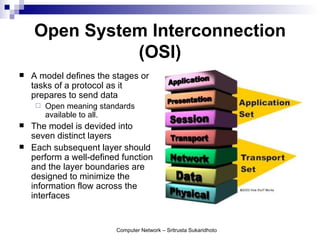
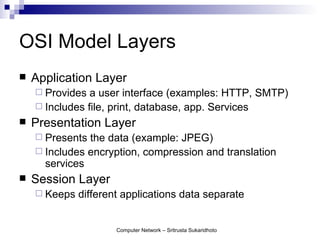
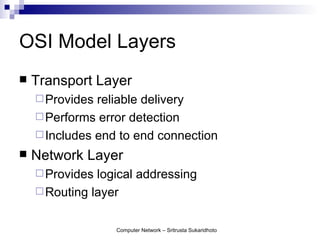
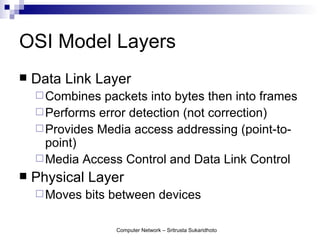
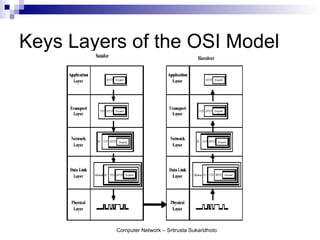
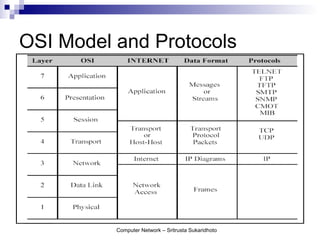
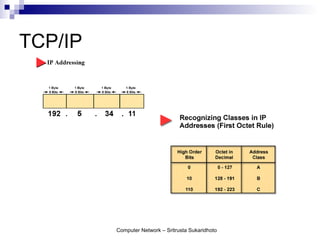
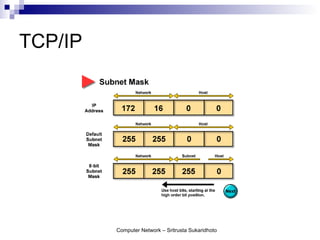
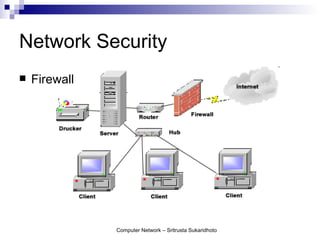
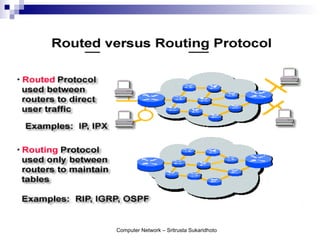
The document discusses computer networks and their benefits. It covers topics like the OSI model layers, network devices, TCP/IP, network security, programming, and certification. It also provides information about network administration advantages and disadvantages. The document is intended to provide an overview of computer network concepts and topics for study.