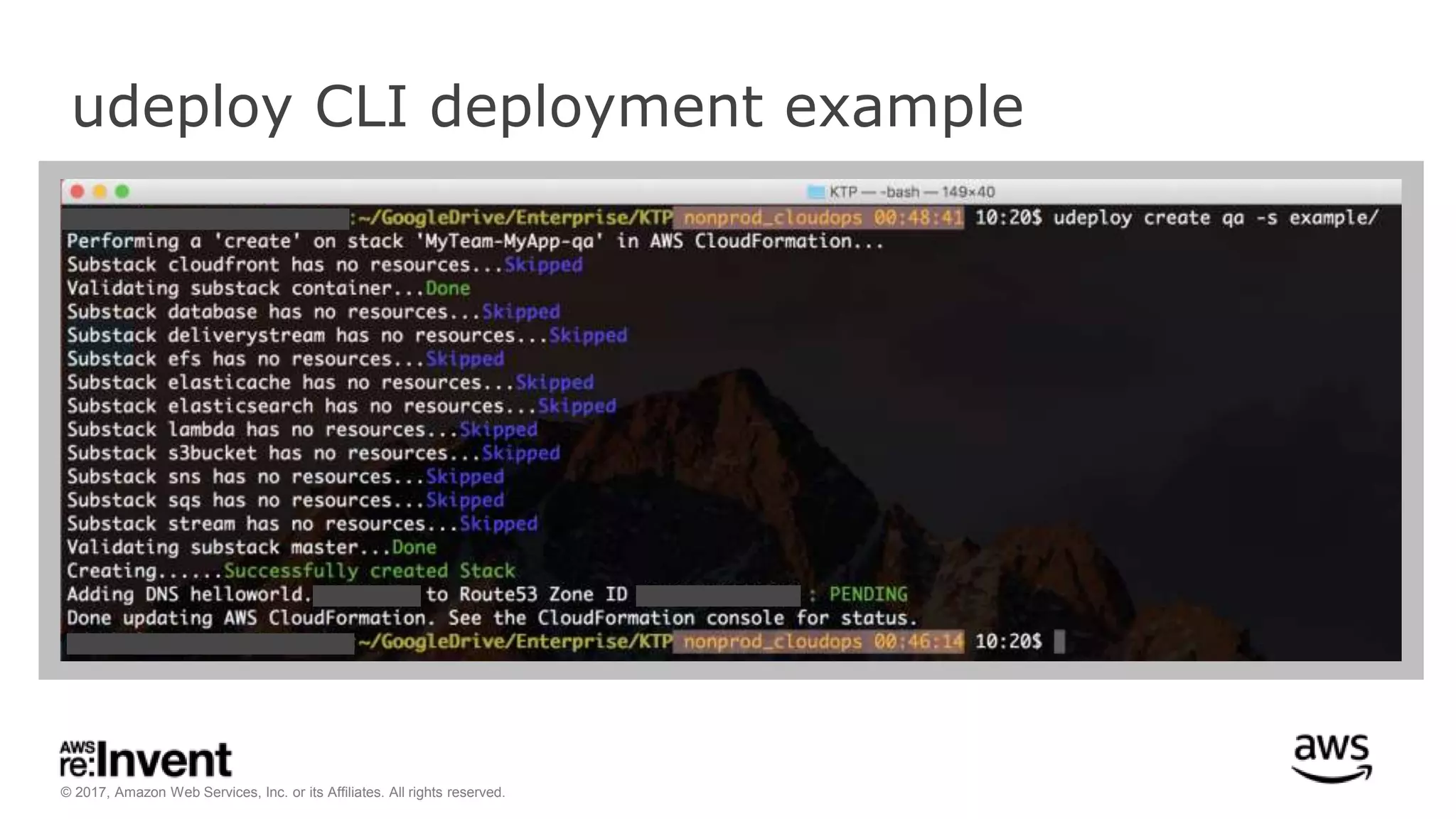
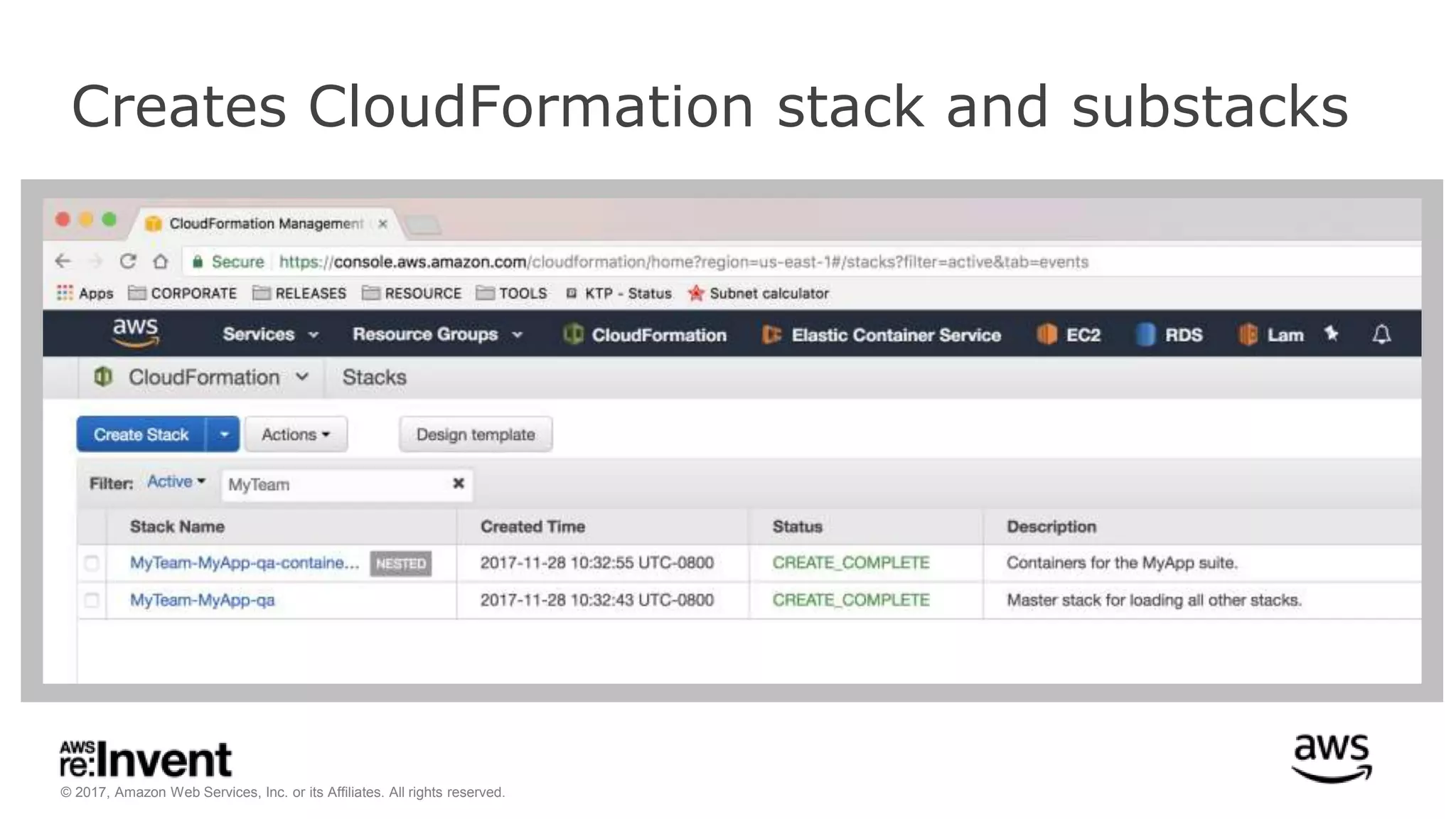
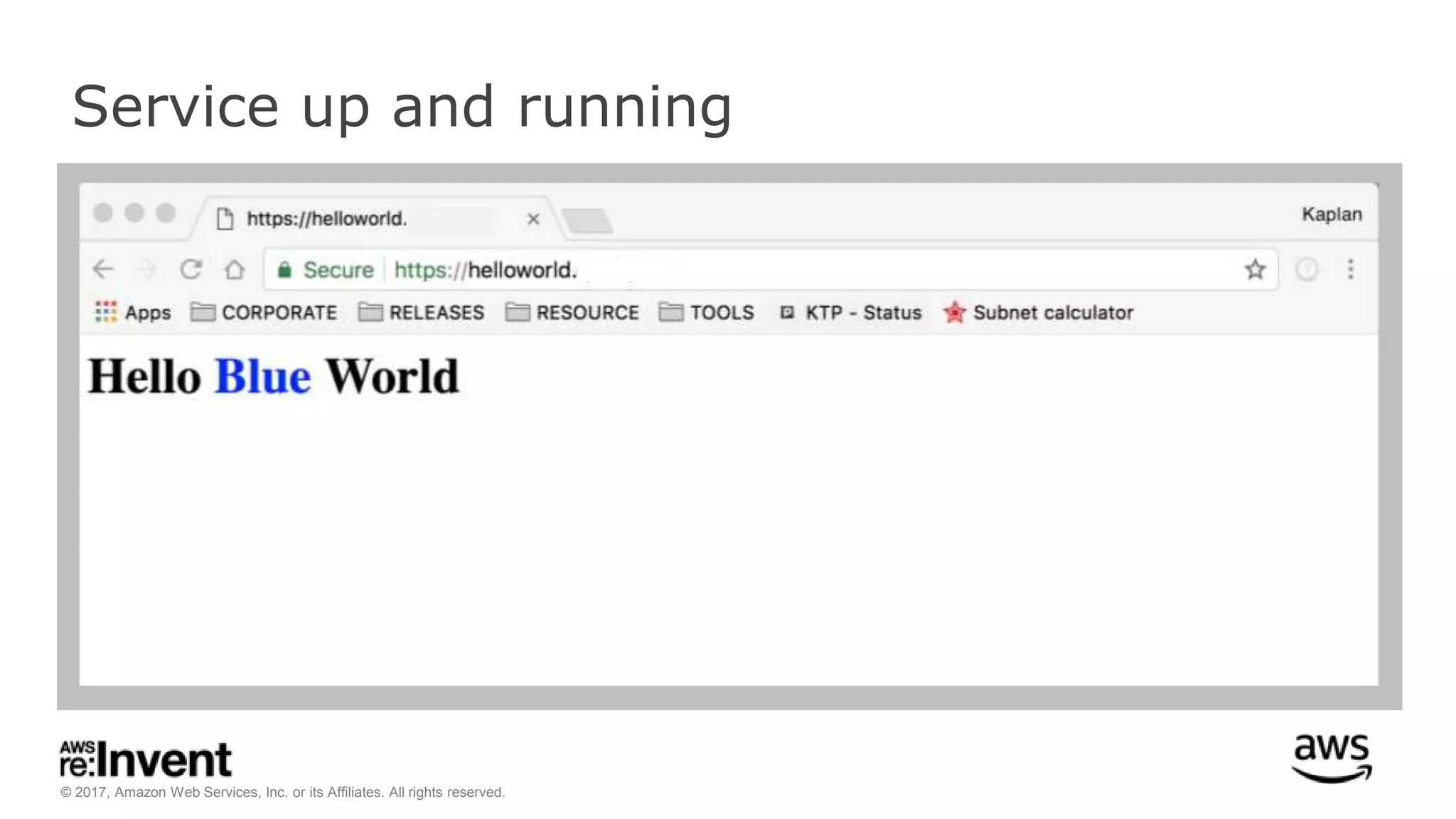
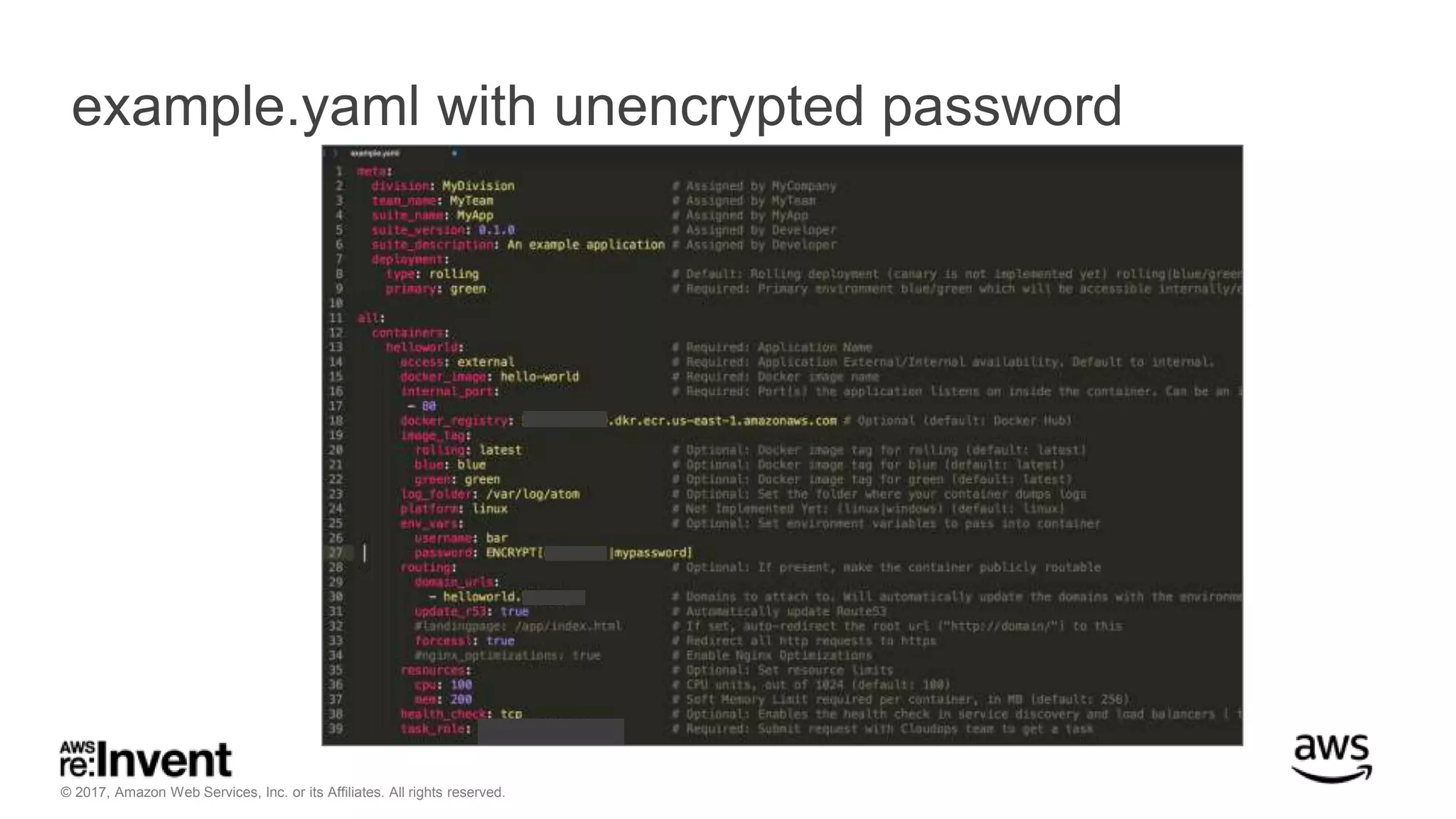
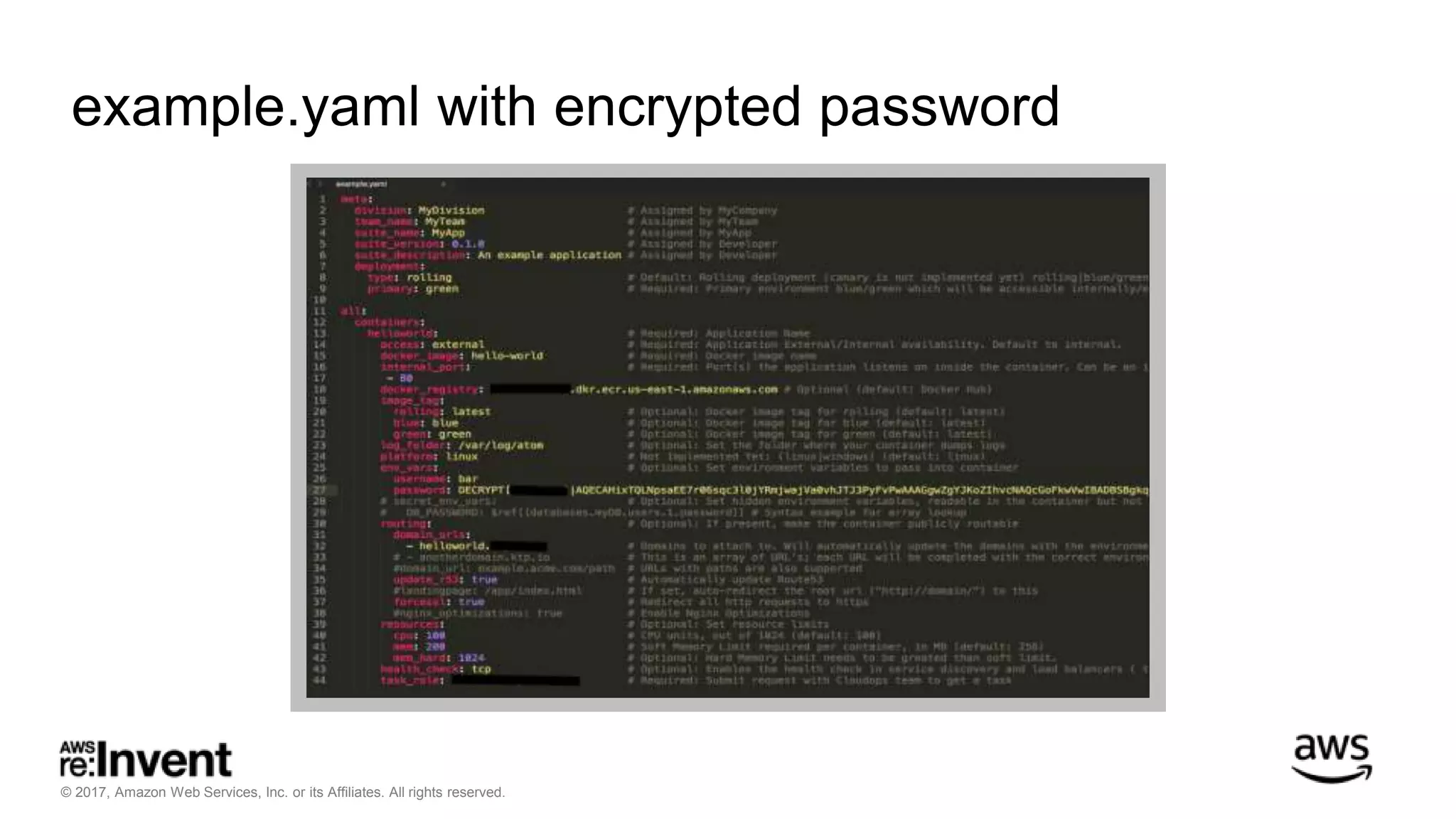
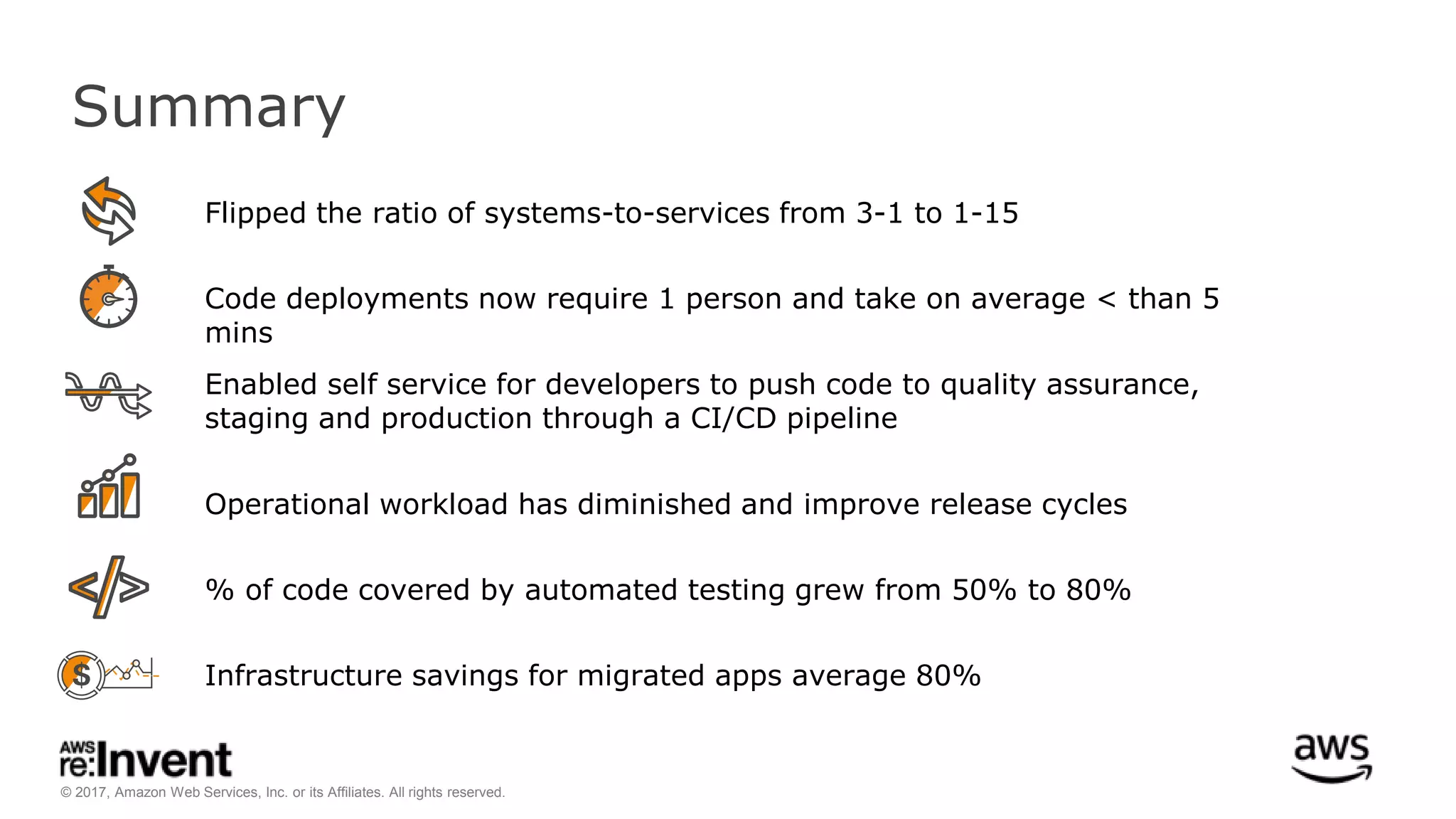
This document discusses service discovery for microservices applications. It begins by explaining that as applications evolve from monoliths to microservices, services need to be able to find and connect to each other dynamically. It then defines service discovery as mapping a service name to its location (IP and port). Several options for implementing service discovery are presented, including using load balancers, DNS, key-value stores, and service meshes. The document concludes with a case study of how Kaplan Test Prep migrated their applications to microservices on AWS and implemented service discovery using Consul and their own orchestration tool.