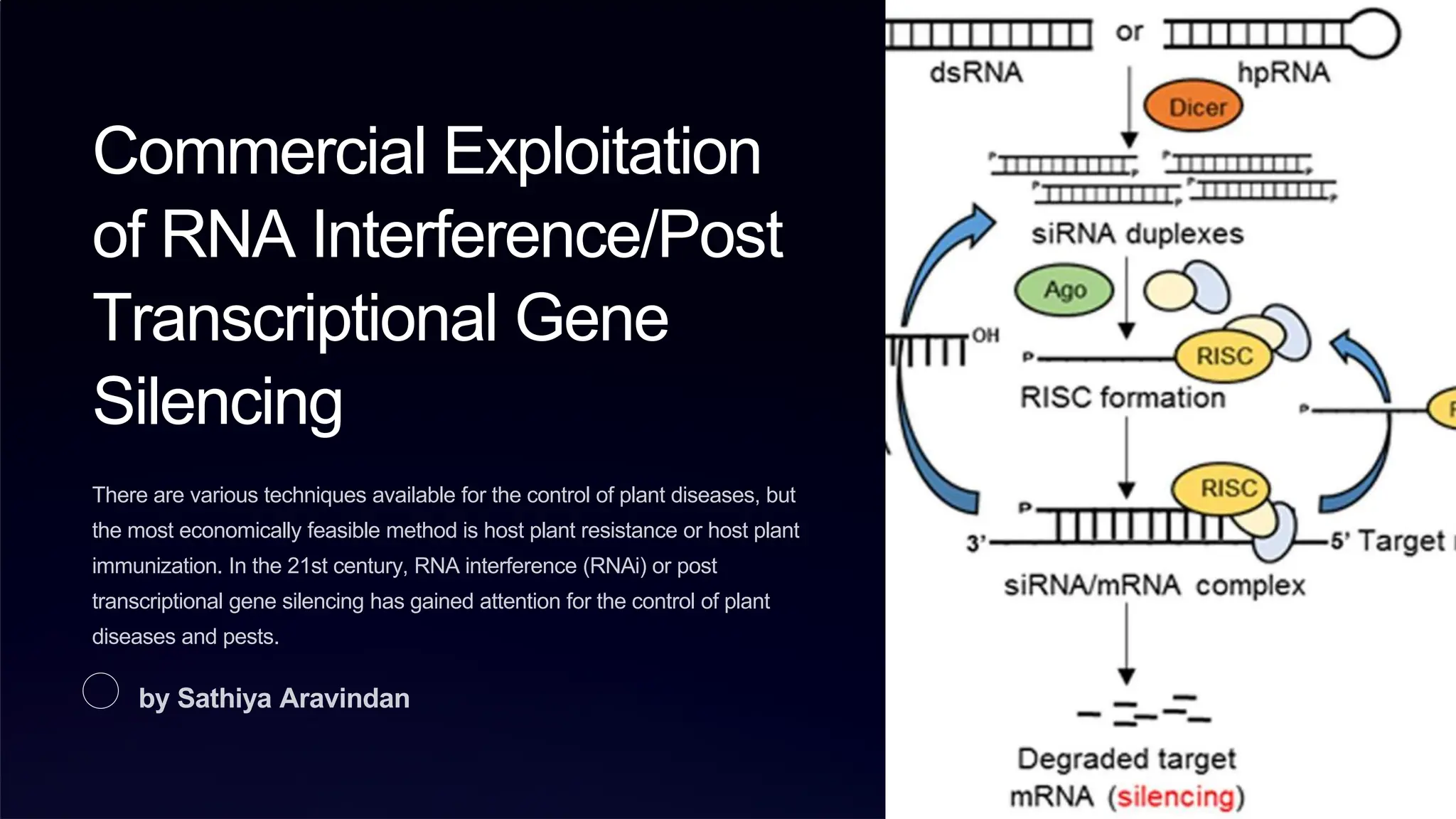
RNA interference (RNAi) and post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS) are prominent techniques for controlling plant diseases and pests, especially through methods like host plant resistance. Applications include effective control of diseases such as citrus greening and tobacco mosaic virus using genetically modified organisms and bio-clay coated ds-RNA. The process involves the activation of the RISC complex in genetically altered plants or treated areas, leading to gene silencing in target pathogens.