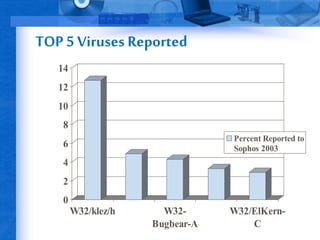
Computer viruses have become widespread due to increased internet usage. A virus is a malicious computer program that can spread itself to other files and computers without permission. While some viruses only cause minor issues, others can severely damage systems by deleting files or rendering computers unusable. Viruses are typically spread by opening infected files from the internet or removable media. It is important to use antivirus software, avoid untrusted sources, and not open potentially risky file types in order to prevent virus infections.