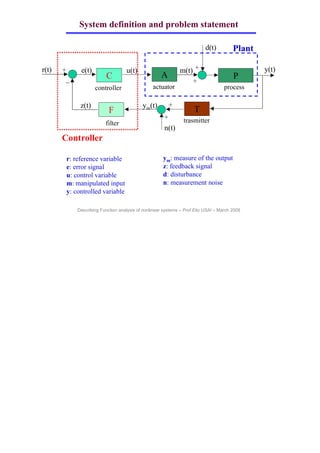
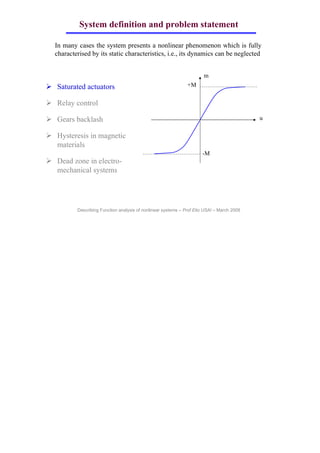
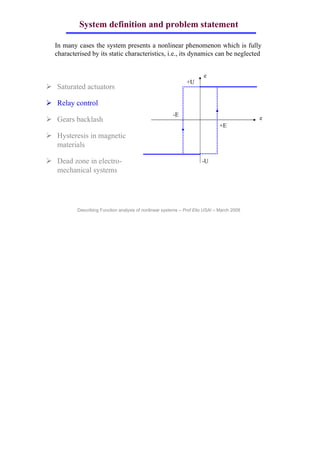
This document discusses describing function analysis of nonlinear systems. It defines various components in a control system including the reference variable, error signal, control variable, manipulated input, controlled variable, measured output, feedback signal, disturbance, measurement noise, actuator, process, controller, transmitter, and filter. It states that in many cases, a system's nonlinearity can be fully characterized by its static characteristics, and its dynamics can be neglected. It provides examples of nonlinearities including saturated actuators, relay control, gear backlash, hysteresis in magnetic materials, and dead zones in electromechanical systems.