This project report presents a physicochemical analysis of groundwater quality in selected urban areas of Bangalore, assessing various parameters through GIS and remote sensing techniques. The study, conducted by civil engineering students at HKBK College of Engineering, involved sampling water from 12 locations and analyzing aspects such as pH, alkalinity, and lead content. The findings aim to evaluate the suitability of groundwater for drinking and highlight the importance of monitoring water quality amidst urbanization and pollution.



![IV
ABSTRACT
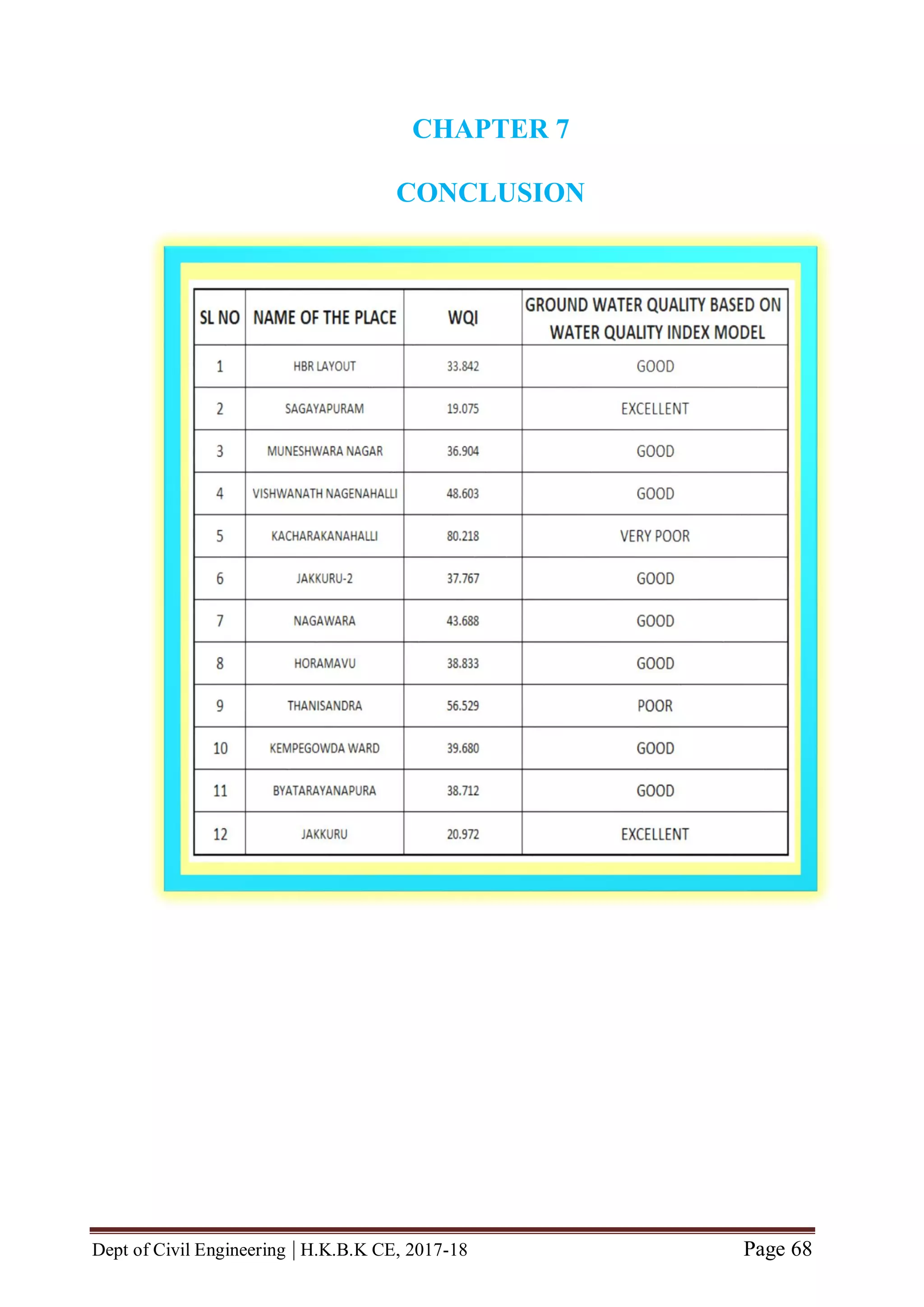
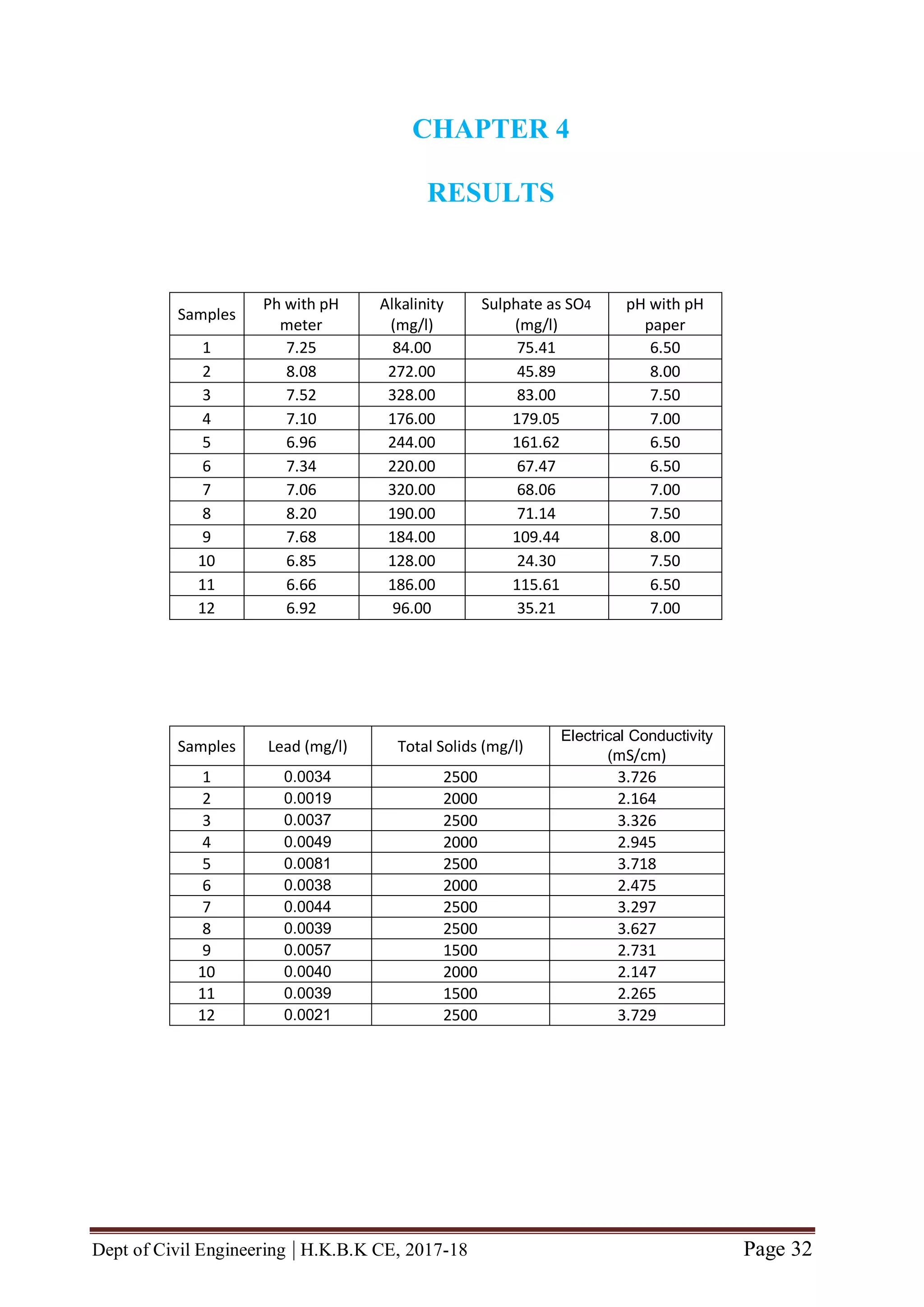
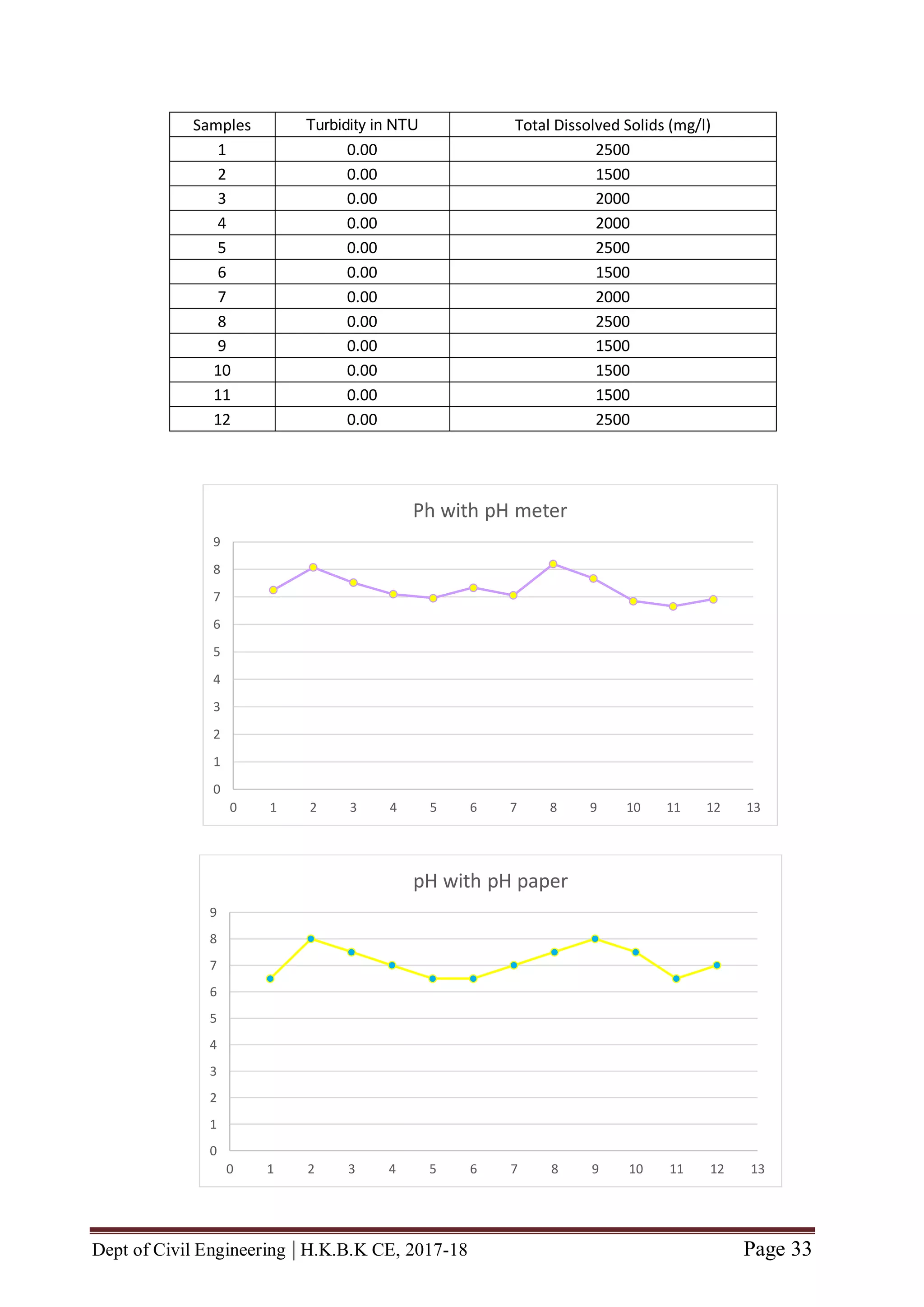
In this project, the physicochemical analysis of various physico-chemical parameters is
carried out for assessment of ground water quality. Total of 12 samples were collected
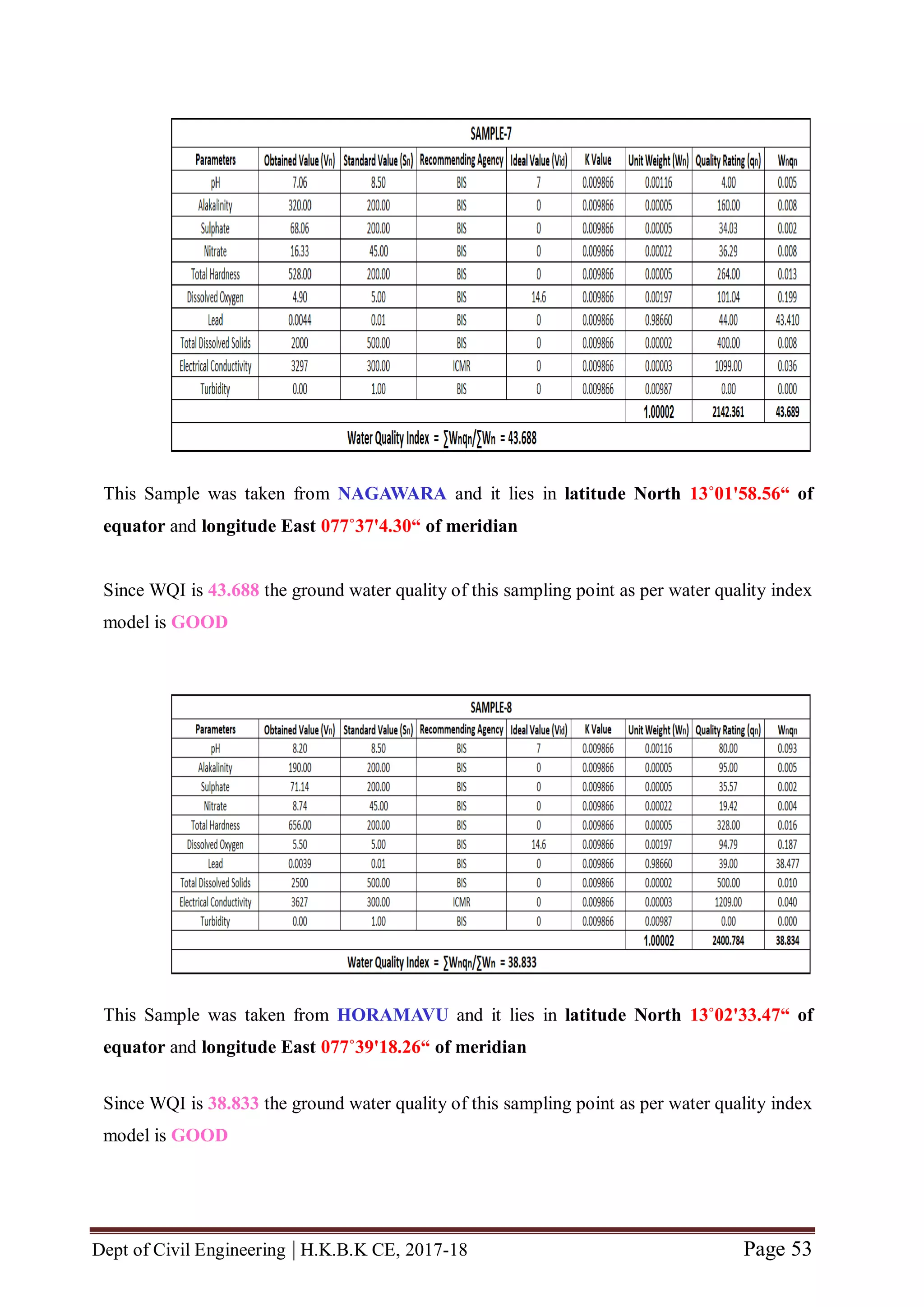
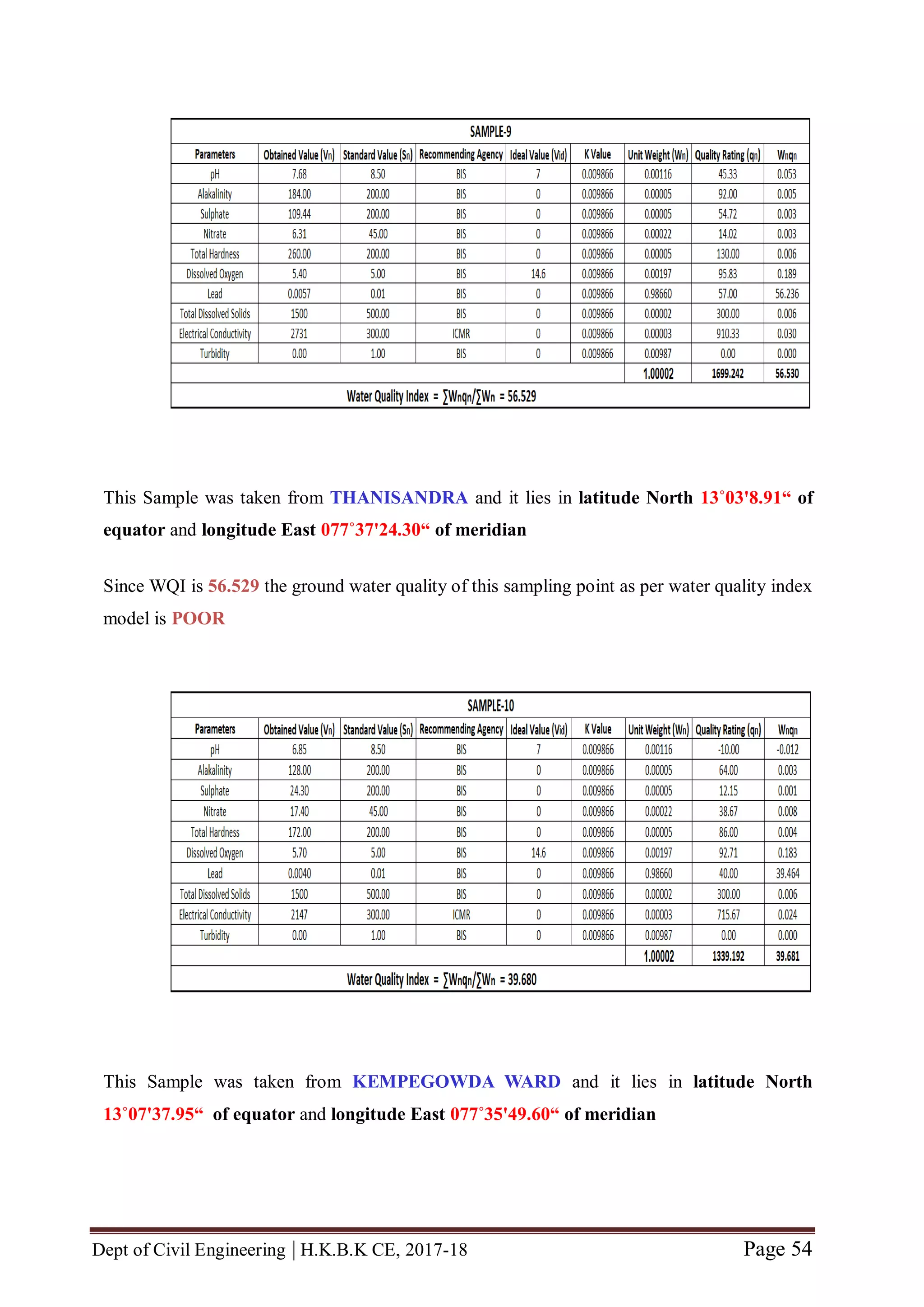
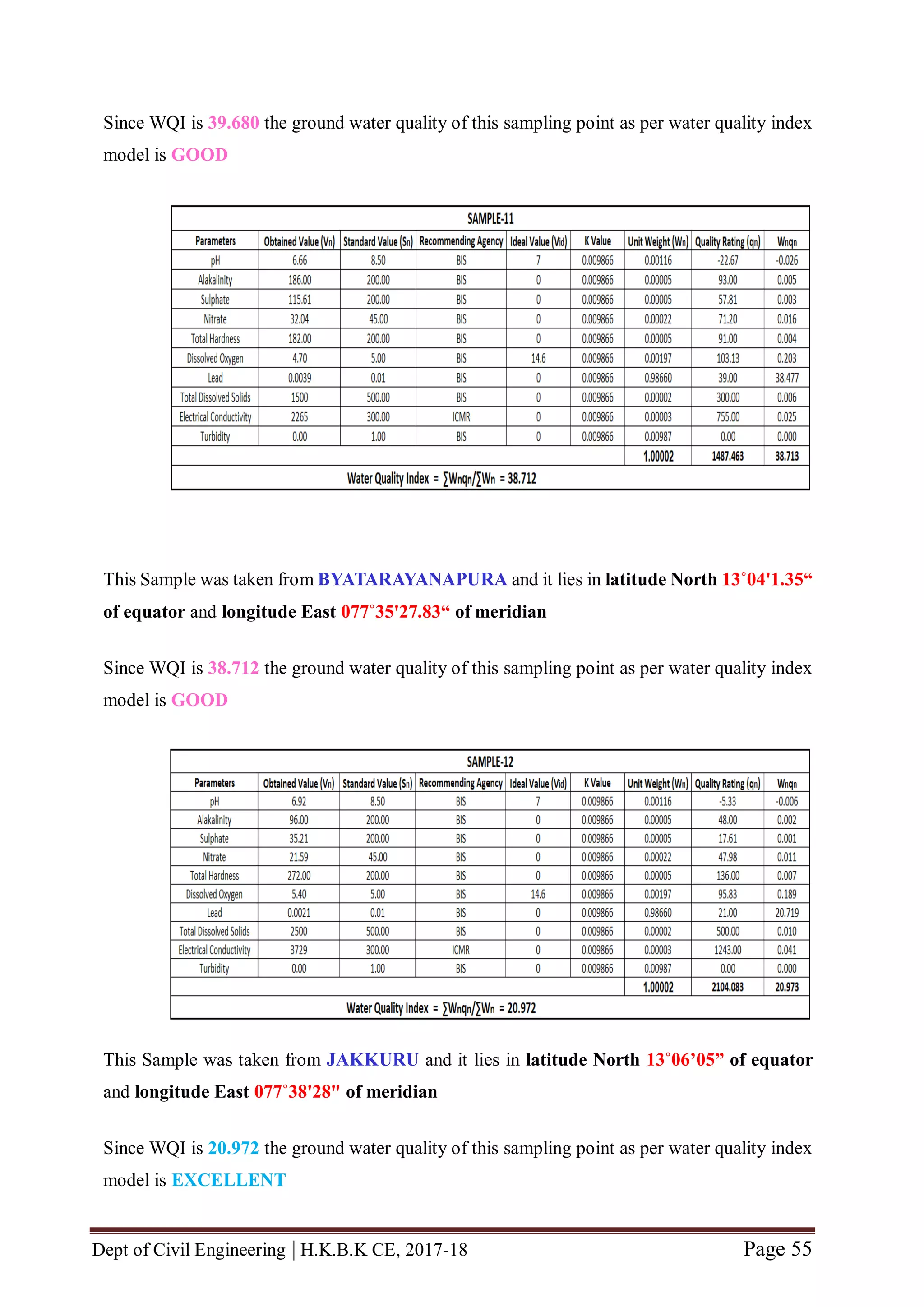
from 12 locations of bangalore urban area viz., HBR Layout, Sagayapuram,
Muneshwara Nagar, Vishwanath Nagenahalli, Kacharakanahalli, Jakkuru-2,
Nagawara, Horamavu, Thanisandra, Kempegowda Ward, Byatarayanapura and
Jakkuru. These 12 water samples were collected from sampling points whose
connection was given to bore wells. Various physico-chemical parameters tested were
pH, alkalinity, sulphate, nitrate, total hardness, dissolved oxygen, lead content, total
solids, total dissolved solids, suspended solids, electrical conductivity, turbidity. For
geo-referencing of study area, Toposheet No D43R12 (57G/12) OF BANGALORE
URBAN – [between latitude (North of Equator) N 13˚0’ to 13˚15’ and between
longitude (East of Meridian) E 077˚30’ to 077˚45’] was used. The quality of
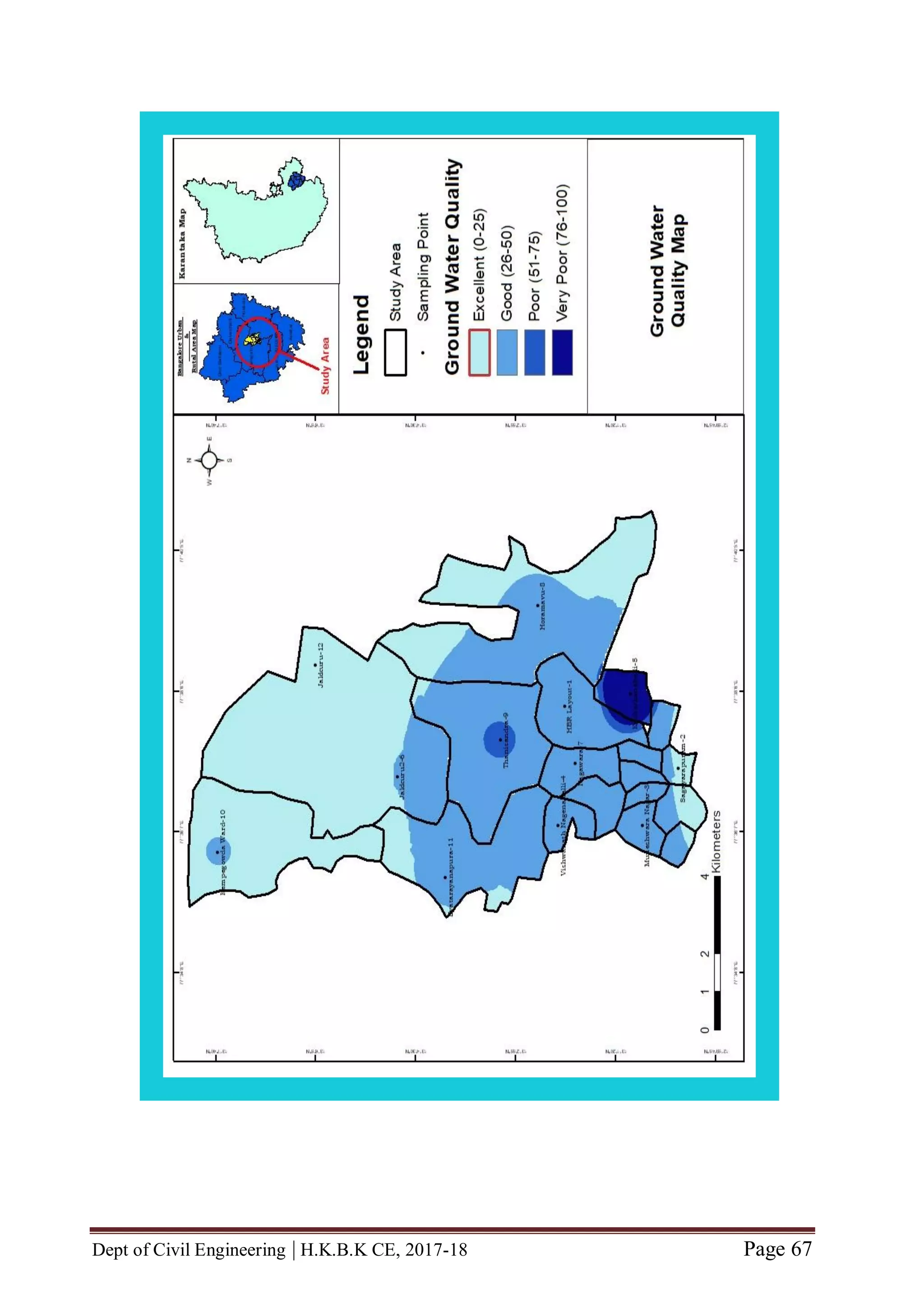
groundwater is assessed in the study area based on water quality index model. The
softwares such as Google Earth Pro and ArcGIS 10.5 were used for the generation of
Study Area Map, spatial variation maps of various physico-chemical parameters and
ground water quality map.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/completefinalyearprojectbecivil-180618071340/75/Complete-final-year-project-BE-CIVIL-4-2048.jpg)






















![Dept of Civil Engineering | H.K.B.K CE, 2017-18 Page 24
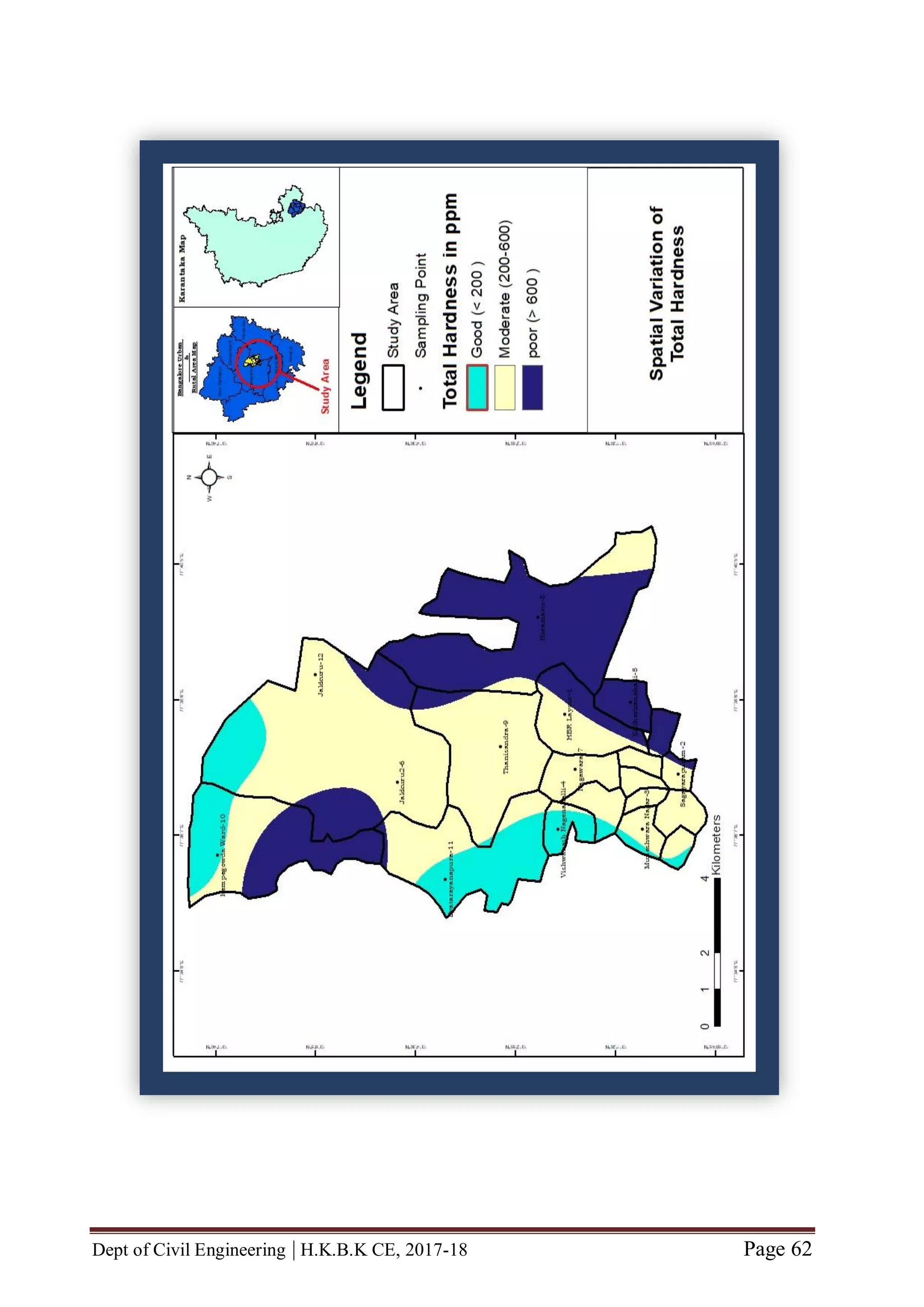
If no concern is given to protect water from hardness it causes formation of scales on
boilers, it makes food tasteless
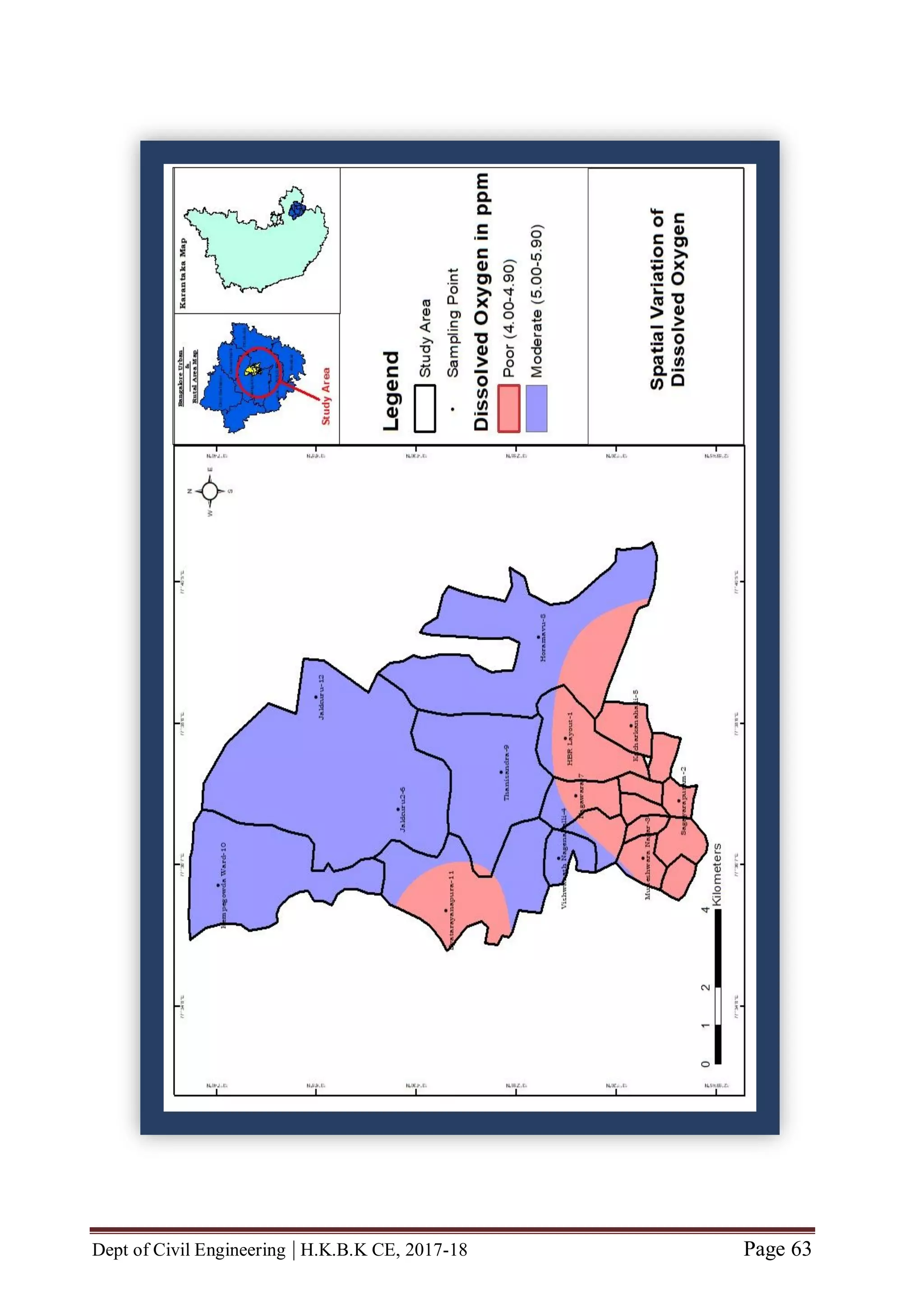
3.6 DISSOLVED OXYGEN
Theory: Dissolved Oxygen is the amount of gaseous oxygen (O2) dissolved in the
water. Oxygen enters the water by direct absorption from the atmosphere, by rapid
movement, or as a waste product of plant photosynthesis.
Water temperature and the volume of moving water can affect dissolved oxygen
levels. Oxygen dissolves easier in cooler water than warmer water.
Adequate dissolved oxygen is important for good water quality and necessary to all
forms of life.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE FOR DETERMINATION OF DISSOLVED
OXYGEN IN WATER
In our project this was carried out by Azide Modification / Winkler’s Method
Apparatus: BOD bottles, titration apparatus
Reagents:
a) Manganous Sulphate (MnSO4.xH2O)
b) Alkali iodide azide
c) Conc. Sulphuric acid (H2SO4)
d) Titrant: Std. Sodium thiosulphate (0.025 N) [NaS2O3]
e) Indicator: Starch
Experimental Procedure:
Take about 300 ml of sample in a clean BOD bottle
Add 2 ml of Alkali iodide azide solution and 2 ml MnSO4, re-stopper the bottle
Mix the solution by repeatedly inverting the bottle
If no DO is present in the sample, the manganous ion reacts with hydroxide ion
due to which a “White precipitate” of Mn(OH)2 is formed.
If oxygen is present, some Mn2+ is oxidized to Mn4+ and precipitates as a
brown coloured manganic oxide.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/completefinalyearprojectbecivil-180618071340/75/Complete-final-year-project-BE-CIVIL-30-2048.jpg)
![Dept of Civil Engineering | H.K.B.K CE, 2017-18 Page 25
i.e., Mn2+ + 2(OH-) →Mn(OH)2 [White precipitate]
Mn2+ + 2(OH-) + (1/2) O2 →MnO2 (Brown) + H2O
After shaking allow sufficient time for all oxygen to react
Due to this the chemical precipitates settles down and a clear liquid is formed
in the upper surface
2 ml of conc. H2SO4 is added to dissolve the precipitate formed
Re stopper the bottle and invert the bottle 2 to 3 times until the suspension is
dissolved & uniform yellow colour is observed
Mn2+ + 2(I-) + 4H+ →Mn2+ I2 + 2H2O
Measure a volume of 203 ml in to the conical flask and titrate it immediately
with sodium thiosulphate (0.025 N) until the colour changes to pale or straw
yellow
Then add 2-3 drops of starch indicator and continue titration with sodium
thiosulphate (0.025 N) until blue colour disappears to colourless.
Note down the volume of titrant used (V) in ml
Formula:
Dissolved Oxygen (mg/L)
=
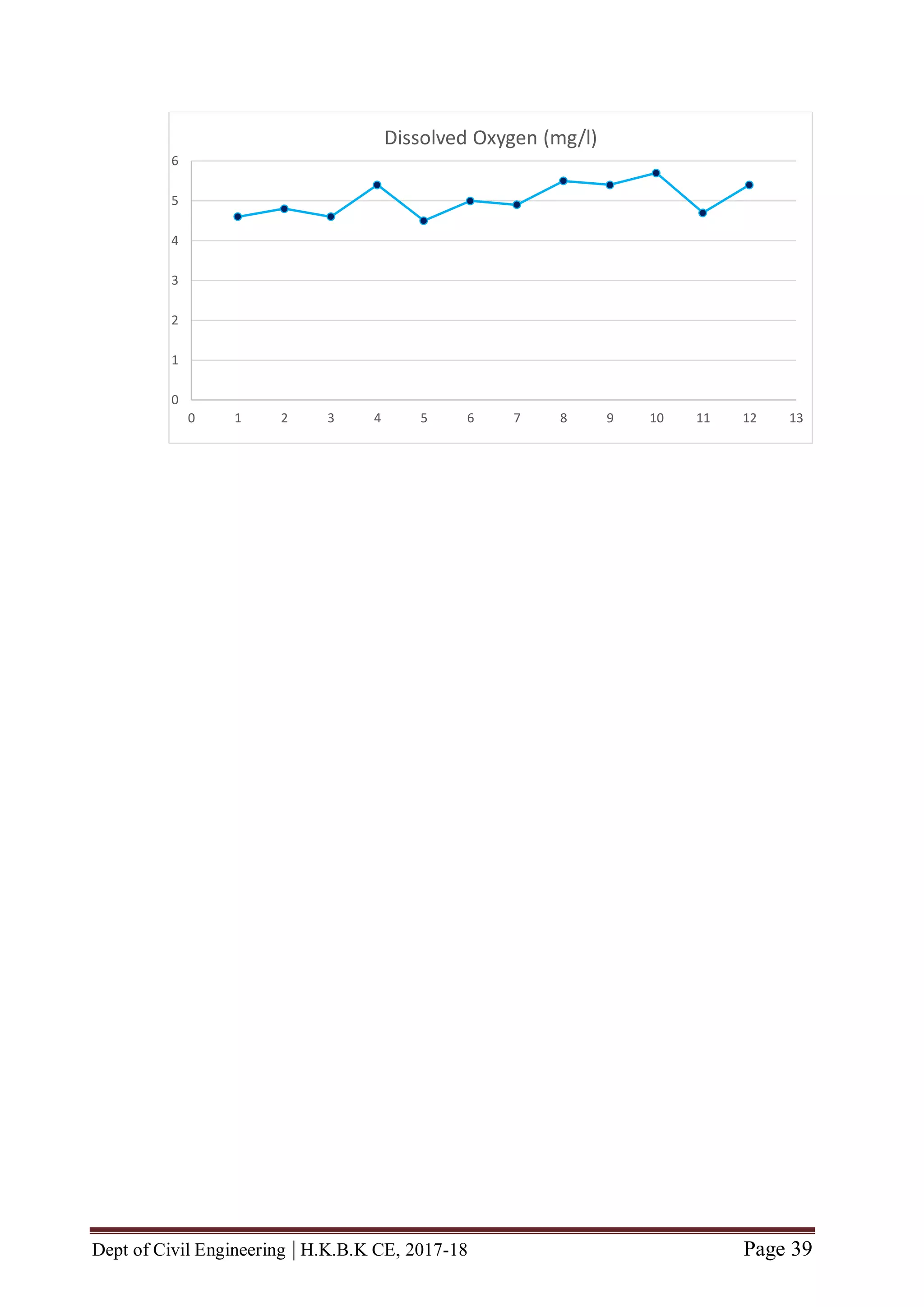
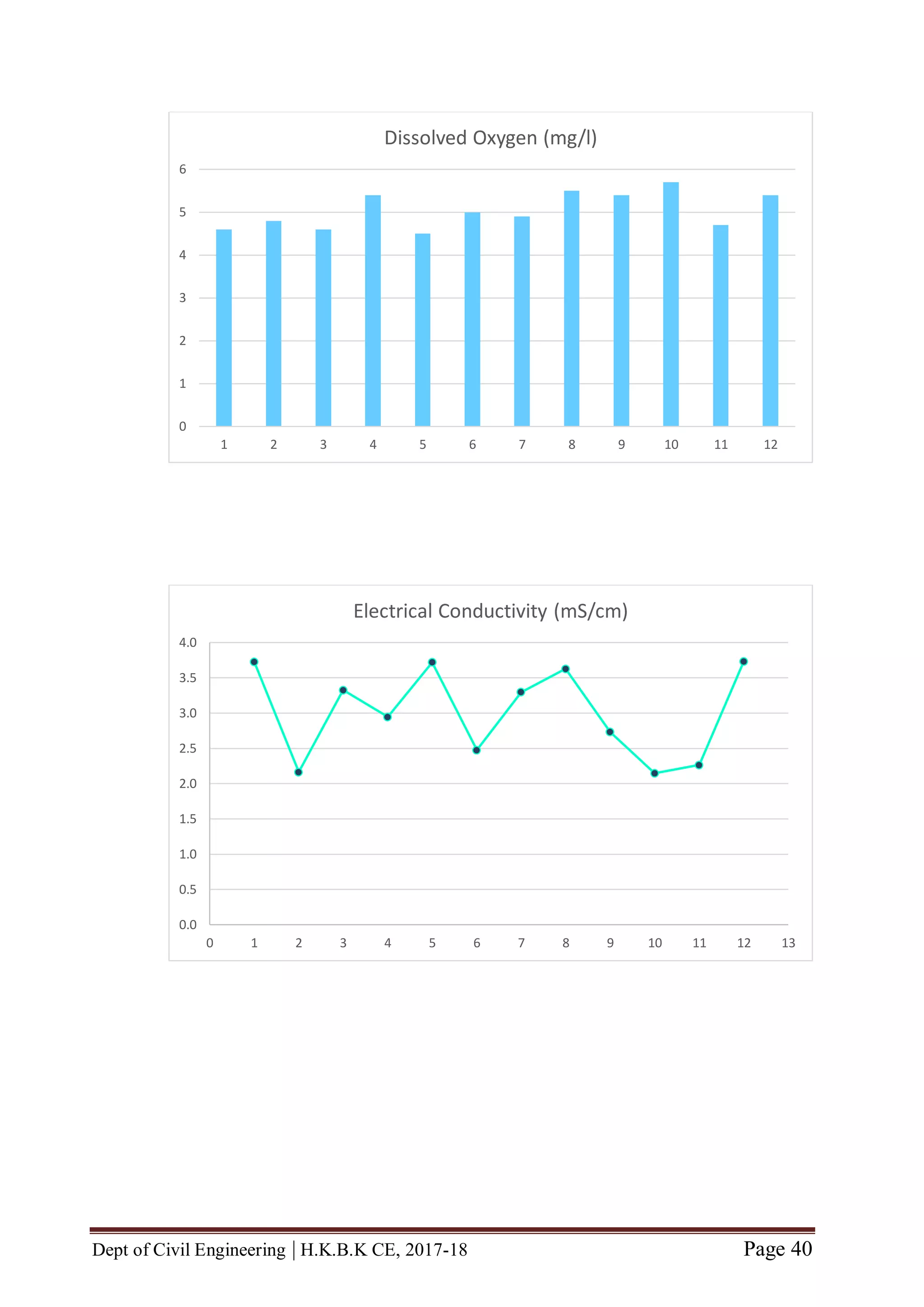
Good range of D.O content: 6 and >6 mg/L
Moderate range of D.O content: 5 to 5.9 mg/L
Poor range of D.O content: 4 to 4.9 mg/L
Environmental Significance of D.O Content determination:
BR x Normality of titrant x Equivalent weight of O2
(8) x 1000
ml of sample taken](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/completefinalyearprojectbecivil-180618071340/75/Complete-final-year-project-BE-CIVIL-31-2048.jpg)







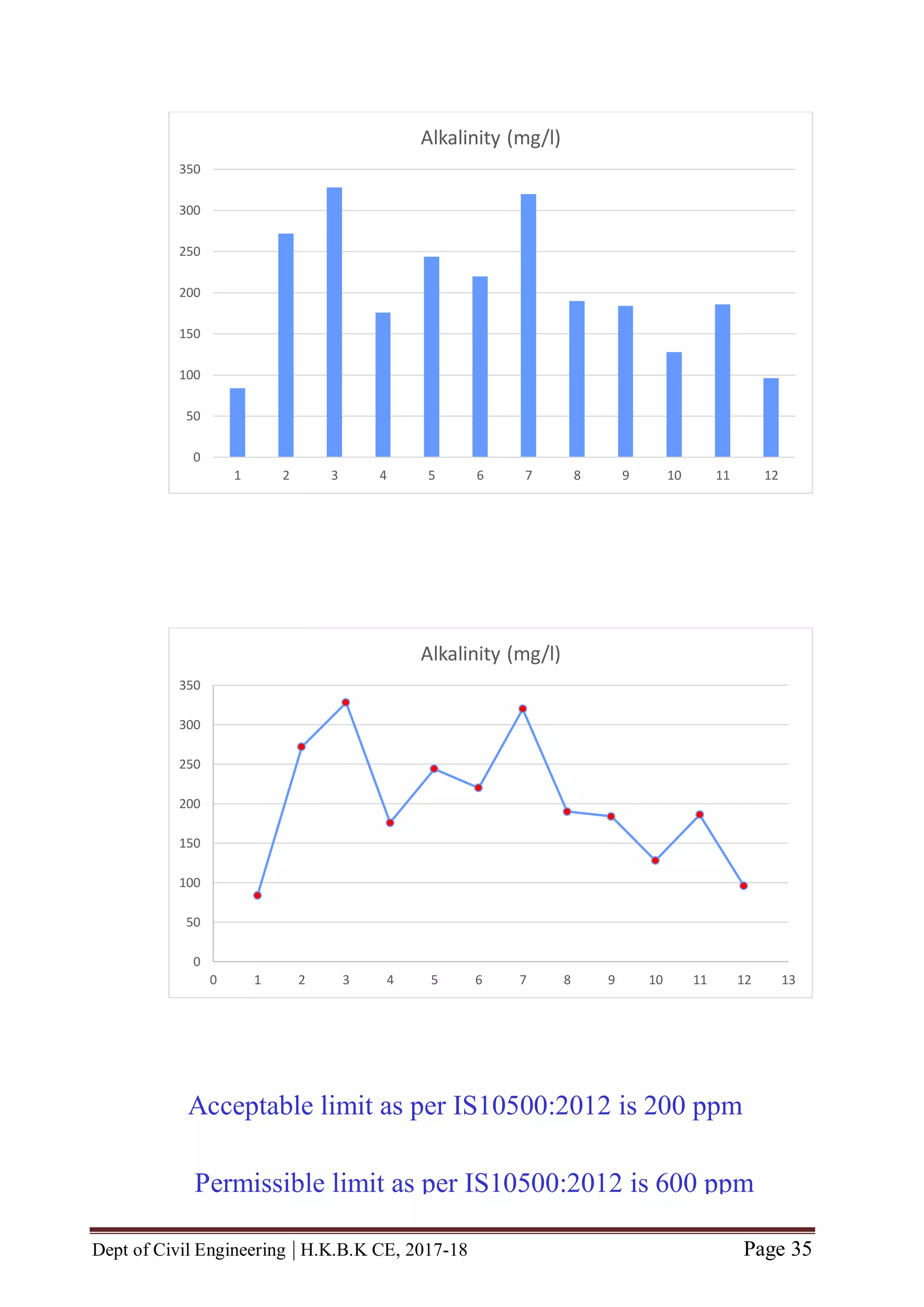
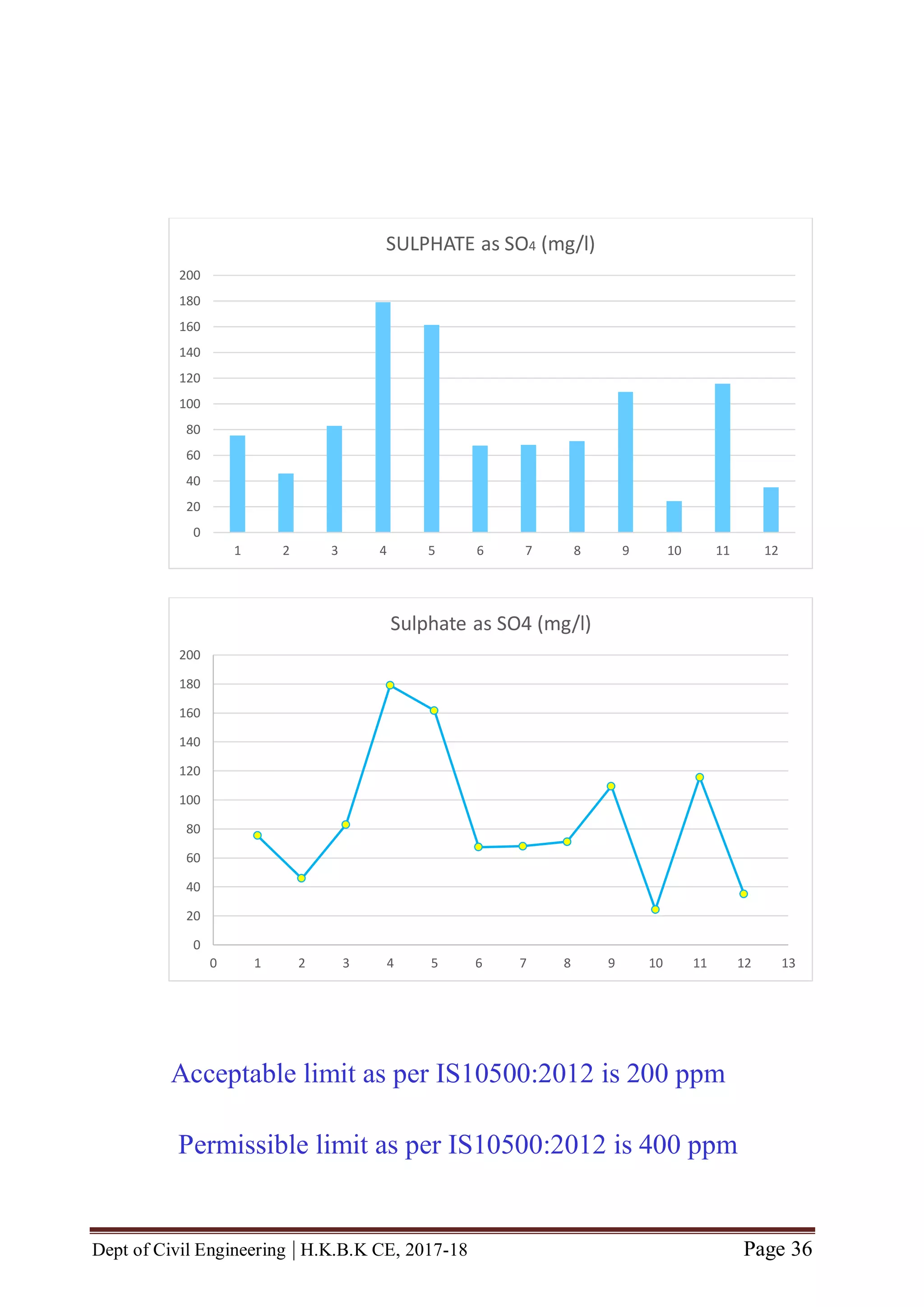
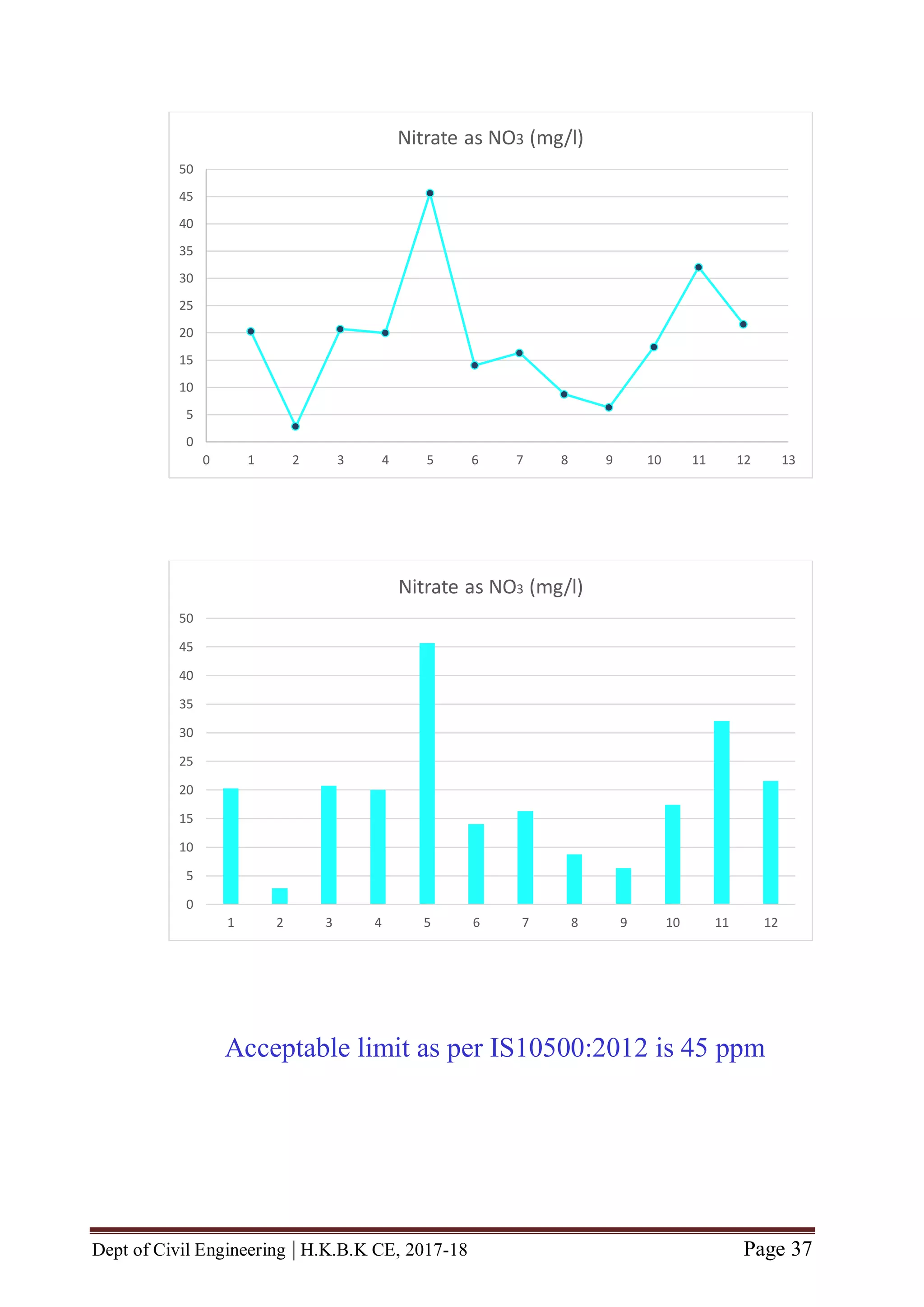
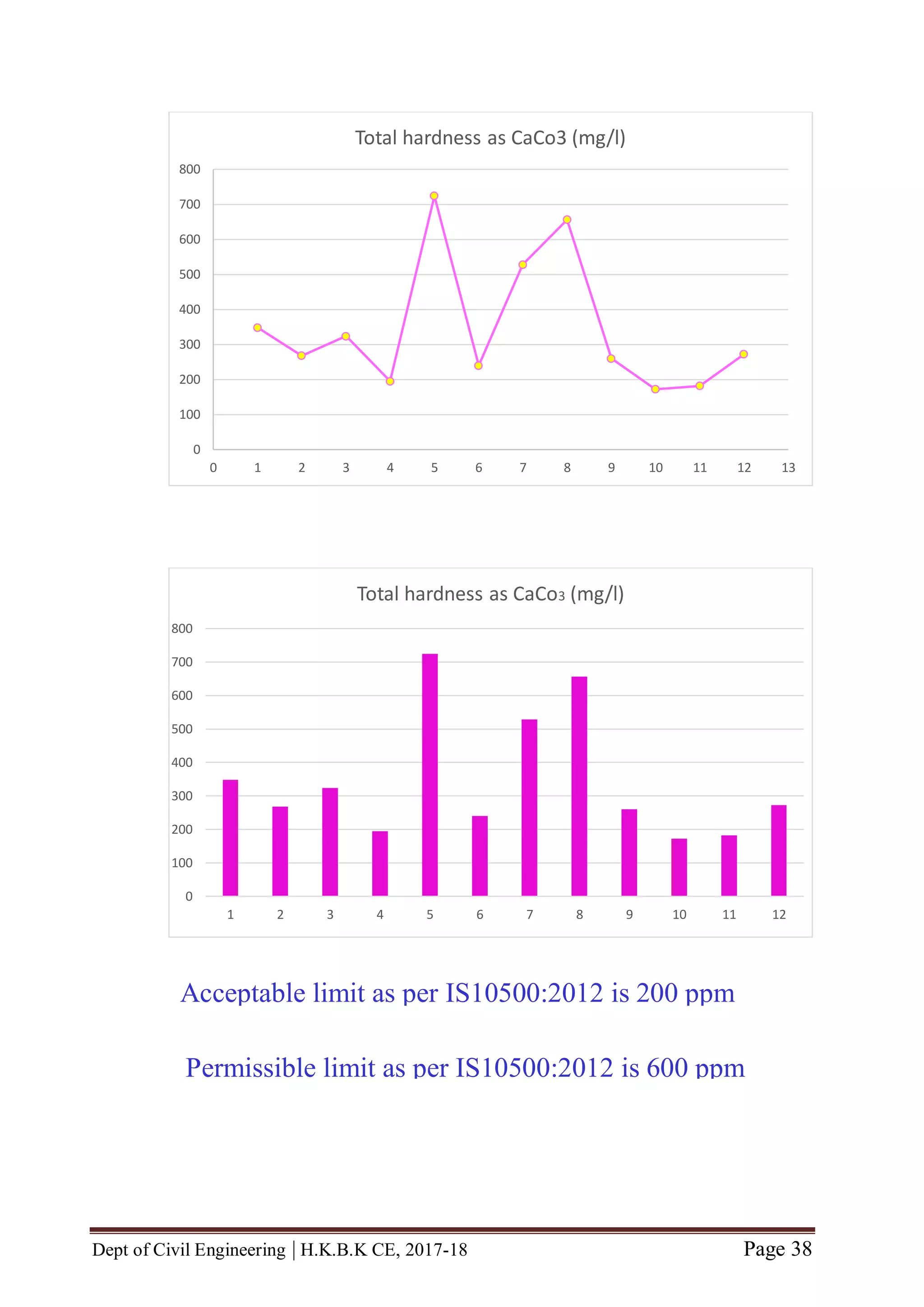

![Dept of Civil Engineering | H.K.B.K CE, 2017-18 Page 46
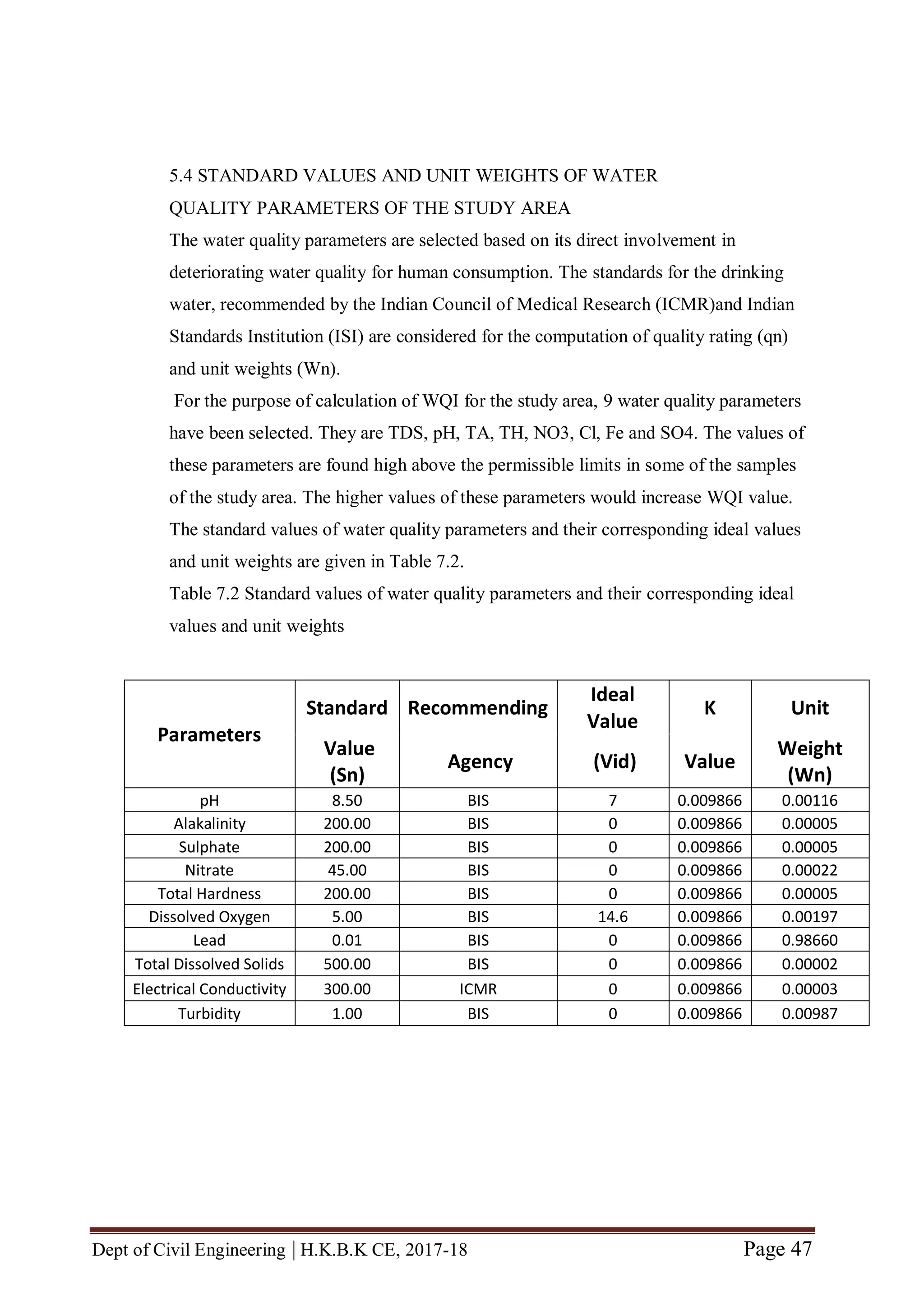
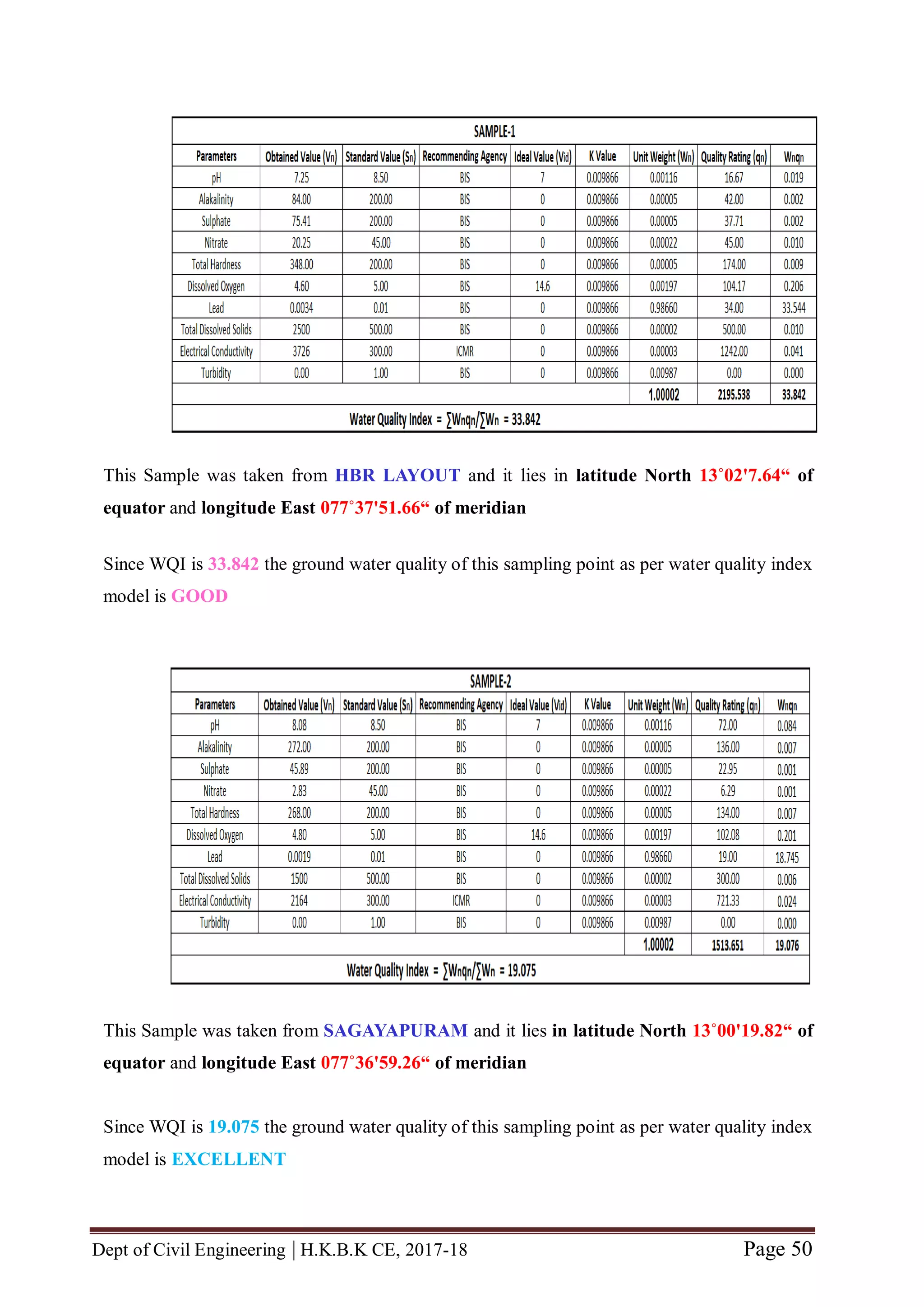
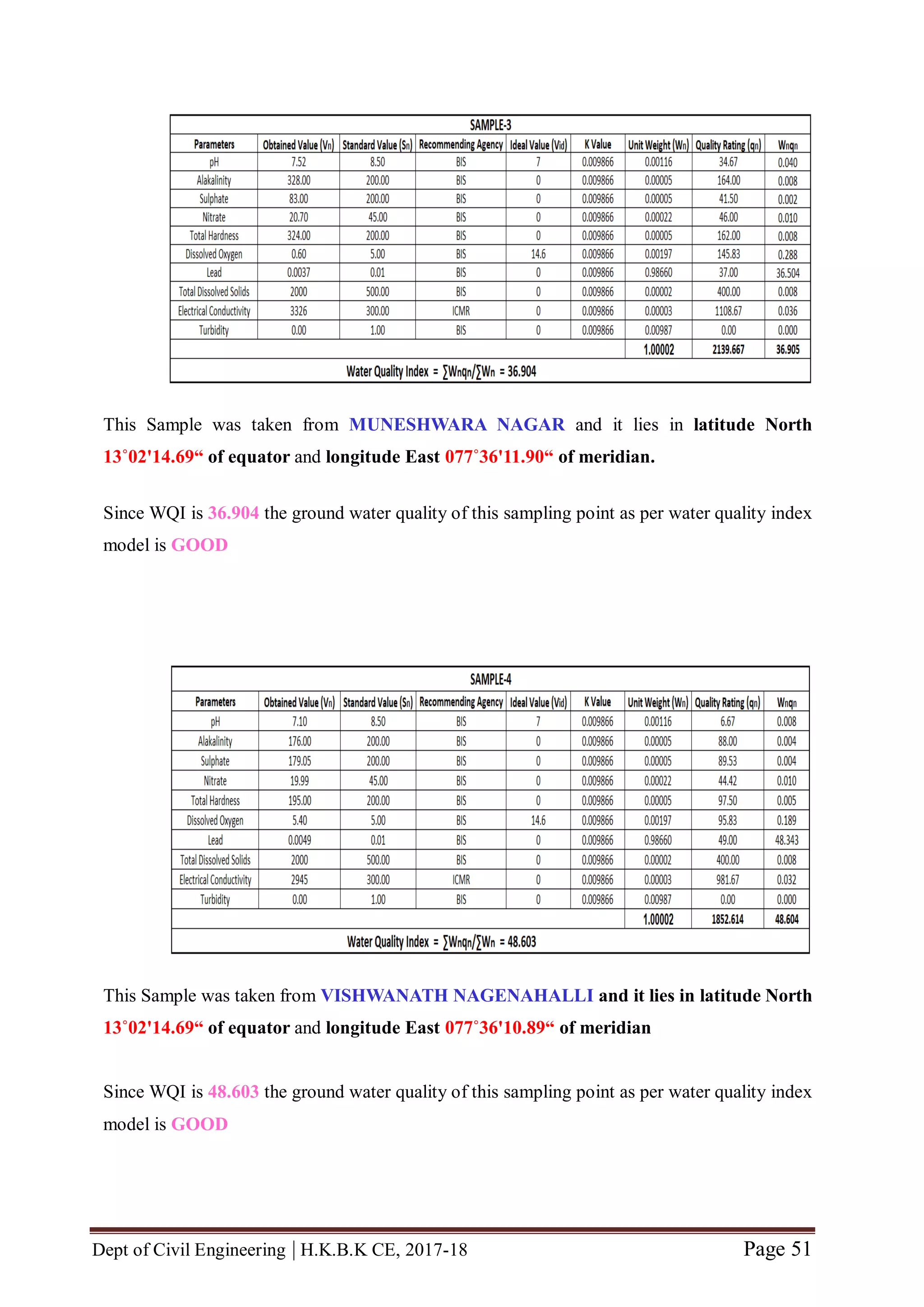
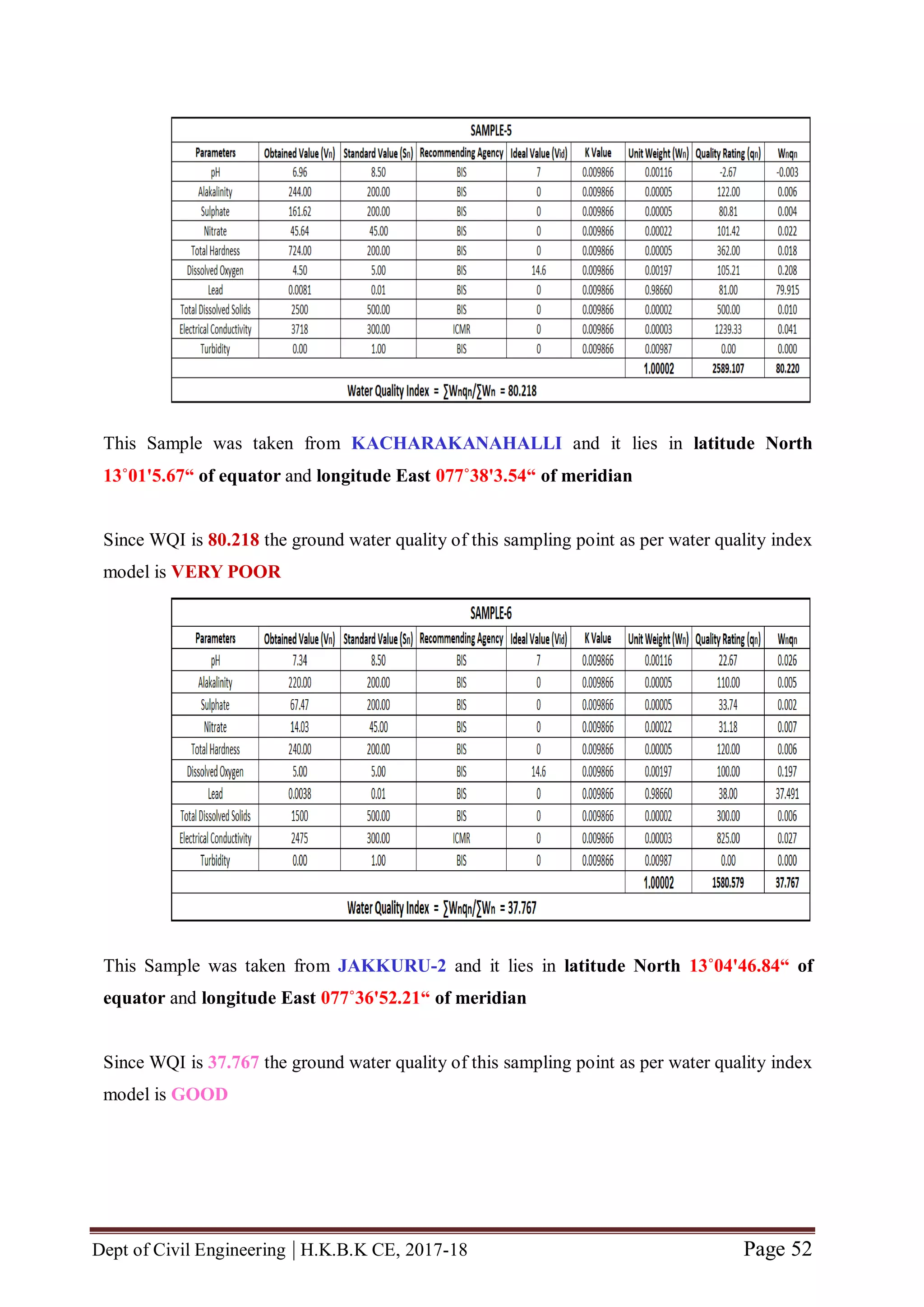
The quality rating (qn) is calculated using the expression given in Equation (7.2).
qn = [ ( Vn – Vid) / ( Sn- Vid) ] x 100 (7.2)
Where,
Vn = Estimated value of nth water quality parameter at a given sample location.
Vid = Ideal value for n th parameter in pure water. (Vid for pH = 7 and 0 for all other
parameters)
Sn = Standard permissible value of n th water quality parameter.
5.2.2 Unit weight
The unit weight (Wn) is calculated using the expression given in Equation (7.3).
Wn = k / Sn (7.3)
Where,
Sn = Standard permissible value of n th water quality parameter.
k = Constant of proportionality and it is calculated by using the expression given in
Equation (7.4).
k = [ 1 / ( 1/ Sn=1,2,..n) ] (7.4).
242
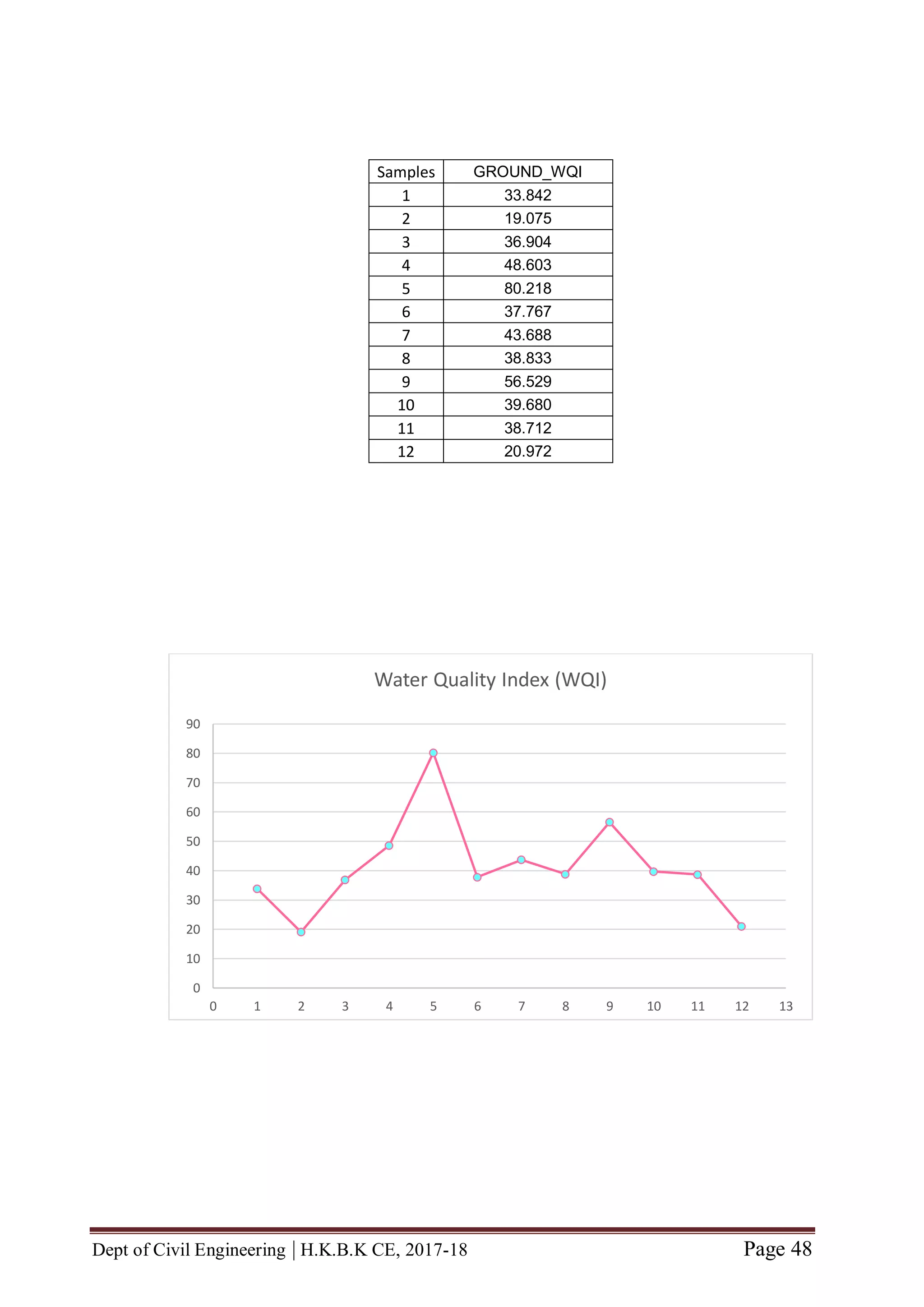
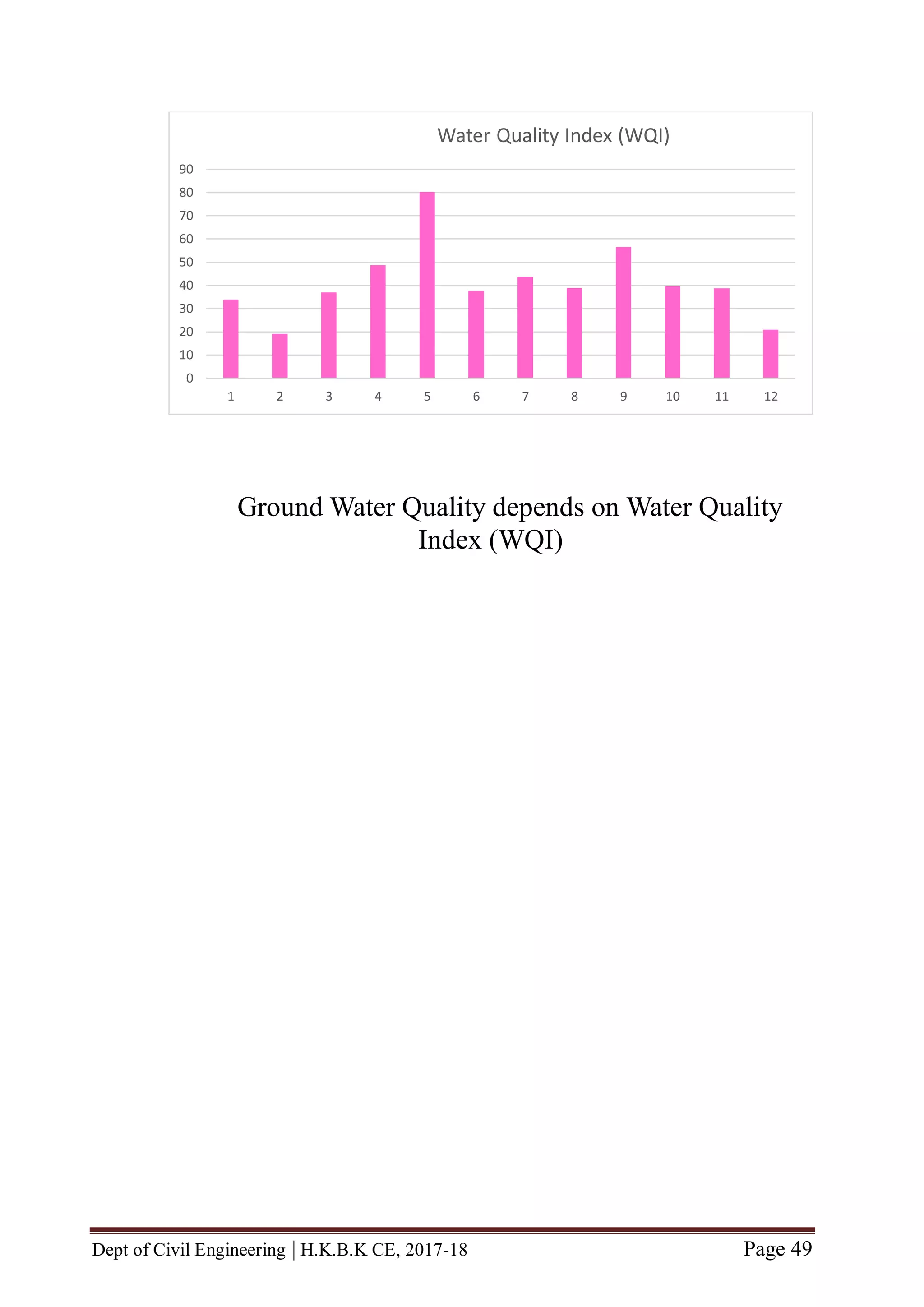
5.3 WQI AND STATUS
The ranges of WQI, the corresponding status of water quality and their possible use are
summarized in Table 7.1.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/completefinalyearprojectbecivil-180618071340/75/Complete-final-year-project-BE-CIVIL-52-2048.jpg)
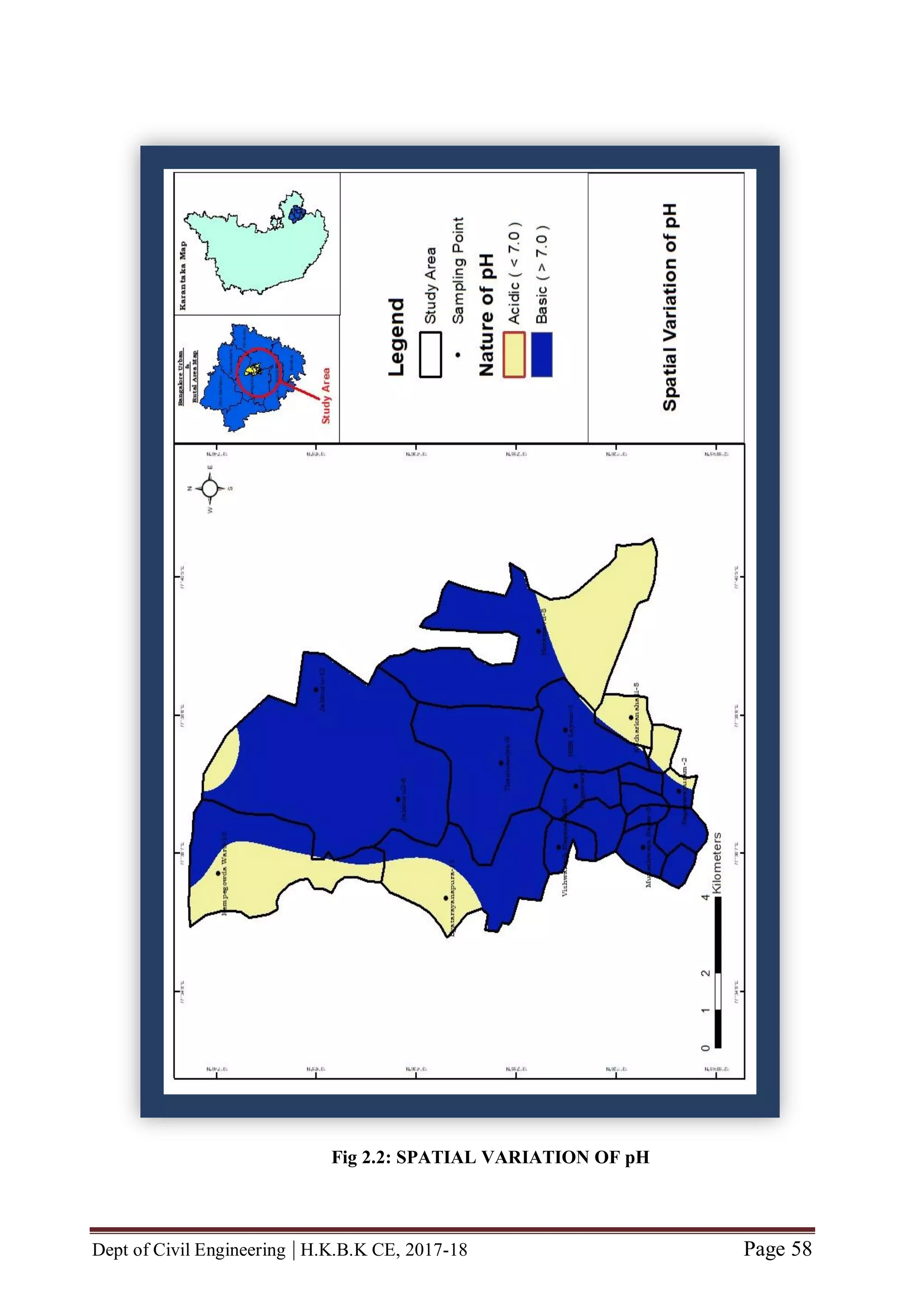
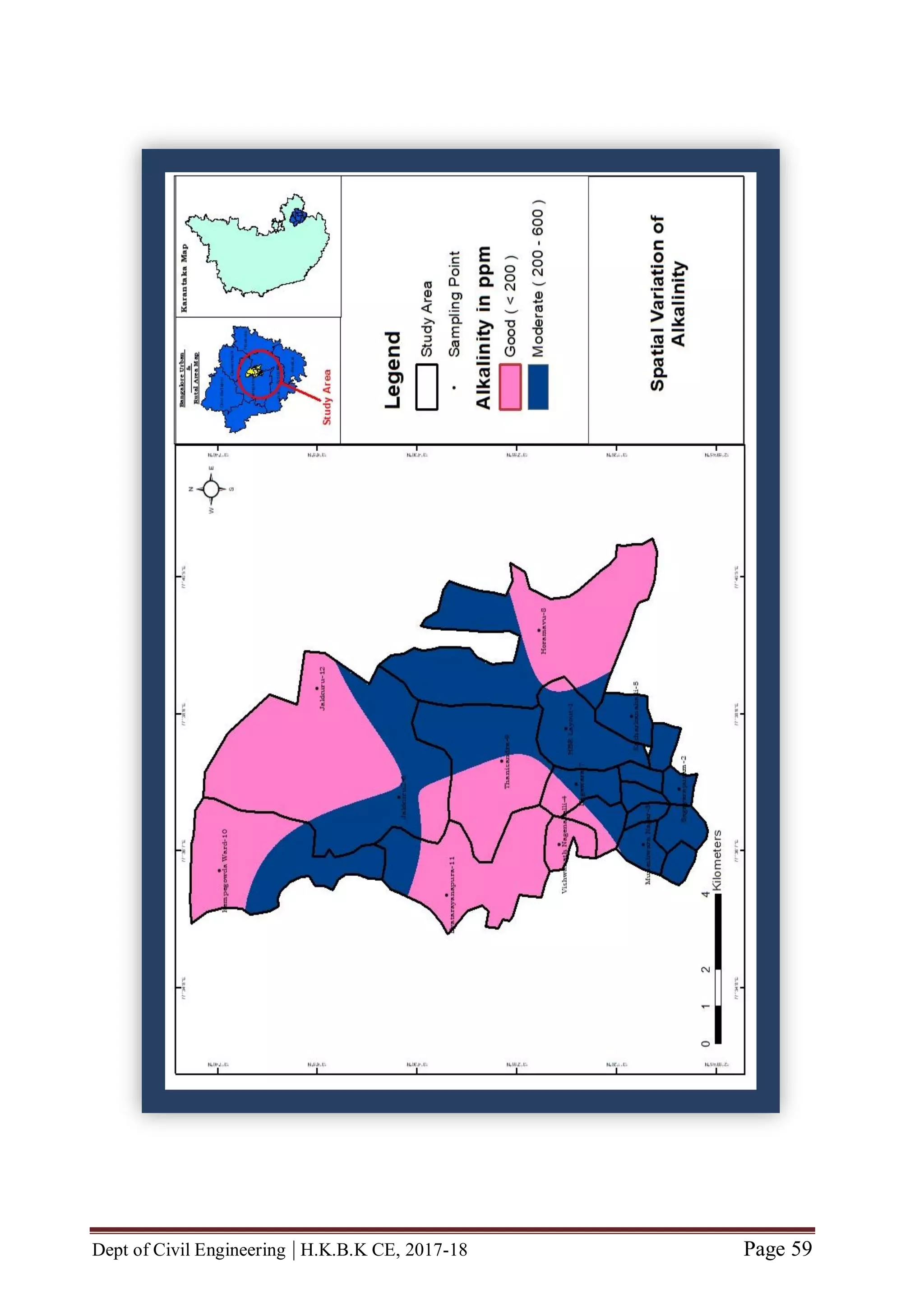
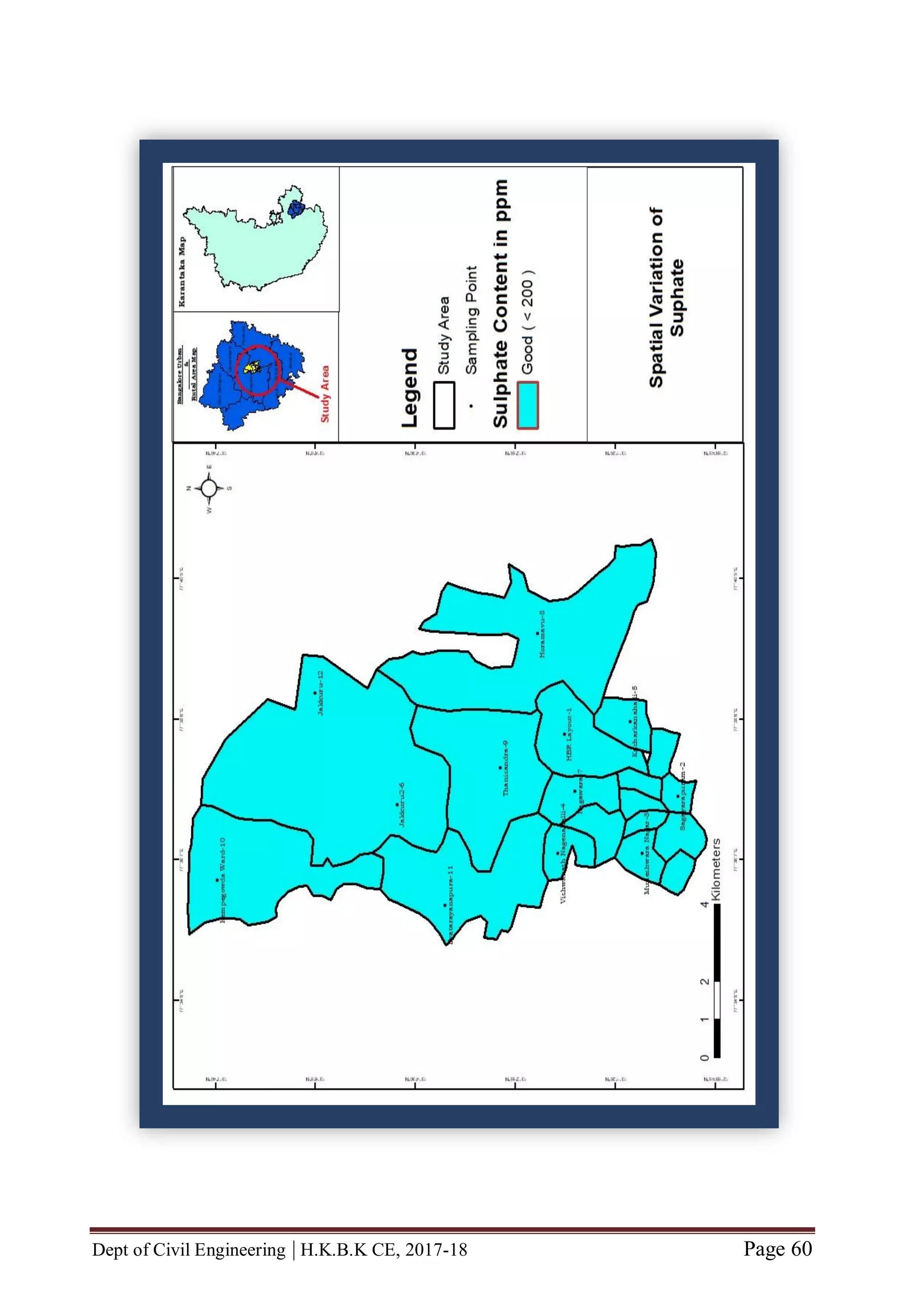
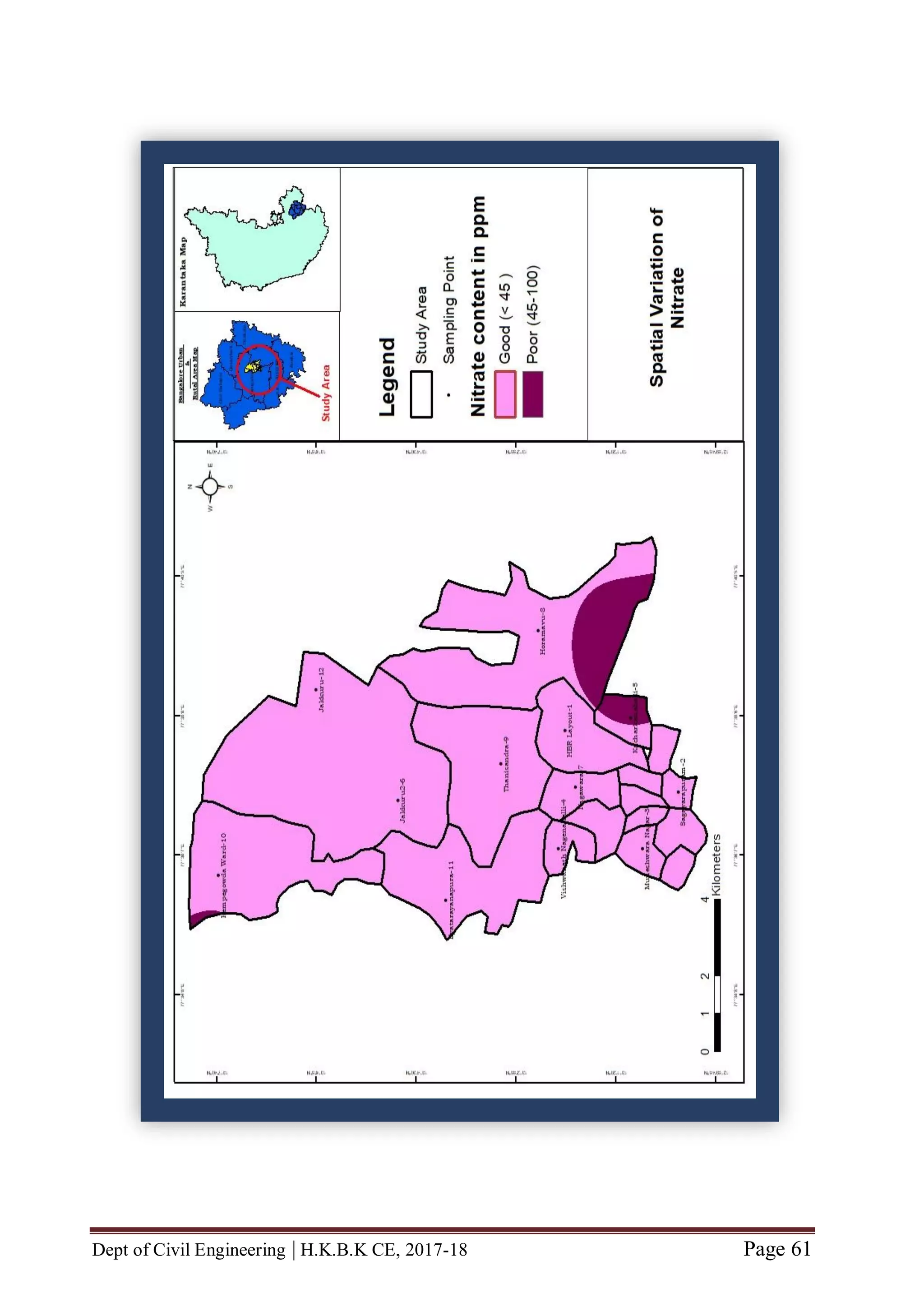
![Dept of Civil Engineering | H.K.B.K CE, 2017-18 Page 56
CHAPTER 6 MAP GENERATION BY USING GIS
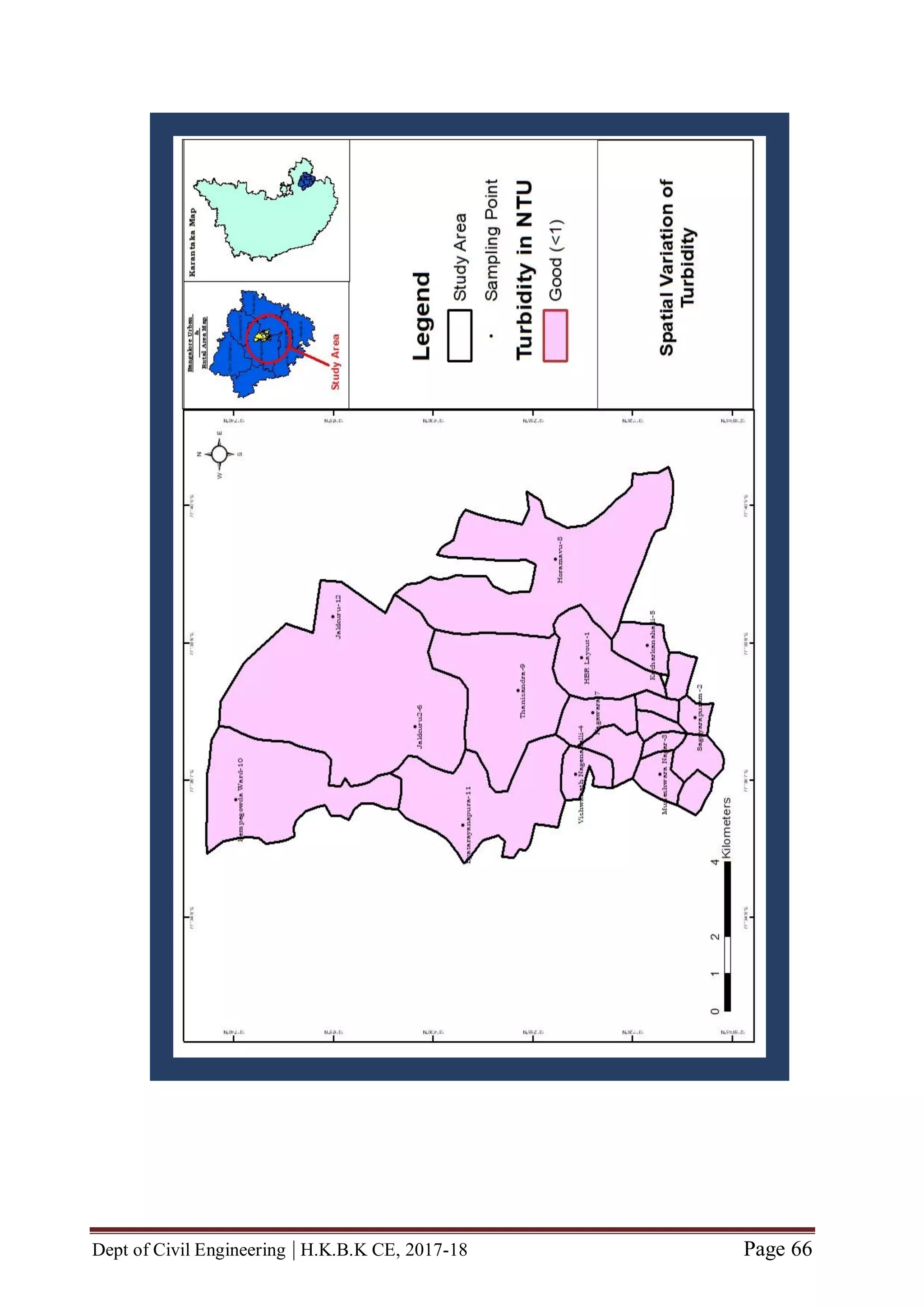
GENERATION OF STUDY AREA
Our Study Area is roughly situated in South-Eastern part of Karnataka state [between
latitude (North of Equator) N 13˚00'19.82" to N 13˚07'37.95" and between
longitude (East of Meridian) E 077˚35'27.83" to E 077˚39'18.26"]
Our study area consists of twelve locations viz., HBR Layout, Sagayapuram,
Muneshwara Nagar, Vishwanath Nagenahalli, Kacharakanahalli, Jakkuru-2,
Nagawara, Horamavu, Thanisandra, Kempegowda Ward, Byatarayanapura and
Jakkuru
Twelve samples from the above mentioned locations were taken from the sampling
points whose connection was given to borewells
The Map of Study Area was generated by google earth pro software and ArcGIS 10.5
The Following steps were taken for generation of study area map
Initaially, lat-long values (Remote Sensing data) was collected from GPS
Device
GPS data of all the 12 Selected Sampling points was collected in terms of
latitude north of equator and longitude east of meridian as shown
Then these lat-long values were entered into the software GOOGLE EARTH
PRO and these points are saved as a KML or KMZ file
After saving it as a KML file, ARCGIS 10.5 is opened and using conversion
tools from arc toolbox, the kml file is converted to a layer file and further this
layer file is converted to am shape file
Then shape file of our desired area is downloaded and incorporated into
ARCGIS 10.5.
After this, geo-referencing was done by incorporating toposheet into ARCGIS
in order to ensure that our study area lies within the boundary of toposheet.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/completefinalyearprojectbecivil-180618071340/75/Complete-final-year-project-BE-CIVIL-62-2048.jpg)
![Dept of Civil Engineering | H.K.B.K CE, 2017-18 Page 57
For geo-referencing of study area, Toposheet No D43R12 (57G/12) OF
BANGALORE URBAN – [between latitude (North of Equator) N 13˚0’ to
13˚15’ and between longitude (East of Meridian) E 077˚30’ to 077˚45’] was
used.
Thus, this is how study area map was created
The Study area so created is as shown
Fig 2.2: MAP OF STUDY AREA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/completefinalyearprojectbecivil-180618071340/75/Complete-final-year-project-BE-CIVIL-63-2048.jpg)