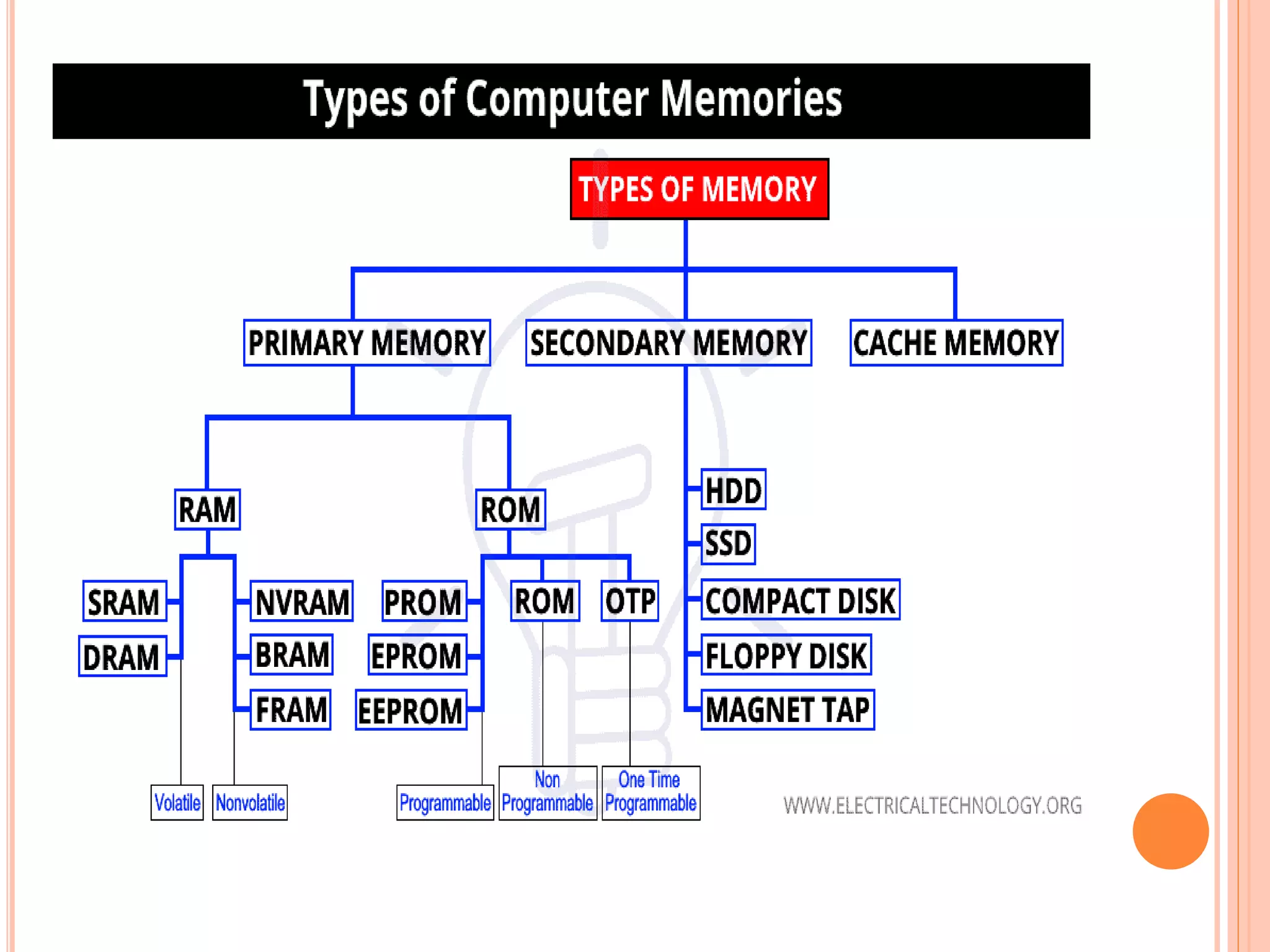
This document provides summaries of key computer science concepts in multiple paragraphs. It discusses discs/diskettes which are magnetic storage devices that can read and write information. It describes computer memory and its three forms: cache, main memory, and secondary storage. It defines the processor (CPU) as the main integrated circuit responsible for arithmetic, logic, and input/output functions. The operating system acts as a bridge between the user and hardware, providing an efficient environment to run applications. Storage devices allow users to safely store and access data and programs. Character representation standards like ASCII are discussed, along with number systems such as binary, octal, and hexadecimal. Binary arithmetic and how to convert between number systems is briefly covered.