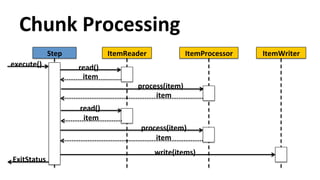
The document discusses Java EE 7 Batch Processing, focusing on the JSR-352 specification which facilitates batch applications in Java by providing features like task-oriented processing, error handling, and parallel execution. It emphasizes the importance of batch processing for efficiency and managing large datasets by using a system of jobs, steps, readers, processors, and writers. Additionally, it includes implementation details and examples, highlighting the use of resources and scheduling for batch jobs.






![The
JSR-‐352
• Batch
ApplicaHons
for
the
Java
pla]orm
• Heavily
inspired
by
Spring
Batch
• Available
since
Java
EE
7
• Also
designed
for
Java
SE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/con2818-javaee7batchprocessingintherealworld-141001120216-phpapp02/85/Java-EE-7-Batch-processing-in-the-Real-World-9-320.jpg)

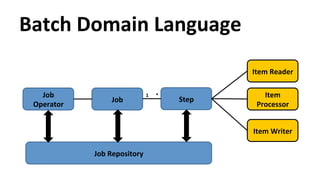














![ParYYon
DefiniYon
(In
Step)
<chunk
item-‐count="3">
<reader
ref="myItemReader">
<properYes>
<property
name="start”
value="#{parYYonPlan['start']}"
/>
</properYes>
</reader>
<processor
ref="myItemProcessor"/>
<writer
ref="myItemWriter"/>
</chunk>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/con2818-javaee7batchprocessingintherealworld-141001120216-phpapp02/85/Java-EE-7-Batch-processing-in-the-Real-World-28-320.jpg)






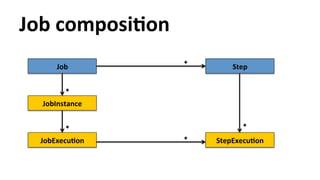
![Decision
@Named
public
class
MyDecider
implements
Decider
{
public
String
decide(StepExecuYon[]
execuYons)
throws
ExcepYon
{…}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/con2818-javaee7batchprocessingintherealworld-141001120216-phpapp02/85/Java-EE-7-Batch-processing-in-the-Real-World-35-320.jpg)











