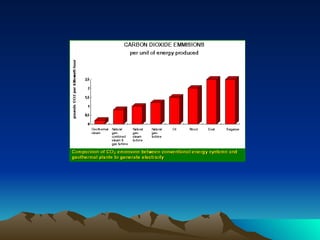
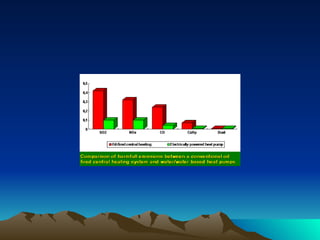
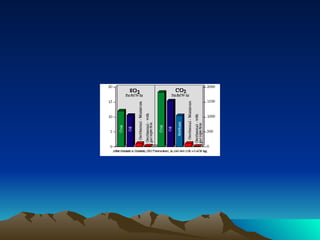
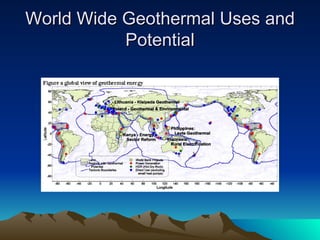
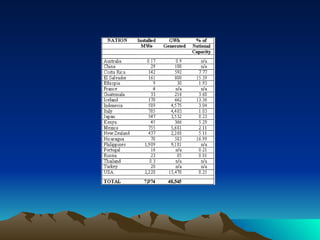
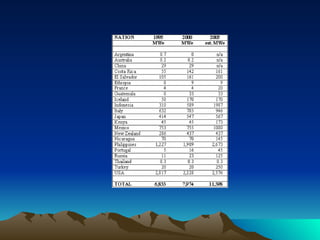
The document discusses different sources and types of geothermal energy. It describes how heat from the Earth's core can be harnessed through various technologies to provide direct heating and electricity. Geothermal energy comes from radioactive decay, residual heat from the Earth's formation, and meteorite impacts deep underground. Technologies like hot water reservoirs, natural steam reservoirs, and hot dry rock systems can extract this heat for applications ranging from home heating to electricity generation. The document also outlines both the environmental benefits and potential harms of geothermal energy development and production.