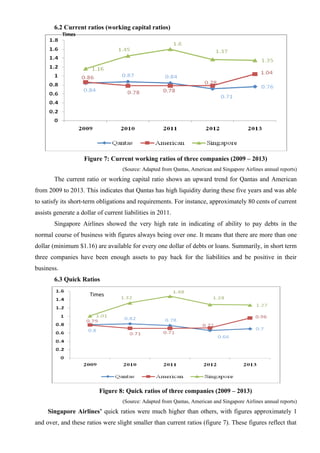
The document provides a comprehensive analysis of the airline industry, focusing on American Airlines, Singapore Airlines, and Qantas Airways, highlighting their operational strategies, financial performance, and challenges. It discusses key metrics such as profitability, asset management, liquidity, and capital structure from 2009 to 2013, emphasizing the impact of fluctuating fuel costs and economic conditions on profitability and stability. The analysis reveals that while Singapore Airlines exhibited stable financial performance, American Airlines struggled under negative equity and Qantas faced operational losses due to rising expenses.