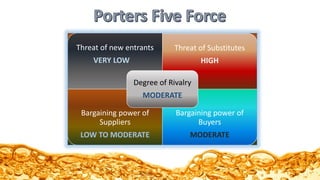
The document discusses the soft drinks market in India and strategies employed by Coca-Cola and Pepsi to gain market share in the country. It provides insights into how the companies expanded distribution, launched new products tailored to local tastes, and acquired other brands to dominate the market. The summary highlights the competitive dynamics between Coca-Cola and Pepsi in areas like bottling operations, rural marketing approaches, and new product introductions.